and Master Programmes in German Higher Education Institutions
and Master Programmes in German Higher Education Institutions
and Master Programmes in German Higher Education Institutions
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
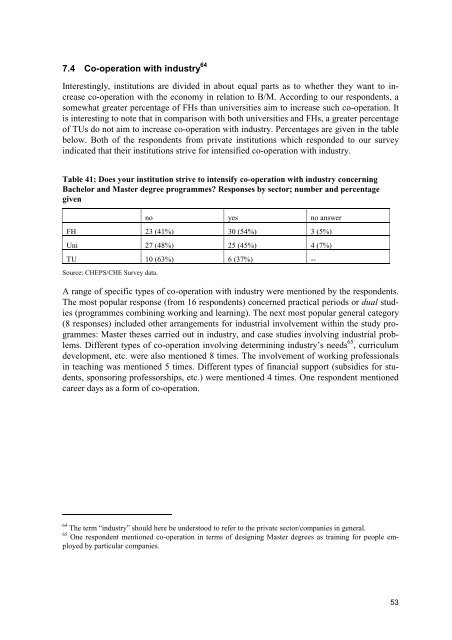
7.4 Co-operation with <strong>in</strong>dustry 64Interest<strong>in</strong>gly, <strong>in</strong>stitutions are divided <strong>in</strong> about equal parts as to whether they want to <strong>in</strong>creaseco-operation with the economy <strong>in</strong> relation to B/M. Accord<strong>in</strong>g to our respondents, asomewhat greater percentage of FHs than universities aim to <strong>in</strong>crease such co-operation. Itis <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g to note that <strong>in</strong> comparison with both universities <strong>and</strong> FHs, a greater percentageof TUs do not aim to <strong>in</strong>crease co-operation with <strong>in</strong>dustry. Percentages are given <strong>in</strong> the tablebelow. Both of the respondents from private <strong>in</strong>stitutions which responded to our survey<strong>in</strong>dicated that their <strong>in</strong>stitutions strive for <strong>in</strong>tensified co-operation with <strong>in</strong>dustry.Table 41: Does your <strong>in</strong>stitution strive to <strong>in</strong>tensify co-operation with <strong>in</strong>dustry concern<strong>in</strong>gBachelor <strong>and</strong> <strong>Master</strong> degree programmes? Responses by sector; number <strong>and</strong> percentagegivenno yes no answerFH 23 (41%) 30 (54%) 3 (5%)Uni 27 (48%) 25 (45%) 4 (7%)TU 10 (63%) 6 (37%) --Source: CHEPS/CHE Survey data.A range of specific types of co-operation with <strong>in</strong>dustry were mentioned by the respondents.The most popular response (from 16 respondents) concerned practical periods or dual studies(programmes comb<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g). The next most popular general category(8 responses) <strong>in</strong>cluded other arrangements for <strong>in</strong>dustrial <strong>in</strong>volvement with<strong>in</strong> the study programmes:<strong>Master</strong> theses carried out <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustry, <strong>and</strong> case studies <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dustrial problems.Different types of co-operation <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dustry’s needs 65 , curriculumdevelopment, etc. were also mentioned 8 times. The <strong>in</strong>volvement of work<strong>in</strong>g professionals<strong>in</strong> teach<strong>in</strong>g was mentioned 5 times. Different types of f<strong>in</strong>ancial support (subsidies for students,sponsor<strong>in</strong>g professorships, etc.) were mentioned 4 times. One respondent mentionedcareer days as a form of co-operation.64 The term “<strong>in</strong>dustry” should here be understood to refer to the private sector/companies <strong>in</strong> general.65 One respondent mentioned co-operation <strong>in</strong> terms of design<strong>in</strong>g <strong>Master</strong> degrees as tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g for people employedby particular companies.53