vgbe energy journal 5 (2022) - International Journal for Generation and Storage of Electricity and Heat
vgbe energy journal - International Journal for Generation and Storage of Electricity and Heat. Issue 5 (2022). Technical Journal of the vgbe energy e.V. - Energy is us! NOTICE: Please feel free to read this free copy of the vgbe energy journal. This is our temporary contribution to support experience exchange in the energy industry during Corona times. The printed edition, subscription as well as further services are available on our website, www.vgbe.energy +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Christopher Weßelmann: Editorial Nuclear power in numbers 2021/2022 Kernenergie in Zahlen 2021/2022 Peter Schluppkothen and Mats-Milan L. Müller: How the digital project twin changes plant engineering in power industry Der Digital Project Twin revolutioniert den Anlagenbau in der Energiewirtschaft Stefan Loubichi: Cyberwar in the energy industry: The current status Cyberwar in der Energiewirtschaft: der aktuelle Stand Antonio Ballesteros Avila and Miguel Peinador Veira: Operating experience from ageing events occurred at nuclear power plants Betriebserfahrungen mit Ereignissen in Bezug auf die Betriebszeit von Kernkraftwerken Minhee Kim, Junkyu Song and Kyungho Nam: Assessment of loss of shutdown cooling system accident during mid-loop operation in LSTF experiment using SPACE Code Bewertung des Ausfalls des Nachkühlsystems während des Mitte-Loop-Betriebs im LSTF-Experiment unter Verwendung des SPACE-Codes Jürgen Knorr and Albert Kerber: TRIPLE C waste container for increased long-term safety of HHGW disposal in salt, clay and crystalline TRIPLE C Abfallbehälter zur Erhöhung der Langzeitsicherheit der Einlagerung radioaktiver Abfälle in Salz, Ton und Kristallin Editorial: Nuclear power plants worldwide: Compact statistic 2021 Kernkraftwerke weltweit: Schnellstatistik 2021 vgbe energy: Operating experience with nuclear power plants 2021 Betriebserfahrungen mit Kernkraftwerken 2021 Paul Baruya: Power and coal prospects in developing Africa Trends der Stromerzeugung und des Kohleeinsatzes in den Entwicklungsländern Afrikas
vgbe energy journal - International Journal for Generation and Storage of Electricity and Heat.
Issue 5 (2022).
Technical Journal of the vgbe energy e.V. - Energy is us!
NOTICE: Please feel free to read this free copy of the vgbe energy journal. This is our temporary contribution to support experience exchange in the energy industry during Corona times. The printed edition, subscription as well as further services are available on our website, www.vgbe.energy
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Christopher Weßelmann: Editorial
Nuclear power in numbers 2021/2022
Kernenergie in Zahlen 2021/2022
Peter Schluppkothen and Mats-Milan L. Müller:
How the digital project twin changes plant engineering in power industry
Der Digital Project Twin revolutioniert den Anlagenbau in der Energiewirtschaft
Stefan Loubichi:
Cyberwar in the energy industry: The current status
Cyberwar in der Energiewirtschaft: der aktuelle Stand
Antonio Ballesteros Avila and Miguel Peinador Veira:
Operating experience from ageing events occurred at nuclear power plants
Betriebserfahrungen mit Ereignissen in Bezug auf die Betriebszeit von Kernkraftwerken
Minhee Kim, Junkyu Song and Kyungho Nam:
Assessment of loss of shutdown cooling system accident during mid-loop operation in LSTF experiment using SPACE Code
Bewertung des Ausfalls des Nachkühlsystems während des Mitte-Loop-Betriebs im LSTF-Experiment unter Verwendung des SPACE-Codes
Jürgen Knorr and Albert Kerber:
TRIPLE C waste container for increased long-term safety of HHGW disposal in salt, clay and crystalline
TRIPLE C Abfallbehälter zur Erhöhung der Langzeitsicherheit der Einlagerung radioaktiver Abfälle in Salz, Ton und Kristallin
Editorial:
Nuclear power plants worldwide: Compact statistic 2021
Kernkraftwerke weltweit: Schnellstatistik 2021
vgbe energy:
Operating experience with nuclear power plants 2021
Betriebserfahrungen mit Kernkraftwerken 2021
Paul Baruya:
Power and coal prospects in developing Africa
Trends der Stromerzeugung und des Kohleeinsatzes in den Entwicklungsländern Afrikas
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Operating experience from ageing events occurred at nuclear power plants<br />
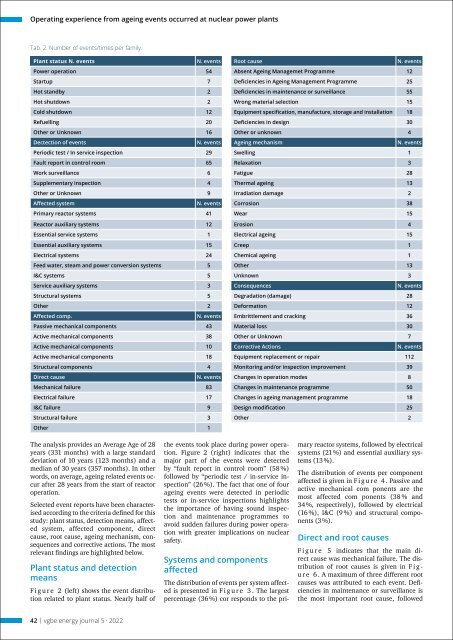
Tab. 2. Number <strong>of</strong> events/times per family.<br />
Plant status N. events N. events Root cause N. events<br />
Power operation 54 Absent Ageing Managemet Programme 12<br />
Startup 7 Deficiencies in Ageing Management Programme 25<br />
Hot st<strong>and</strong>by 2 Deficiencies in maintenance or surveillance 55<br />
