OSIS? 2.0.1 User's Manual - Web services are running on AMBIB
OSIS? 2.0.1 User's Manual - Web services are running on AMBIB
OSIS? 2.0.1 User's Manual - Web services are running on AMBIB
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
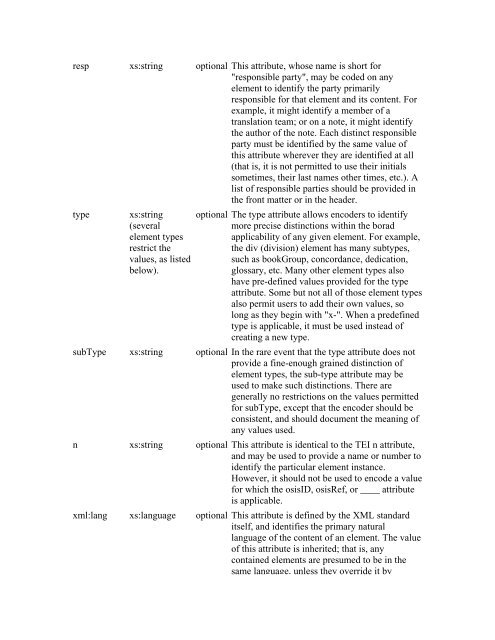
esp xs:string opti<strong>on</strong>al This attribute, whose name is short for<br />
"resp<strong>on</strong>sible party", may be coded <strong>on</strong> any<br />
element to identify the party primarily<br />
resp<strong>on</strong>sible for that element and its c<strong>on</strong>tent. For<br />
example, it might identify a member of a<br />
translati<strong>on</strong> team; or <strong>on</strong> a note, it might identify<br />
the author of the note. Each distinct resp<strong>on</strong>sible<br />
party must be identified by the same value of<br />
this attribute wherever they <str<strong>on</strong>g>are</str<strong>on</strong>g> identified at all<br />
(that is, it is not permitted to use their initials<br />
sometimes, their last names other times, etc.). A<br />
list of resp<strong>on</strong>sible parties should be provided in<br />
the fr<strong>on</strong>t matter or in the header.<br />
type xs:string<br />
(several<br />
element types<br />
restrict the<br />
values, as listed<br />
below).<br />
opti<strong>on</strong>al The type attribute allows encoders to identify<br />
more precise distincti<strong>on</strong>s within the borad<br />
applicability of any given element. For example,<br />
the div (divisi<strong>on</strong>) element has many subtypes,<br />
such as bookGroup, c<strong>on</strong>cordance, dedicati<strong>on</strong>,<br />
glossary, etc. Many other element types also<br />
have pre-defined values provided for the type<br />
attribute. Some but not all of those element types<br />
also permit users to add their own values, so<br />
l<strong>on</strong>g as they begin with "x-". When a predefined<br />
type is applicable, it must be used instead of<br />
creating a new type.<br />
subType xs:string opti<strong>on</strong>al In the r<str<strong>on</strong>g>are</str<strong>on</strong>g> event that the type attribute does not<br />
provide a fine-enough grained distincti<strong>on</strong> of<br />
element types, the sub-type attribute may be<br />
used to make such distincti<strong>on</strong>s. There <str<strong>on</strong>g>are</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
generally no restricti<strong>on</strong>s <strong>on</strong> the values permitted<br />
for subType, except that the encoder should be<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sistent, and should document the meaning of<br />
any values used.<br />
n xs:string opti<strong>on</strong>al This attribute is identical to the TEI n attribute,<br />
and may be used to provide a name or number to<br />
identify the particular element instance.<br />
However, it should not be used to encode a value<br />
for which the osisID, osisRef, or ____ attribute<br />
is applicable.<br />
xml:lang xs:language opti<strong>on</strong>al This attribute is defined by the XML standard<br />
itself, and identifies the primary natural<br />
language of the c<strong>on</strong>tent of an element. The value<br />
of this attribute is inherited; that is, any<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tained elements <str<strong>on</strong>g>are</str<strong>on</strong>g> presumed to be in the<br />
same language, unless they override it by