E M I S S I O N S M E S S T E C H N I K - Ribble Enviro Ltd
E M I S S I O N S M E S S T E C H N I K - Ribble Enviro Ltd
E M I S S I O N S M E S S T E C H N I K - Ribble Enviro Ltd
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
EiUK USER MANUAL RASI 700<br />
OK<br />
F1<br />
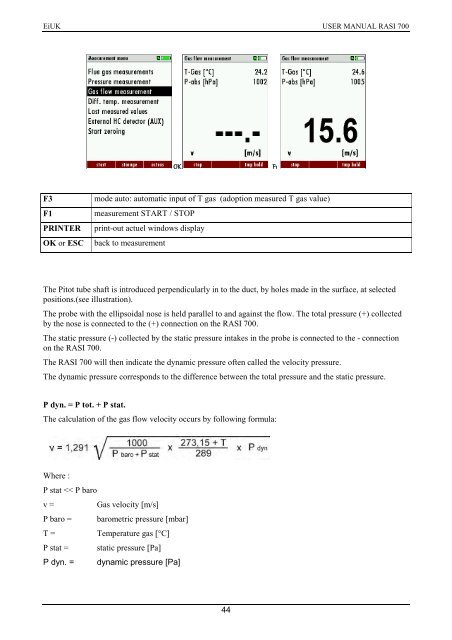
F3<br />
F1<br />
PRINTER<br />
OK or ESC<br />
mode auto: automatic input of T gas (adoption measured T gas value)<br />
measurement START / STOP<br />
print-out actuel windows display<br />
back to measurement<br />
The Pitot tube shaft is introduced perpendicularly in to the duct, by holes made in the surface, at selected<br />
positions.(see illustration).<br />
The probe with the ellipsoidal nose is held parallel to and against the flow. The total pressure (+) collected<br />
by the nose is connected to the (+) connection on the RASI 700.<br />
The static pressure (-) collected by the static pressure intakes in the probe is connected to the - connection<br />
on the RASI 700.<br />
The RASI 700 will then indicate the dynamic pressure often called the velocity pressure.<br />
The dynamic pressure corresponds to the difference between the total pressure and the static pressure.<br />
P dyn. = P tot. + P stat.<br />
The calculation of the gas flow velocity occurs by following formula:<br />
Where :<br />
P stat