Hot shutdown 2 Wrong material selection 15<br />
Cold shutdown 12 Equipment specification, manufacture, storage <strong>and</strong> installation 18<br />
Refuelling 20 Deficiencies in design 30<br />
Other or Unknown 16 Other or unknown 4<br />
Dectection <strong>of</strong> events N. events Ageing mechanism N. events<br />
Periodic test / In service inspection 29 Swelling 1<br />
Fault report in control room 65 Relaxation 3<br />
Work surveillance 6 Fatigue 28<br />
Supplementary inspection 4 Thermal ageing 13<br />
Other or Unknown 9 Irradiation damage 2<br />
Affected system N. events Corrosion 38<br />
Primary reactor systems 41 Wear 15<br />
Reactor auxiliary systems 12 Erosion 4<br />
Essential service systems 1 Electrical ageing 15<br />
Essential auxiliary systems 15 Creep 1<br />
Electrical systems 24 Chemical ageing 1<br />
Feed water, steam <strong>and</strong> power conversion systems 5 Other 13<br />
I&C systems 5 Unknown 3<br />
Service auxiliary systems 3 Consequences N. events<br />
Structural systems 5 Degradation (damage) 28<br />
Other 2 De<strong>for</strong>mation 12<br />
Affected comp. N. events Embrittlement <strong>and</strong> cracking 36<br />
Passive mechanical components 43 Material loss 30<br />
Active mechanical components 38 Other or Unknown 7<br />
Active mechanical components 10 Corrective Actions N. events<br />
Active mechanical components 18 Equipment replacement or repair 112<br />
Structural components 4 Monitoring <strong>and</strong>/or inspection improvement 39<br />
Direct cause N. events Changes in operation modes 8<br />
Mechanical failure 83 Changes in maintenance programme 50<br />
Electrical failure 17 Changes in ageing management programme 18<br />
I&C failure 9 Design modification 25<br />
Structural failure 3 Other 2<br />
Other 1<br />
The analysis provides an Average Age <strong>of</strong> 28<br />
years (331 months) with a large st<strong>and</strong>ard<br />
deviation <strong>of</strong> 10 years (123 months) <strong>and</strong> a<br />
median <strong>of</strong> 30 years (357 months). In other<br />
words, on average, ageing related events occur<br />
after 28 years from the start <strong>of</strong> reactor<br />
operation.<br />
Selected event reports have been characterised<br />
according to the criteria defined <strong>for</strong> this<br />
study: plant status, detection means, affected<br />
system, affected component, direct<br />
cause, root cause, ageing mechanism, consequences<br />
<strong>and</strong> corrective actions. The most<br />
relevant findings are highlighted below.<br />
Plant status <strong>and</strong> detection<br />
means<br />
F i g u r e 2 (left) shows the event distribution<br />
related to plant status. Nearly half <strong>of</strong><br />
the events took place during power operation.<br />
Figure 2 (right) indicates that the<br />
major part <strong>of</strong> the events were detected<br />
by “fault report in control room” (58 %)<br />
followed by “periodic test / in-service inspection”<br />
(26 %). The fact that one <strong>of</strong> four<br />
ageing events were detected in periodic<br />
tests or in-service inspections highlights<br />
the importance <strong>of</strong> having sound inspection<br />
<strong>and</strong> maintenance programmes to<br />
avoid sudden failures during power operation<br />
with greater implications on nuclear<br />
safety.<br />
Systems <strong>and</strong> components<br />
affected<br />
The distribution <strong>of</strong> events per system affected<br />
is presented in F i g u r e 3 . The largest<br />
percentage (36 %) cor responds to the primary<br />
reactor systems, followed by electrical<br />
systems (21 %) <strong>and</strong> essential auxiliary systems<br />
(13 %).<br />
The distribution <strong>of</strong> events per component<br />
affected is given in F i g u r e 4 . Passive <strong>and</strong><br />
active mechanical com ponents are the<br />
most affected com ponents (38 % <strong>and</strong><br />
34 %, respectively), followed by electrical<br />
(16 %), I&C (9 %) <strong>and</strong> structural components<br />
(3 %).<br />
Direct <strong>and</strong> root causes<br />
F i g u r e 5 indicates that the main direct<br />
cause was mechanical failure. The distribution<br />
<strong>of</strong> root causes is given in F i g -<br />
u r e 6 . A maximum <strong>of</strong> three different root<br />
causes was attributed to each event. Deficiencies<br />
in maintenance or surveillance is<br />
the most important root cause, followed<br />
42 | <strong>vgbe</strong> <strong>energy</strong> <strong>journal</strong> 5 · <strong>2022</strong>