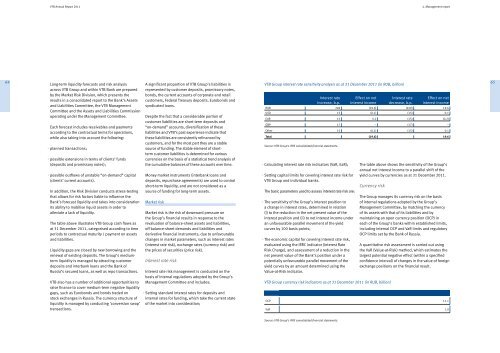
<strong>VTB</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> Report <strong>2011</strong>4. Management <strong>report</strong>64Long-term liquidity forecasts and risk analysisacross <strong>VTB</strong> Group and within <strong>VTB</strong> Bank are preparedby the Market Risk Division, which presents theresults in a consolidated <strong>report</strong> to the Bank’s Assetsand Liabilities Committee, the <strong>VTB</strong> ManagementCommittee and the Assets and Liabilities Commissionoperating under the Management Committee.Each forecast includes receivables and paymentsaccording to the contractual terms for operations,while also taking into account the following:planned transactions;possible extensions in terms of clients’ funds(deposits and promissory notes);possible outflows of unstable “on-demand” capital(clients’ current accounts).In addition, the Risk Division conducts stress-testingthat allows for risk factors liable to influence theBank’s forecast liquidity and takes into considerationits ability to mobilise liquid assets in order toalleviate a lack of liquidity.The table above illustrates <strong>VTB</strong> Group cash flows asat 31 December <strong>2011</strong>, categorised according to timeperiods to contractual maturity / payment on assetsand liabilities.Liquidity gaps are closed by new borrowing and therenewal of existing deposits. The Group’s mediumtermliquidity is managed by attracting customerdeposits and interbank loans and the Bank ofRussia’s secured loans, as well as repo transactions.<strong>VTB</strong> also has a number of additional opportunities toraise finance to cover medium-term negative liquiditygaps, such as Eurobonds and bonds traded onstock exchanges in Russia. The currency structure ofliquidity is managed by conducting ‘conversion swap’transactions.A significant proportion of <strong>VTB</strong> Group’s liabilities isrepresented by customer deposits, promissory notes,bonds, the current accounts of corporate and retailcustomers, Federal Treasury deposits, Eurobonds andsyndicated loans.Despite the fact that a considerable portion ofcustomer liabilities are short-term deposits and“on-demand” accounts, diversification of theseliabilities and <strong>VTB</strong>’s past experience indicate thatthese liabilities are consistently refinanced bycustomers, and for the most part they are a stablesource of funding. The stable element of shorttermcustomer liabilities is determined for variouscurrencies on the basis of a statistical trend analysis ofthe cumulative balances of these accounts over time.Money market instruments (interbank loans anddeposits, repurchase agreements) are used to controlshort-term liquidity, and are not considered as asource of funding for long-term assets.Market riskMarket risk is the risk of downward pressure onthe Group’s financial results in response to therevaluation of balance-sheet assets and liabilities,off balance-sheet demands and liabilities andderivative financial instruments, due to unfavourablechanges in market parameters, such as interest rates(interest rate risk), exchange rates (currency risk) andthe prices of securities (price risk).Interest rate riskInterest rate risk management is conducted on thebasis of internal regulations adopted by the Group’sManagement Committee and includes:Setting standard interest rates for deposits andinternal rates for funding, which take the current stateof the market into consideration;<strong>VTB</strong> Group interest rate sensitivity analysis as at 31 December <strong>2011</strong> (in RUB, billion)Interest rateincrease, b.p.Calculating interest rate risk indicators (VaR, EaR);Setting capital limits for covering interest rate risk for<strong>VTB</strong> Group and individual banks.The basic parameters used to assess interest rate risk are:The sensitivity of the Group’s interest position toa change in interest rates, determined in relation(i) to the reduction in the net present value of theinterest position and (ii) to net interest income underan unfavourable parallel movement of the yieldcurves by 100 basis points;The economic capital for covering interest rate risk,evaluated using the IRRC indicator (Interest RateRisk Charge), and assessment of a reduction in thenet present value of the Bank’s position under apotentially unfavourable parallel movement of theyield curves by an amount determined using theValue-at-Risk indicator.Effect on netinterest incomeThe table above shows the sensitivity of the Group’sannual net interest income to a parallel shift of theyield curves by currencies as at 31 December <strong>2011</strong>.Currency riskInterest ratedecrease, b.p.Effect on netinterest incomeRUB 249 (19.6) (249) 19.6USD 15 (0.1) (15) 0.1EUR 15 0.2 (15) (0.2)GBP 17 – (17) –Other 15 (0.1) (15) 0.1Total (19.6) 19.6Source: <strong>VTB</strong> Group’s IFRS consolidated financial statements.<strong>VTB</strong> Group currency risk indicators as at 31 December <strong>2011</strong> (in RUB, billion)The Group manages its currency risk on the basisof internal regulations adopted by the Group’sManagement Committee, by matching the currencyof its assets with that of its liabilities and bymaintaining an open currency position (OCP) ineach of the Group’s banks within established limits,including internal OCP and VaR limits and regulatoryOCP limits set by the Bank of Russia.A quantitative risk assessment is carried out usingthe VaR (Value-at-Risk) method, which estimates thelargest potential negative effect (within a specifiedconfidence interval) of changes in the value of foreignexchange positions on the financial result.OCP 11.1VaR 1.065Source: <strong>VTB</strong> Group’s IFRS consolidated financial statements.
