You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
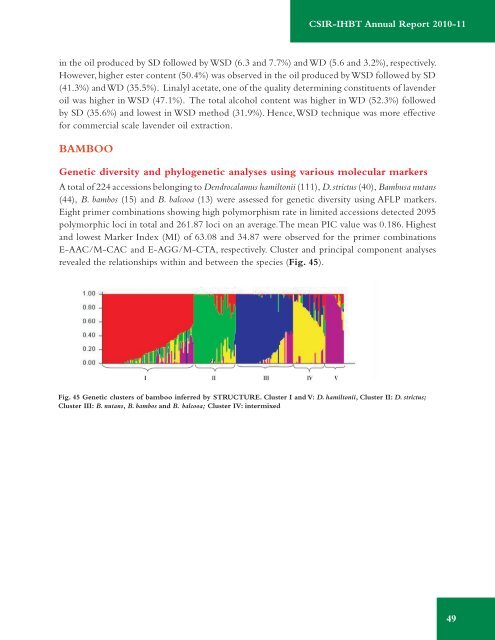
CSIR-<strong>IHBT</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> 2010-11in the oil produced by SD followed by WSD (6.3 and 7.7%) and WD (5.6 and 3.2%), respectively.However, higher ester content (50.4%) was observed in the oil produced by WSD followed by SD(41.3%) and WD (35.5%). Linalyl acetate, one of the quality determining constituents of lavenderoil was higher in WSD (47.1%). The total alcohol content was higher in WD (52.3%) followedby SD (35.6%) and lowest in WSD method (31.9%). Hence, WSD technique was more effectivefor commercial scale lavender oil extraction.BambooGenetic diversity and phylogenetic analyses using various molecular markersA total of 224 accessions belonging to Dendrocalamus hamiltonii (111), D. strictus (40), Bambusa nutans(44), B. bambos (15) and B. balcooa (13) were assessed for genetic diversity using AFLP markers.Eight primer combinations showing high polymorphism rate in limited accessions detected 2095polymorphic loci in total and 261.87 loci on an average. The mean PIC value was 0.186. Highestand lowest Marker Index (MI) of 63.08 and 34.87 were observed for the primer combinationsE-AAC/M-CAC and E-AGG/M-CTA, respectively. Cluster and principal component analysesrevealed the relationships within and between the species (Fig. 45).Fig. 45 Genetic clusters of bamboo inferred by STRUCTURE. Cluster I and V: D. hamiltonii, Cluster II: D. strictus;Cluster III: B. nutans, B. bambos and B. balcooa; Cluster IV: intermixed49