CAPITOLO 6 6.1 – L'iperbole sferica ed ellissoidica Siano A e B due ...
CAPITOLO 6 6.1 – L'iperbole sferica ed ellissoidica Siano A e B due ...
CAPITOLO 6 6.1 – L'iperbole sferica ed ellissoidica Siano A e B due ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
243<br />
Mario Vultaggio<br />
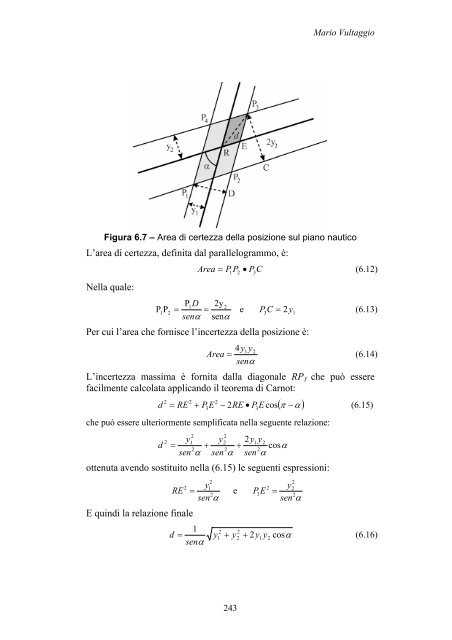
Figura 6.7 <strong>–</strong> Area di certezza della posizione sul piano nautico<br />
L’area di certezza, definita dal parallelogrammo, è:<br />
Nella quale:<br />
P D<br />
senα<br />
Area = P1<br />
P2<br />
• P3C<br />
(<strong>6.1</strong>2)<br />
2y<br />
senα<br />
1<br />
2<br />
P1P2 = =<br />
P3C<br />
= y1<br />
Per cui l’area che fornisce l’incertezza della posizione è:<br />
e<br />
2<br />
(<strong>6.1</strong>3)<br />
4y1<br />
y2<br />
Area = (<strong>6.1</strong>4)<br />
senα<br />
L’incertezza massima è fornita dalla diagonale RP3 che può essere<br />
facilmente calcolata applicando il teorema di Carnot:<br />
( π − α )<br />
2 2 2<br />
d = RE + P E − RE • P E cos<br />
(<strong>6.1</strong>5)<br />
3<br />
2 3<br />
che può essere ulteriormente semplificata nella seguente relazione:<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2 y1<br />
y2<br />
2y1<br />
y2<br />
d = + + cosα<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
sen α sen α sen α<br />
ottenuta avendo sostituito nella (<strong>6.1</strong>5) le seguenti espressioni:<br />
2<br />
2 y1<br />
RE = 2<br />
sen α<br />
E quindi la relazione finale<br />
e<br />
2<br />
2 y2<br />
P3<br />
E = 2<br />
sen α<br />
1<br />
d =<br />
senα<br />
2 2<br />
y1<br />
+ y2<br />
+ 2y1<br />
y2<br />
cosα<br />
(<strong>6.1</strong>6)