89-91 - Polskie Stowarzyszenie Biomateriałów
89-91 - Polskie Stowarzyszenie Biomateriałów
89-91 - Polskie Stowarzyszenie Biomateriałów
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
128<br />
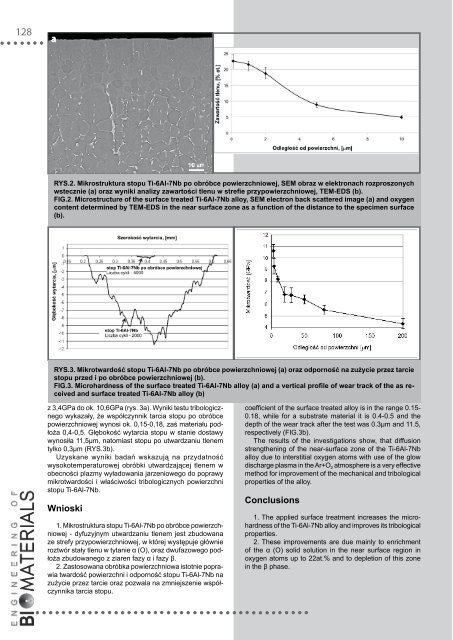
rys.2. mikrostruktura stopu ti-6al-7nb po obróbce powierzchniowej, sem obraz w elektronach rozproszonych<br />
wstecznie (a) oraz wyniki analizy zawartości tlenu w strefie przypowierzchniowej, tem-eds (b).<br />
FIg.2. microstructure of the surface treated ti-6al-7nb alloy, sem electron back scattered image (a) and oxygen<br />
content determined by tem-eds in the near surface zone as a function of the distance to the specimen surface<br />
(b).<br />
rys.3. mikrotwardość stopu ti-6al-7nb po obróbce powierzchniowej (a) oraz odporność na zużycie przez tarcie<br />
stopu przed i po obróbce powierzchniowej (b).<br />
Fig.3. microhardness of the surface treated ti-6al-7nb alloy (a) and a vertical profile of wear track of the as received<br />
and surface treated ti-6al-7nb alloy (b)<br />
z 3,4GPa do ok. 10,6GPa (rys. 3a). Wyniki testu tribologicznego<br />
wykazały, że współczynnik tarcia stopu po obróbce<br />
powierzchniowej wynosi ok. 0,15-0,18, zaś materiału podłoża<br />
0,4-0,5. Głębokość wytarcia stopu w stanie dostawy<br />
wynosiła 11,5µm, natomiast stopu po utwardzaniu tlenem<br />
tylko 0,3µm (rYS.3b).<br />
uzyskane wyniki badań wskazują na przydatność<br />
wysokotemperaturowej obróbki utwardzającej tlenem w<br />
obecności plazmy wyładowania jarzeniowego do poprawy<br />
mikrotwardości i właściwości tribologicznych powierzchni<br />
stopu Ti-6Al-7Nb.<br />
wnioski<br />
1. Mikrostruktura stopu Ti-6Al-7Nb po obróbce powierzchniowej<br />
- dyfuzyjnym utwardzaniu tlenem jest zbudowana<br />
ze strefy przypowierzchniowej, w której występuje głównie<br />
roztwór stały tlenu w tytanie α (O), oraz dwufazowego podłoża<br />
zbudowanego z ziaren fazy α i fazy β.<br />
2. Zastosowana obróbka powierzchniowa istotnie poprawia<br />
twardość powierzchni i odporność stopu Ti-6Al-7Nb na<br />
zużycie przez tarcie oraz pozwala na zmniejszenie współczynnika<br />
tarcia stopu.<br />
coefficient of the surface treated alloy is in the range 0.15-<br />
0.18, while for a substrate material it is 0.4-0.5 and the<br />
depth of the wear track after the test was 0.3µm and 11.5,<br />
respectively (FIG.3b).<br />
The results of the investigations show, that diffusion<br />
strengthening of the near-surface zone of the Ti-6Al-7Nb<br />
alloy due to interstitial oxygen atoms with use of the glow<br />
discharge plasma in the Ar+O 2 atmosphere is a very effective<br />
method for improvement of the mechanical and tribological<br />
properties of the alloy.<br />
conclusions<br />
1. The applied surface treatment increases the microhardness<br />
of the Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy and improves its tribological<br />
properties.<br />
2. These improvements are due mainly to enrichment<br />
of the α (O) solid solution in the near surface region in<br />
oxygen atoms up to 22at.% and to depletion of this zone<br />
in the β phase.