- Page 1 and 2:
Elemente de mecanica punctului mate
- Page 3 and 4:
CUPRINS 32.1.15 O formulă asimptot
- Page 5 and 6:
CUPRINS 53.2 Cinematica ...........
- Page 7 and 8:
Capitolul 1Mecanică geometrică”
- Page 9 and 10:
1.1. MODELUL MATEMATIC AL SPAŢIULU
- Page 11 and 12:
1.3. GEOMETRIA SPAŢIULUI FIZIC 11E
- Page 13 and 14:
1.4. REPERE CARTEZIENE 13Introducem
- Page 15 and 16:
1.4. REPERE CARTEZIENE 15Atunci,POM
- Page 17 and 18:
Capitolul 2Mecanica punctului mater
- Page 19 and 20:
2.1. CINEMATICA 19fizice care carac
- Page 21 and 22:
2.1. CINEMATICA 21încât γ = ζ
- Page 23 and 24:
2.1. CINEMATICA 23Spaţiul (Γ, T
- Page 25 and 26:
2.1. CINEMATICA 25formulaOM = x a (
- Page 27 and 28:
2.1. CINEMATICA 27Un fapt esenţial
- Page 29 and 30:
2.1. CINEMATICA 29Versorul ν defin
- Page 31 and 32:
2.1. CINEMATICA 31Cum d (|v × a|)
- Page 33 and 34:
2.1. CINEMATICA 33Evident, ¯ f(0)
- Page 35 and 36:
2.1. CINEMATICA 352.1.7 Mişcarea c
- Page 37 and 38:
2.1. CINEMATICA 37Să proiectăm ve
- Page 39 and 40:
2.1. CINEMATICA 39ş.a.m.d.). Să z
- Page 41 and 42:
2.1. CINEMATICA 41Derivând relaţi
- Page 43 and 44:
2.1. CINEMATICA 43Mărimea v A (t)+
- Page 45 and 46:
2.1. CINEMATICA 45Să justificăm,
- Page 47 and 48:
2.1. CINEMATICA 47Pentru demonstrar
- Page 49 and 50:
2.1. CINEMATICA 49În schimb, dacă
- Page 51 and 52:
2.1. CINEMATICA 51Justificarea noţ
- Page 53 and 54:
2.1. CINEMATICA 532) λ(∆) =+∞,
- Page 55 and 56:
2.1. CINEMATICA 55(cf. [39], p. 179
- Page 57 and 58:
2.1. CINEMATICA 573) f(0) poate fi
- Page 59 and 60:
2.1. CINEMATICA 59O parametrizare l
- Page 61 and 62:
2.1. CINEMATICA 61Planul {N ∈ E 3
- Page 63 and 64:
2.1. CINEMATICA 63adevăr, prin der
- Page 65 and 66:
2.1. CINEMATICA 65Reperul 10 R = (M
- Page 67 and 68:
2.1. CINEMATICA 67Relaţiile (2.55)
- Page 69 and 70:
2.1. CINEMATICA 69Pe baza celor de
- Page 71 and 72:
2.1. CINEMATICA 71Fie γ : U → E
- Page 73 and 74:
2.1. CINEMATICA 73De asemeni, mulţ
- Page 75 and 76:
2.1. CINEMATICA 75În concluzie,Z
- Page 77 and 78:
2.1. CINEMATICA 77===ZFr(G)Z−ZF (
- Page 79 and 80:
2.1. CINEMATICA 796 6D0 2b · b ·
- Page 81 and 82:
2.1. CINEMATICA 81µ a+1 1 ¯· co
- Page 83 and 84:
2.1. CINEMATICA 83Aplicaţia f e :
- Page 85 and 86:
2.1. CINEMATICA 85Conform (2.62), (
- Page 87 and 88:
2.1. CINEMATICA 87Apoi,=Z" Ã ! #1
- Page 89 and 90:
2.1. CINEMATICA 89¯unde θ = ](OM,
- Page 91 and 92:
2.1. CINEMATICA 91Aria suprafeţei
- Page 93 and 94:
2.1. CINEMATICA 933) Fie A ∈ E 3
- Page 95 and 96:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 95există
- Page 97 and 98:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 972.2.1 P
- Page 99 and 100:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 99acest f
- Page 101 and 102:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 101unde
- Page 103 and 104:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 103Pe de
- Page 105 and 106:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 105ţinem
- Page 107 and 108:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 107de und
- Page 109 and 110:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 109= m ·
- Page 111 and 112:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 111cinema
- Page 113 and 114:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 113(solu
- Page 115 and 116:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 115Forma
- Page 117 and 118:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 1172.2.9
- Page 119 and 120:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 119desemn
- Page 121 and 122:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 121În ac
- Page 123 and 124:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 123Mai î
- Page 125 and 126:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 125=(2.98
- Page 127 and 128:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 127[34],
- Page 129 and 130:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 129luat c
- Page 131 and 132:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 131Să co
- Page 133 and 134:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 133posibi
- Page 135 and 136:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 135(cf. [
- Page 137 and 138:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 137Rezolv
- Page 139 and 140:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 139= 1 2
- Page 141 and 142:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 141Am ar
- Page 143 and 144:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 143Însă
- Page 145 and 146:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 145respec
- Page 147 and 148:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 147În co
- Page 149 and 150:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 149Confor
- Page 151 and 152:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 151Figura
- Page 153 and 154:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 153Rezolv
- Page 155 and 156:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 155şiÎn
- Page 157 and 158:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 157Ceea c
- Page 159 and 160:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 159făcut
- Page 161 and 162:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 161Figura
- Page 163 and 164:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 163unde
- Page 165 and 166:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 165de mul
- Page 167 and 168:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 167rezult
- Page 169 and 170:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 169de und
- Page 171 and 172:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 171în co
- Page 173 and 174:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 173Figura
- Page 175 and 176:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 175că ϕ
- Page 177 and 178:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 177Cum ϕ
- Page 179 and 180:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 179v(t) =
- Page 181 and 182:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 181existe