<strong>VTB</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> Report <strong>2011</strong>4. Management <strong>report</strong>66The VaR assessment is based on an historicalmodelling approach over a period of two years witha ten trading day time horizon and a confidenceinterval of 99%.Price riskThe general principles for managing price risk at <strong>VTB</strong>are as follows:Restricting the size of price risk that is taken on bysetting limits across instruments, portfolios andtypes of transactions;Controlling adherence to established limits andrestrictions for taking on price risk (for example, aminimum discount size on “reverse repo” operationsand margin call conditions);Organisation of ongoing monitoring, analysis and<strong>report</strong>ing of price risk.A quantitative risk assessment is carried out usingthe VaR method and the above parameters forcurrency risk. Original historical data was used forinstruments with a quote history of at least 100trading days in the previous year, no more than tensuccessive trading days without quotes, and an issuedate no later than the beginning of the <strong>report</strong>ing year.The vast majority of such instruments in the Group’sportfolio had a history of 250 trading days in the<strong>report</strong>ing year.For instruments not satisfying these criteria (butnevertheless circulating in the market and carryingmarket risk), the price history used was that ofequivalent (proxy) instruments, expertly selectedusing the following criteria:the proxy instrument is the same type of financialinstrument as the original instrument (bonds/Eurobonds);the issuer of the proxy instrument is in the same sectorand the same country as the original instrument, andthe issuers have comparable credit ratings;the proxy instrument and original instrument aredenominated in the same currency;the proxy instrument and original instrument havecomparable durations.Proxy instruments are used for the VaR calculation inrespect of approximately a quarter of the securities inthe portfolio. In 2010, the Group implemented a VaRassessment method adjusted for diversification.As at 31 December <strong>2011</strong>, this indicator stood atRUB 19.0 billion.Operational riskOperational risk is the risk of loss resulting fromhuman factors, possible flaws in internal processesor inconsistency between them and legislativerequirements, breakdowns in IT and othertechnological systems, or damaging external events(natural disasters).<strong>VTB</strong> Bank’s operational risk management system isdesigned to prevent potential losses and to reducethe possibility of business process failures and theinability to provide high-quality services to the Bank’sclients caused by staff errors, system breakdowns,internal or external fraud or violations of the law.In managing operational risk, the Bank followsthe principles contained in the Bank of Russiaregulations as well as the recommendations of theBasel Committee on Banking Supervision (includingBasel II). To implement its strategy, <strong>VTB</strong> carries outregular procedures to identify, assess, control andlimit operational risk. All significant deficienciesfrom a risk perspective, identified within the internalcontrol system, are subjected to rigorous analysis.Based on the analysis, measures are developed andimplemented to eliminate the causes and sources ofthe risk.To monitor and assess the consolidated operationalrisk, the Bank and its subsidiary financial companieshave implemented unified mechanisms to collectinformation on incidents of operational risk andrelated operating losses, as well as key risk andcontrol indicators.The procedure used by the Group’s subsidiaries tosubmit regular operational risk indicator updates to<strong>VTB</strong> Bank’s centralized risk management service issupported by the Report on Operational Risk moduleon the Group’s Corporate Information System (CIS).This module provides multi-level control over thequality of downloaded data and the possibility tocreate intra-group analytical <strong>report</strong>s with an optionallevel of consolidation.The key methods for limiting operational risk are:Maintaining a complex system of current and followupinternal control that is common to all businessunits and operations throughout the Bank;The regulation of all key operations by internalstandards and codes of practice;The registration and documentation of bankingoperations and transactions and consistent controlover primary documents and operating accounts;The application of the principles of dividing andlimiting the functions, authorities and responsibilitiesof employees; implementation of dual controls;collective decision-making and the setting of limitson the terms and scale of operations;The automation of banking operations based onthe use of high-performance IT systems that areconstantly monitored, and repaired promptly in caseof breakdown;Good systems of physical and information securityand control over access to the Bank’s facilities;A well-managed HR policy, good staff training andeducation.These risk limitation strategies are augmented byinsurance programmes that cover the various typesand scopes of operations. In <strong>2011</strong>, the Group’stotal operational risk insurance amounted toapproximately RUB 137 billion, includingRUB 11 billion coverage of the Bank’s risks. Theseinsurance programmes have traditionally includedinsurance against criminal acts under the FinancialInstitution’s Blanket Bond scheme (includingelectronic and computer crime), insurance ofvaluables during transit and while in storage, liabilityinsurance, and the insurance of the “card business”,including cash machines and cover against bank cardfraud.Programme for implementing Basel IIstandardsIn <strong>2011</strong>, <strong>VTB</strong> Group banks continued working oncomprehensive diagnostics regarding their degree ofreadiness for the implementation of Basel II standardsand a general analysis of the potential impact on thebanks’ activities 1 . Key aspects of this work have beencoordinated at the level of <strong>VTB</strong> Bank (primarily by theRisk Management Department of <strong>VTB</strong>).At the same time, <strong>VTB</strong> Bank and <strong>VTB</strong>24 participatedin a working group for the implementation of theBasel II IRB approach, organised by the Bank ofRussia jointly with the European Union’s leadingexperts on banking regulation.The Bank has also participated in the work ofthe Committee on Basel II Standards and RiskManagement, organised by the Association ofRussian Banks. In particular, a number of topicalmeetings and contacts with Bank of Russiarepresentatives took place within the frameworkof this committee, in which the capabilities andlimitations of the prospective implementation ofBasel II standards were fully assessed.1 <strong>VTB</strong> Group’s Western European banks have been operating according to Basel II standards since 1 January 2008.67