FAMBB
FAMBB
FAMBB
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
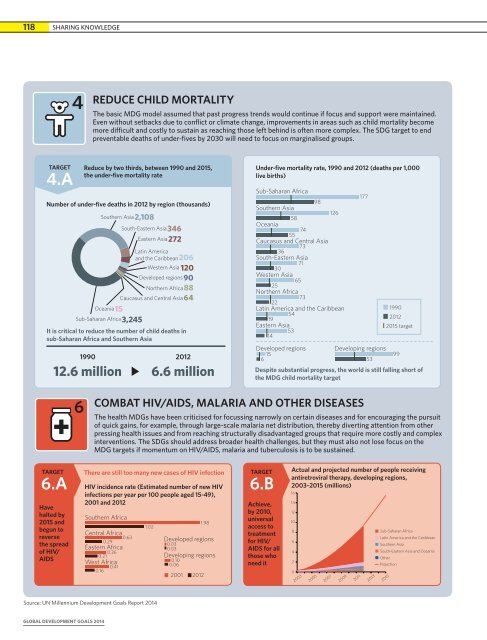
118 SHARING KNOWLEDGE4REDUCE CHILD MORTALITYThe basic MDG model assumed that past progress trends would continue if focus and support were maintained.Even without setbacks due to conflict or climate change, improvements in areas such as child mortality becomemore difficult and costly to sustain as reaching those left behind is often more complex. The SDG target to endpreventable deaths of under-fives by 2030 will need to focus on marginalised groups.TARGET4.AReduce by two thirds, between 1990 and 2015,the under-five mortality rateNumber of under-five deaths in 2012 by region (thousands)Southern Asia2,108South-Eastern Asia346Eastern Asia272Latin Americaand the Caribbean206Western Asia 120Developed regions90Northern Africa88Caucasus and Central Asia64Oceania15Sub-Saharan Africa3,245It is critical to reduce the number of child deaths insub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia1990201212.6 million 6.6 millionUnder-five mortality rate, 1990 and 2012 (deaths per 1,000live births)Sub-Saharan Africa98Southern Asia12658Oceania7455Caucasus and Central Asia7336South-Eastern Asia7130Western Asia6525Northern Africa7322Latin America and the Caribbean5419Eastern Asia5314199020122015 targetDeveloped regions Developing regions1599653Despite substantial progress, the world is still falling short ofthe MDG child mortality target1776COMBAT HIV/AIDS, MALARIA AND OTHER DISEASESThe health MDGs have been criticised for focussing narrowly on certain diseases and for encouraging the pursuitof quick gains, for example, through large-scale malaria net distribution, thereby diverting attention from otherpressing health issues and from reaching structurally disadvantaged groups that require more costly and complexinterventions. The SDGs should address broader health challenges, but they must also not lose focus on theMDG targets if momentum on HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis is to be sustained.TARGET6.AHavehalted by2015 andbegun toreversethe spreadof HIV/AIDSThere are still too many new cases of HIV infectionHIV incidence rate (Estimated number of new HIVinfections per year per 100 people aged 15-49),2001 and 2012Southern AfricaCentral Africa0.630.29Eastern Africa0.360.21West Africa0.410.161.021.98Developed regions0.030.03Developing regions0.100.062001 20121.98TARGET6.BAchieve,by 2010,universalaccess totreatmentfor HIV/AIDS for allthose whoneed itActual and projected number of people receivingantiretroviral therapy, developing regions,2003–2015 (millions)16141210864202003200520072009201120132015Sub-Saharan AfricaLatin America and the CaribbeanSouthern AsiaSouth-Eastern Asia and OceaniaOtherProjectionSource: UN Millennium Development Goals Report 2014GLOBAL DEVELOPMENT GOALS 2014