Buffering in the Layout Environment - Computer Engineering ...
Buffering in the Layout Environment - Computer Engineering ...
Buffering in the Layout Environment - Computer Engineering ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
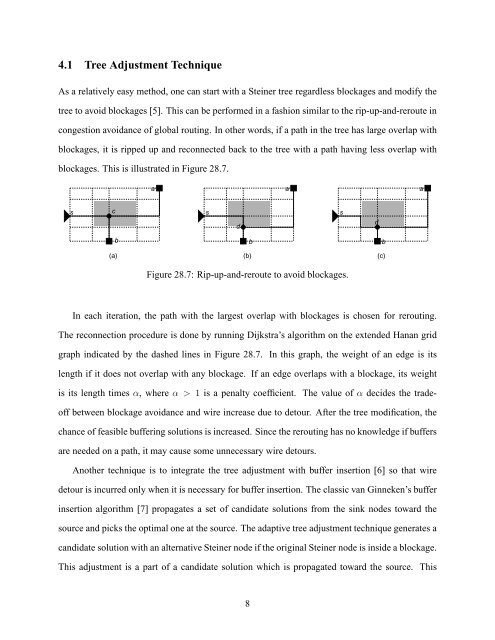
4.1 Tree Adjustment TechniqueAs a relatively easy method, one can start with a Ste<strong>in</strong>er tree regardless blockages and modify <strong>the</strong>tree to avoid blockages [5]. This can be performed <strong>in</strong> a fashion similar to <strong>the</strong> rip-up-and-reroute <strong>in</strong>congestion avoidance of global rout<strong>in</strong>g. In o<strong>the</strong>r words, if a path <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> tree has large overlap withblockages, it is ripped up and reconnected back to <strong>the</strong> tree with a path hav<strong>in</strong>g less overlap withblockages. This is illustrated <strong>in</strong> Figure 28.7.aaascsdsdbbb(a) (b) (c)Figure 28.7: Rip-up-and-reroute to avoid blockages.In each iteration, <strong>the</strong> path with <strong>the</strong> largest overlap with blockages is chosen for rerout<strong>in</strong>g.The reconnection procedure is done by runn<strong>in</strong>g Dijkstra’s algorithm on <strong>the</strong> extended Hanan gridgraph <strong>in</strong>dicated by <strong>the</strong> dashed l<strong>in</strong>es <strong>in</strong> Figure 28.7. In this graph, <strong>the</strong> weight of an edge is itslength if it does not overlap with any blockage. If an edge overlaps with a blockage, its weightis its length times α, where α > 1 is a penalty coefficient. The value of α decides <strong>the</strong> tradeoffbetween blockage avoidance and wire <strong>in</strong>crease due to detour. After <strong>the</strong> tree modification, <strong>the</strong>chance of feasible buffer<strong>in</strong>g solutions is <strong>in</strong>creased. S<strong>in</strong>ce <strong>the</strong> rerout<strong>in</strong>g has no knowledge if buffersare needed on a path, it may cause some unnecessary wire detours.Ano<strong>the</strong>r technique is to <strong>in</strong>tegrate <strong>the</strong> tree adjustment with buffer <strong>in</strong>sertion [6] so that wiredetour is <strong>in</strong>curred only when it is necessary for buffer <strong>in</strong>sertion. The classic van G<strong>in</strong>neken’s buffer<strong>in</strong>sertion algorithm [7] propagates a set of candidate solutions from <strong>the</strong> s<strong>in</strong>k nodes toward <strong>the</strong>source and picks <strong>the</strong> optimal one at <strong>the</strong> source. The adaptive tree adjustment technique generates acandidate solution with an alternative Ste<strong>in</strong>er node if <strong>the</strong> orig<strong>in</strong>al Ste<strong>in</strong>er node is <strong>in</strong>side a blockage.This adjustment is a part of a candidate solution which is propagated toward <strong>the</strong> source. This8