N° 3 - Salute per tutti
N° 3 - Salute per tutti
N° 3 - Salute per tutti
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Figure 4.<br />
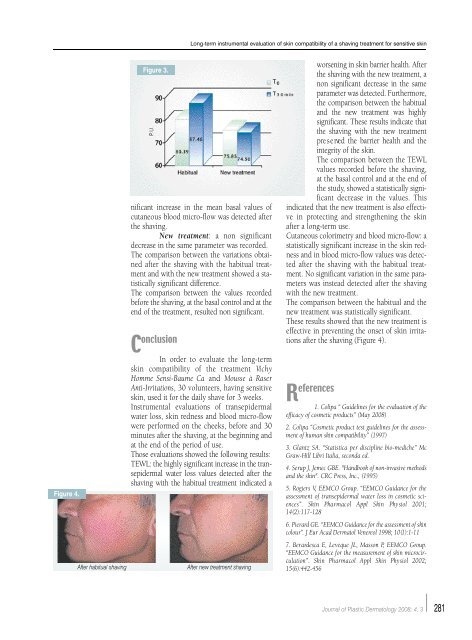
Figure 3.<br />
nificant increase in the mean basal values of<br />
cutaneous blood micro-flow was detected after<br />
the shaving.<br />
New tre a t m e n t: a non significant<br />
decrease in the same parameter was recorded.<br />
The comparison between the variations obtained<br />
after the shaving with the habitual treatment<br />
and with the new treatment showed a statistically<br />
significant difference.<br />
The comparison between the values re c o rd e d<br />
b e f o re the shaving, at the basal control and at the<br />
end of the treatment, resulted non significant.<br />
C onclusion<br />
In order to evaluate the long-term<br />
skin compatibility of the treatment Vi c h y<br />
Homme Sensi-Baume Ca and Mousse à Raser<br />
Anti-Irritations, 30 volunteers, having sensitive<br />
skin, used it for the daily shave for 3 weeks.<br />
Instrumental evaluations of transepidermal<br />
water loss, skin redness and blood micro-flow<br />
were <strong>per</strong>formed on the cheeks, before and 30<br />
minutes after the shaving, at the beginning and<br />
at the end of the <strong>per</strong>iod of use.<br />
Those evaluations showed the following re s u l t s :<br />
TEWL: the highly significant increase in the transepidermal<br />
water loss values detected after the<br />
shaving with the habitual treatment indicated a<br />
After habitual shaving After new treatment shaving<br />
Long-term instrumental evaluation of skin compatibility of a shaving treatment for sensitive skin<br />
worsening in skin barrier health. After<br />
the shaving with the new treatment, a<br />
non significant decrease in the same<br />
parameter was detected. Furthermore ,<br />
the comparison between the habitual<br />
and the new treatment was highly<br />
significant. These results indicate that<br />
the shaving with the new tre a t m e n t<br />
p re s e rved the barrier health and the<br />
integrity of the skin.<br />
The comparison between the TEWL<br />
values recorded before the shaving,<br />
at the basal control and at the end of<br />
the study, showed a statistically significant<br />
decrease in the values. This<br />
indicated that the new treatment is also effective<br />
in protecting and strengthening the skin<br />
after a long-term use.<br />
Cutaneous colorimetry and blood micro-flow: a<br />
statistically significant increase in the skin redness<br />
and in blood micro-flow values was detected<br />
after the shaving with the habitual treatment.<br />
No significant variation in the same parameters<br />
was instead detected after the shaving<br />
with the new treatment.<br />
The comparison between the habitual and the<br />
new treatment was statistically significant.<br />
These results showed that the new treatment is<br />
effective in preventing the onset of skin irritations<br />
after the shaving (Figure 4).<br />
R eferences<br />
1. Colipa “ Guidelines for the evaluation of the<br />
efficacy of cosmetic products” (May 2008)<br />
2. Colipa “Cosmetic product test guidelines for the assessment<br />
of human skin compatibility” (1997)<br />
3. Glantz SA. “Statistica <strong>per</strong> discipline bio-mediche” Mc<br />
Graw-Hill Libri Italia, seconda ed.<br />
4. Serup J, Jemec GBE. "Handbook of non-invasive methods<br />
and the skin". CRC Press, Inc., (1995)<br />
5. Rogiers V, EEMCO Group. “EEMCO Guidance for the<br />
assessment of transepidermal water loss in cosmetic sciences”.<br />
Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol 2001;<br />
14(2):117-128<br />
6. Pierard GE. “EEMCO Guidance for the assessment of skin<br />
colour”. J Eur Acad Dermatol Ve n e reol 1998; 10(1):1-11<br />
7. Berardesca E, Leveque JL, Masson P, EEMCO Group.<br />
“EEMCO Guidance for the measurement of skin microcirculation”.<br />
Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol 2002;<br />
15(6):442-456<br />
Journal of Plastic Dermatology 2008; 4, 3<br />
281