Identificação do efeito antitumoral de um polipeptÃdeo isolado da ...
Identificação do efeito antitumoral de um polipeptÃdeo isolado da ...
Identificação do efeito antitumoral de um polipeptÃdeo isolado da ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
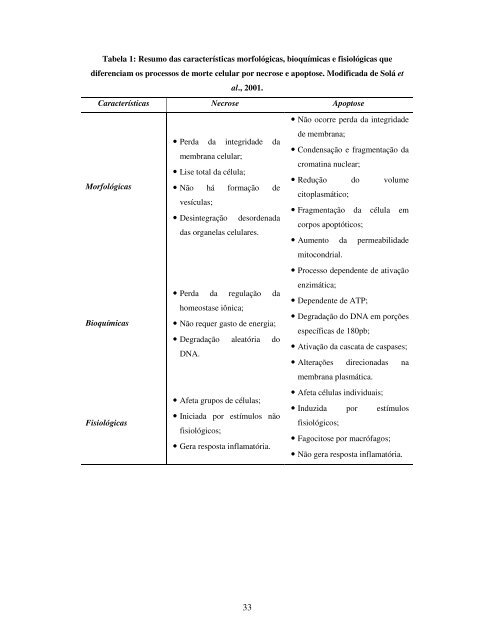
Tabela 1: Res<strong>um</strong>o <strong>da</strong>s características morfológicas, bioquímicas e fisiológicas quediferenciam os processos <strong>de</strong> morte celular por necrose e apoptose. Modifica<strong>da</strong> <strong>de</strong> Solá etal., 2001.Características Necrose ApoptoseMorfológicasBioquímicasFisiológicas• Per<strong>da</strong> <strong>da</strong> integri<strong>da</strong><strong>de</strong> <strong>da</strong>membrana celular;• Lise total <strong>da</strong> célula;• Não há formação <strong>de</strong>vesículas;• Desintegração <strong>de</strong>sor<strong>de</strong>na<strong>da</strong><strong>da</strong>s organelas celulares.• Per<strong>da</strong> <strong>da</strong> regulação <strong>da</strong>homeostase iônica;• Não requer gasto <strong>de</strong> energia;• Degra<strong>da</strong>ção aleatória <strong>do</strong>DNA.• Afeta grupos <strong>de</strong> células;• Inicia<strong>da</strong> por estímulos nãofisiológicos;• Gera resposta inflamatória.• Não ocorre per<strong>da</strong> <strong>da</strong> integri<strong>da</strong><strong>de</strong><strong>de</strong> membrana;• Con<strong>de</strong>nsação e fragmentação <strong>da</strong>cromatina nuclear;• Redução <strong>do</strong> vol<strong>um</strong>ecitoplasmático;• Fragmentação <strong>da</strong> célula emcorpos apoptóticos;• A<strong>um</strong>ento <strong>da</strong> permeabili<strong>da</strong><strong>de</strong>mitocondrial.• Processo <strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nte <strong>de</strong> ativaçãoenzimática;• Depen<strong>de</strong>nte <strong>de</strong> ATP;• Degra<strong>da</strong>ção <strong>do</strong> DNA em porçõesespecíficas <strong>de</strong> 180pb;• Ativação <strong>da</strong> cascata <strong>de</strong> caspases;• Alterações direciona<strong>da</strong>s namembrana plasmática.• Afeta células individuais;• Induzi<strong>da</strong> por estímulosfisiológicos;• Fagocitose por macrófagos;• Não gera resposta inflamatória.33