Precise Orbit Determination of Global Navigation Satellite System of ...
Precise Orbit Determination of Global Navigation Satellite System of ...
Precise Orbit Determination of Global Navigation Satellite System of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 4 Major Error Sources <strong>of</strong> <strong>Satellite</strong> Observations<br />
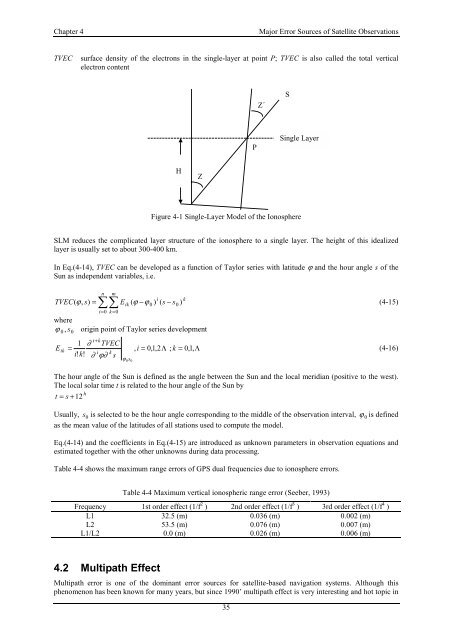
TVEC surface density <strong>of</strong> the electrons in the single-layer at point P; TVEC is also called the total vertical<br />
electron content<br />
Figure 4-1 Single-Layer Model <strong>of</strong> the Ionosphere<br />
SLM reduces the complicated layer structure <strong>of</strong> the ionosphere to a single layer. The height <strong>of</strong> this idealized<br />
layer is usually set to about 300-400 km.<br />
In Eq.(4-14), TVEC can be developed as a function <strong>of</strong> Taylor series with latitude ϕ and the hour angle s <strong>of</strong> the<br />
Sun as independent variables, i.e.<br />
n m<br />
i k<br />
TVEC(<br />
, s)<br />
= ��Eik<br />
( ϕ −ϕ<br />
0 ) ( s − s0<br />
)<br />
i=<br />
0 k=<br />
0<br />
where<br />
ϕ 0, s0 origin point <strong>of</strong> Taylor series development<br />
E<br />
ik<br />
ϕ (4-15)<br />
i+<br />
k<br />
1 ∂ TVEC<br />
=<br />
i!<br />
k!<br />
i k<br />
∂ ϕ∂ s<br />
ϕ<br />
0s0<br />
, i =<br />
0,<br />
1,<br />
2Λ<br />
; k = 0,<br />
1,<br />
Λ<br />
35<br />
(4-16)<br />
The hour angle <strong>of</strong> the Sun is defined as the angle between the Sun and the local meridian (positive to the west).<br />
The local solar time t is related to the hour angle <strong>of</strong> the Sun by<br />
h<br />
t = s+12<br />
Usually, s 0 is selected to be the hour angle corresponding to the middle <strong>of</strong> the observation interval, ϕ 0 is defined<br />
as the mean value <strong>of</strong> the latitudes <strong>of</strong> all stations used to compute the model.<br />
Eq.(4-14) and the coefficients in Eq.(4-15) are introduced as unknown parameters in observation equations and<br />
estimated together with the other unknowns during data processing.<br />
Table 4-4 shows the maximum range errors <strong>of</strong> GPS dual frequencies due to ionosphere errors.<br />
Table 4-4 Maximum vertical ionospheric range error (Seeber, 1993)<br />
Frequency 1st order effect (1/f 2 ) 2nd order effect (1/f 3 ) 3rd order effect (1/f 4 )<br />
L1<br />
L2<br />
L1/L2<br />
4.2 Multipath Effect<br />
H<br />
32.5 (m)<br />
53.5 (m)<br />
0.0 (m)<br />
Z<br />
0.036 (m)<br />
0.076 (m)<br />
0.026 (m)<br />
0.002 (m)<br />
0.007 (m)<br />
0.006 (m)<br />
Multipath error is one <strong>of</strong> the dominant error sources for satellite-based navigation systems. Although this<br />
phenomenon has been known for many years, but since 1990’ multipath effect is very interesting and hot topic in<br />
P<br />
Z´<br />
S<br />
Single Layer