Equilibrium Growth, Inflation, and Bond Yields - Duke University's ...
Equilibrium Growth, Inflation, and Bond Yields - Duke University's ...
Equilibrium Growth, Inflation, and Bond Yields - Duke University's ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
a<br />
" n<br />
E[" z]<br />
5.5<br />
5<br />
4.5<br />
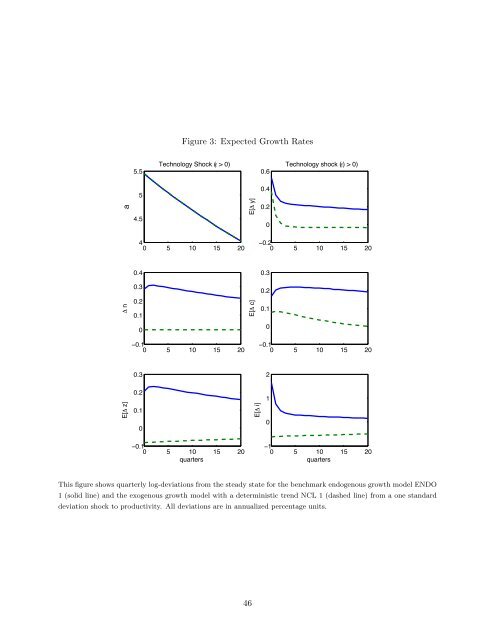
Figure 3: Expected <strong>Growth</strong> Rates<br />
Technology Shock (! > 0)<br />
4<br />
0 5 10 15 20<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
−0.1<br />
0 5 10 15 20<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
−0.1<br />
0 5 10<br />
quarters<br />
15 20<br />
E[" y]<br />
E[" c]<br />
E[" i]<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
Technology shock (!) > 0)<br />
−0.2<br />
0 5 10 15 20<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
−0.1<br />
0 5 10 15 20<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
−1<br />
0 5 10<br />
quarters<br />
15 20<br />
This figure shows quarterly log-deviations from the steady state for the benchmark endogenous growth model ENDO<br />
1 (solid line) <strong>and</strong> the exogenous growth model with a deterministic trend NCL 1 (dashed line) from a one st<strong>and</strong>ard<br />
deviation shock to productivity. All deviations are in annualized percentage units.<br />
46