- Page 183 and 184:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 183avemli
- Page 185 and 186:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 185josres
- Page 187 and 188:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 187adică
- Page 189 and 190:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 189Aşada
- Page 191 and 192:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 1912.2.27
- Page 193 and 194:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 193Figura
- Page 195 and 196:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 195De ase
- Page 197 and 198:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 197Confor
- Page 199 and 200:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 199astfel
- Page 201 and 202:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 201Figura
- Page 203 and 204:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 203y = y
- Page 205 and 206:
2.2. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 205(linia
- Page 207 and 208:
207unde 1 6 i, j 6 n. Cu alte cuvin
- Page 209 and 210:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 209forţă
- Page 211 and 212:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 2113.1.2 M
- Page 213 and 214:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 213În sf
- Page 215 and 216:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 215doilea
- Page 217 and 218:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 217egale
- Page 219 and 220:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 219alcătu
- Page 221 and 222:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 221Torsoru
- Page 223 and 224:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 223Discuţ
- Page 225 and 226:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 225axei ce
- Page 227 and 228:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 227arată
- Page 229 and 230:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 229µ n µ
- Page 231 and 232:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 231f 0 = A
- Page 233 and 234:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 233La rân
- Page 235 and 236:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 235de unde
- Page 237 and 238:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 237Deoarec
- Page 239 and 240:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 239ceea ce
- Page 241 and 242:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 241pentru
- Page 243 and 244:
3.1. VECTORI ŞI TENSORI 243Să con
- Page 245 and 246:
3.2. CINEMATICA 245Să presupunem a
- Page 247 and 248:
3.2. CINEMATICA 247deoarece B se af
- Page 249 and 250:
3.2. CINEMATICA 2493.2.2 Interpreta
- Page 251 and 252:
3.2. CINEMATICA 251λ ∈ R, şi, c
- Page 253 and 254:
3.2. CINEMATICA 253vitezelor lor, u
- Page 255 and 256:
3.2. CINEMATICA 255Introducem acum
- Page 257 and 258:
3.2. CINEMATICA 257În concluzie, Y
- Page 259 and 260:
3.2. CINEMATICA 259ale sistemului d
- Page 261 and 262: 3.2. CINEMATICA 261(cf. [15], p. 85
- Page 263 and 264: 3.2. CINEMATICA 263Impunând ca λ
- Page 265 and 266: 3.2. CINEMATICA 265Două problemepo
- Page 267 and 268: 3.2. CINEMATICA 267(cf. [32], p. 10
- Page 269 and 270: 3.2. CINEMATICA 269Figura 3.21Notă
- Page 271 and 272: 3.2. CINEMATICA 271trei centre de r
- Page 273 and 274: 3.2. CINEMATICA 273adică centrele
- Page 275 and 276: 3.2. CINEMATICA 275= v M0 × [ω ×
- Page 277 and 278: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 277extern
- Page 279 and 280: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 279de und
- Page 281 and 282: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 281şi, d
- Page 283 and 284: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 283(cf. [
- Page 285 and 286: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 285rezult
- Page 287 and 288: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 287(cf. [
- Page 289 and 290: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 289Figura
- Page 291 and 292: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 291unde
- Page 293 and 294: şi ½I13 · ε − I 23 · ω 2 =
- Page 295 and 296: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 295însea
- Page 297 and 298: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 297Un caz
- Page 299 and 300: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 299ceea c
- Page 301 and 302: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 301Subsec
- Page 303 and 304: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 303= 1289
- Page 305 and 306: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 305Făcâ
- Page 307 and 308: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 307de und
- Page 309 and 310: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 3092) o r
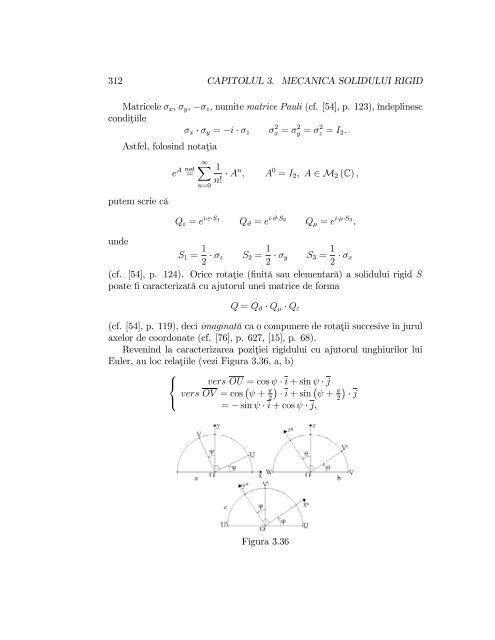
- Page 311: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 311Orota
- Page 315 and 316: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 315T O R
- Page 317 and 318: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 317fie di
- Page 319 and 320: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 319ceea c
- Page 321 and 322: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 321unde C
- Page 323 and 324: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 323Utiliz
- Page 325 and 326: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 325Am ţi
- Page 327 and 328: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 327Relaţ
- Page 329 and 330: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 329Teorem
- Page 331 and 332: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 331656).
- Page 333 and 334: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 333± p f
- Page 335 and 336: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 3353) u 0
- Page 337 and 338: 3.3. STATICA ŞI DINAMICA 337solidu
- Page 339 and 340: Bibliografie[1] V. Arnold, Ecuaţii
- Page 341 and 342: BIBLIOGRAFIE 341[25] D. Drăghicesc
- Page 343 and 344: BIBLIOGRAFIE 343[55] V. Novacu, Baz