SENIOR HANDBOOK for 2012
PRINCIPAL'S MESSAGE - St Margaret Mary's College
PRINCIPAL'S MESSAGE - St Margaret Mary's College
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MATHEMATICS<br />
Why study Mathematics?<br />
Mathematics is an integral part of general education. In recent years, the range of career opportunities<br />
requiring mathematical competence has expanded significantly. Mathematics is not only a significant<br />
component of science and technology, but it is also used <strong>for</strong> developments in industry and commerce, in the<br />
provision of social and community services and in government policy and planning. Studying Mathematics will<br />
help students to develop their analytical, problem solving and decision making skills.<br />
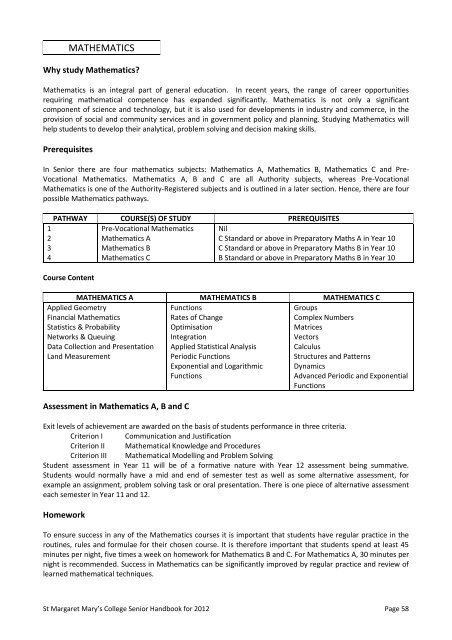
Prerequisites<br />
In Senior there are four mathematics subjects: Mathematics A, Mathematics B, Mathematics C and Pre-<br />
Vocational Mathematics. Mathematics A, B and C are all Authority subjects, whereas Pre-Vocational<br />
Mathematics is one of the Authority-Registered subjects and is outlined in a later section. Hence, there are four<br />
possible Mathematics pathways.<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
PATHWAY COURSE(S) OF STUDY PREREQUISITES<br />
Pre-Vocational Mathematics<br />
Mathematics A<br />
Mathematics B<br />
Mathematics C<br />
Course Content<br />
Applied Geometry<br />
Financial Mathematics<br />
Statistics & Probability<br />
Networks & Queuing<br />
Data Collection and Presentation<br />
Land Measurement<br />
Nil<br />
C Standard or above in Preparatory Maths A in Year 10<br />
C Standard or above in Preparatory Maths B in Year 10<br />
B Standard or above in Preparatory Maths B in Year 10<br />
MATHEMATICS A MATHEMATICS B MATHEMATICS C<br />
Functions<br />
Rates of Change<br />
Optimisation<br />
Integration<br />
Applied Statistical Analysis<br />
Periodic Functions<br />
Exponential and Logarithmic<br />
Functions<br />
Assessment in Mathematics A, B and C<br />
Groups<br />
Complex Numbers<br />
Matrices<br />
Vectors<br />
Calculus<br />
Structures and Patterns<br />
Dynamics<br />
Advanced Periodic and Exponential<br />
Functions<br />
Exit levels of achievement are awarded on the basis of students per<strong>for</strong>mance in three criteria.<br />
Criterion I Communication and Justification<br />
Criterion II Mathematical Knowledge and Procedures<br />
Criterion III Mathematical Modelling and Problem Solving<br />
Student assessment in Year 11 will be of a <strong>for</strong>mative nature with Year 12 assessment being summative.<br />
Students would normally have a mid and end of semester test as well as some alternative assessment, <strong>for</strong><br />
example an assignment, problem solving task or oral presentation. There is one piece of alternative assessment<br />
each semester in Year 11 and 12.<br />
Homework<br />
To ensure success in any of the Mathematics courses it is important that students have regular practice in the<br />
routines, rules and <strong>for</strong>mulae <strong>for</strong> their chosen course. It is there<strong>for</strong>e important that students spend at least 45<br />
minutes per night, five times a week on homework <strong>for</strong> Mathematics B and C. For Mathematics A, 30 minutes per<br />
night is recommended. Success in Mathematics can be significantly improved by regular practice and review of<br />
learned mathematical techniques.<br />
St Margaret Mary’s College Senior Handbook <strong>for</strong> <strong>2012</strong> Page 58