- Page 1 and 2:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE Clinica
- Page 3 and 4:
© World Health Organization 2007 A
- Page 5 and 6:
iv Acknowledgements The editors wou
- Page 7 and 8:
vi Marco Vitoria (WHO headquarters)
- Page 9 and 10:
viii CRP C-reactive protein CS caes
- Page 11 and 12:
x LFT liver function test LGE linea
- Page 13 and 14:
xii TDM therapeutic drug monitoring
- Page 15 and 16:
xiv Introduction HIV is a chronic i
- Page 18 and 19:
�� ���������
- Page 20 and 21:
Annex 7. Glossary .................
- Page 22 and 23:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINICA
- Page 24 and 25:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINICA
- Page 26 and 27:
10 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 28 and 29:
12 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 30 and 31:
14 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 32 and 33:
1 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 34 and 35:
1 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 36 and 37:
20 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 38 and 39:
22 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 40 and 41:
24 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 42 and 43:
2 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 44 and 45:
2 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 46 and 47:
30 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 48 and 49:
32 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 50 and 51:
34 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 52 and 53:
3 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 54 and 55:
3 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 56 and 57:
40 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 58 and 59:
42 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 60 and 61:
44 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLIN
- Page 62 and 63:
4 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLINI
- Page 65 and 66:
�� ���������
- Page 68 and 69:
I. Principles management of opportu
- Page 70 and 71:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 72 and 73:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 74 and 75:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 76 and 77:
Table 8. pcp second-line treatment
- Page 78 and 79:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 80 and 81:
Table 12. oesophageal and dissemina
- Page 82 and 83:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 84 and 85:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 86 and 87:
5.9.1.2. Treatment Table 15. treatm
- Page 88 and 89:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 90 and 91:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 92 and 93:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 94 and 95:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 96 and 97:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 98 and 99:
management of opportunistic infecti
- Page 100 and 101:
�� ���������
- Page 103 and 104:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 105 and 106:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 107 and 108:
III. Initial evaluation palliative
- Page 109 and 110:
IV. Treatment palliative care for p
- Page 111 and 112:
Fig. 2. who analgesic ladder for ma
- Page 113 and 114:
Type of pain or treatment Usual sta
- Page 115 and 116:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 117 and 118:
Table 5. prevalence of symptoms in
- Page 119 and 120:
Type Symptoms Possible causes Disea
- Page 121 and 122:
Type Symptoms Possible causes Disea
- Page 123 and 124:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 125 and 126:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 127 and 128:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 129 and 130:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 131 and 132:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 133 and 134:
Table 22. Management of mania and B
- Page 135 and 136:
Table 24. Management of cough or di
- Page 137 and 138:
V. Special advice for terminal care
- Page 139 and 140:
Table 27. common manifestations in
- Page 141 and 142:
palliative care for people living w
- Page 143 and 144:
References palliative care for peop
- Page 145 and 146:
�� ���������
- Page 147 and 148:
VI. Suggested minimum data to be co
- Page 149 and 150:
136 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 151 and 152:
138 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 153 and 154:
140 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 155 and 156:
142 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 157 and 158:
144 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 159 and 160:
146 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 161 and 162:
148 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 163 and 164:
150 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 165 and 166:
152 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 167 and 168:
154 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 169 and 170:
156 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 171 and 172:
158 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 173 and 174:
Contents I. Policy and principles .
- Page 175 and 176:
I. Policy and principles HIV/AIDS T
- Page 177 and 178:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 179 and 180:
° bacterial pneumonia ° endocardi
- Page 181 and 182:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 183 and 184:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 185 and 186:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 187 and 188:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 189 and 190:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 191 and 192:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 193 and 194:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 195 and 196:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 197 and 198:
Social factors are: • homelessnes
- Page 199 and 200:
Table 3. Interactions between ARV d
- Page 201 and 202:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 203 and 204:
Other medications Use Rifampicin (R
- Page 205 and 206:
Table 5. Interactions of illicit dr
- Page 207 and 208:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 209 and 210:
ANNEX 1 ASI6 C © 2004 University o
- Page 211 and 212:
ANNEX 1 ASI6 C © 2004 University o
- Page 213 and 214:
ANNEX 1 ASI6 C © 2004 University o
- Page 215 and 216:
ANNEX 1 ASI6 C © 2004 University o
- Page 217 and 218:
ANNEX 1 ASI6 C © 2004 University o
- Page 219 and 220:
ANNEX 1 ASI6 C © 2004 University o
- Page 221 and 222:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 223 and 224:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 225 and 226:
• Cardiovascular Hypertension Tac
- Page 227 and 228:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 229 and 230:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 231 and 232:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 233 and 234:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 235:
HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE FOR INJ
- Page 238 and 239:
Contents I. Epidemiology and natura
- Page 240 and 241:
ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 242 and 243:
ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 244 and 245:
ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 246 and 247:
ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 248 and 249:
ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 250 and 251: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 252 and 253: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 254 and 255: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 256 and 257: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 258 and 259: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 260 and 261: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 262 and 263: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 264 and 265: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 266 and 267: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 268 and 269: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 270 and 271: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 272 and 273: Annex 3. Alcohol screening question
- Page 274 and 275: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 276 and 277: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 278 and 279: Table 16. a sample of the drug pipe
- Page 280 and 281: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 282 and 283: ManageMent of Hepatitis C and HiV C
- Page 284 and 285: �� ���������
- Page 286 and 287: 3.2. Considerations regarding treat
- Page 288 and 289: 278 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 290 and 291: 280 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 292 and 293: 282 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 294 and 295: 284 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 296 and 297: 286 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 298 and 299: 288 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
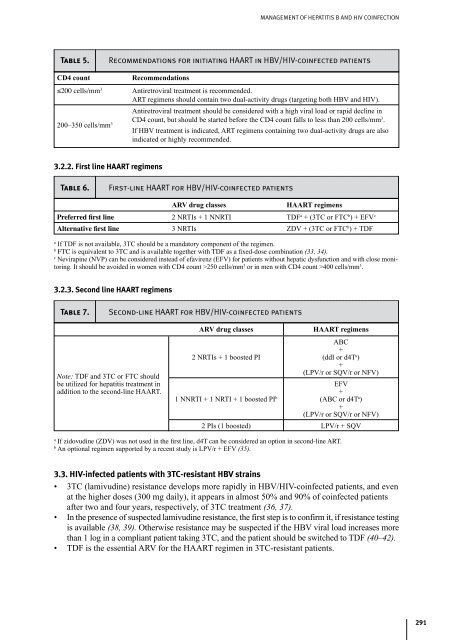
- Page 302 and 303: 292 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 304 and 305: 294 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 306 and 307: 296 hiv/aids tReatment and caRe cLi
- Page 309 and 310: �� ���������
- Page 312 and 313: I. Prevention strategies Prevention
- Page 314 and 315: Prevention of HePatitis a, B, C and
- Page 316 and 317: Prevention of HePatitis a, B, C and
- Page 318 and 319: �� ���������
- Page 320 and 321: 5. Contraceptive methods for women
- Page 322 and 323: 314 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 324 and 325: 316 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 326 and 327: 318 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 328 and 329: 320 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 330 and 331: 322 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 332 and 333: 324 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 334 and 335: 326 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 336 and 337: 328 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 338 and 339: 330 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 340 and 341: 332 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 342 and 343: 334 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 344 and 345: 336 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 346 and 347: 338 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 348 and 349: 340 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 350 and 351:
342 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 352 and 353:
344 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 354 and 355:
346 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 356 and 357:
348 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 358 and 359:
350 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 360 and 361:
352 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 362 and 363:
354 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 364 and 365:
356 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 366 and 367:
358 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 368:
�����������
- Page 372 and 373:
I. Policy issues Prevention of Hiv
- Page 374 and 375:
III. Initial evaluation Prevention
- Page 376 and 377:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 378 and 379:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 380 and 381:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 382 and 383:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 384 and 385:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 386 and 387:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 388 and 389:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 390 and 391:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 392 and 393:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 394 and 395:
Prevention of Hiv transmission from
- Page 396 and 397:
�����������
- Page 398 and 399:
6. Fungal infections...............
- Page 400 and 401:
394 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 402 and 403:
396 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 404 and 405:
398 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 406 and 407:
400 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 408 and 409:
402 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 410 and 411:
404 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 412 and 413:
406 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 414 and 415:
408 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 416 and 417:
410 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 418 and 419:
412 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 420 and 421:
414 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 422 and 423:
416 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 424 and 425:
418 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 426 and 427:
420 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 428:
422 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 431 and 432:
• Disseminated non-tuberculous my
- Page 434 and 435:
428 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 436 and 437:
430 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 438 and 439:
432 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 440 and 441:
434 HIV/AIDS TREATMENT AND CARE CLI
- Page 443 and 444:
�����������
- Page 445 and 446:
Annex 3. Rabies vaccines ..........
- Page 447 and 448:
442 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 449 and 450:
444 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 451 and 452:
446 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 453 and 454:
448 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 455 and 456:
450 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 457 and 458:
452 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 459 and 460:
454 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 461 and 462:
456 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 463 and 464:
458 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 465 and 466:
460 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 467 and 468:
462 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 469 and 470:
464 hIv/aIds tReatment and caRe clI
- Page 471 and 472:
Contents I. Policy issues .........
- Page 473 and 474:
I. Policy issues post-exposure prop
- Page 475 and 476:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 477 and 478:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 479 and 480:
° condom use ° presence of STIs (
- Page 481 and 482:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 483 and 484:
Table 3. thre- drug arv regimens Pr
- Page 485 and 486:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 487 and 488:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 489 and 490:
VI. Suggested minimum data to be co
- Page 491 and 492:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 493 and 494:
History of antiretroviral treatment
- Page 495 and 496:
Test results: HBV: HCV: HIV: Post-t
- Page 497 and 498:
Infection control standard precauti
- Page 499 and 500:
post-exposure prophylaxis for hiv i
- Page 501:
The World Health Organization (WHO)