- Page 2 and 3:
CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS
- Page 4 and 5:
CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS Evidence-B
- Page 6 and 7:
We dedicate this book to all infant
- Page 8 and 9:
For more information about this tit
- Page 10 and 11:
CONTENTS ix 23. Congenital Cystic A
- Page 12 and 13:
CONTENTS xi Part IX Miscellaneous M
- Page 14 and 15:
Contributors Brad Angle, MD Associa
- Page 16 and 17:
Preface Based on a World Health Org
- Page 18 and 19:
Part I General Considerations Copyr
- Page 20 and 21:
Chapter 1 Dysmorphology PRAVEEN KUM
- Page 22 and 23:
CHAPTER 1 DYSMORPHOLOGY 5 Almost 15
- Page 24 and 25:
CHAPTER 1 DYSMORPHOLOGY 7 TABLE 1-
- Page 26 and 27:
CHAPTER 1 DYSMORPHOLOGY 9 malformat
- Page 28 and 29:
CHAPTER 1 DYSMORPHOLOGY 11 examples
- Page 30 and 31:
Chapter 2 Assessment of an Infant w
- Page 32 and 33:
CHAPTER 2 ASSESSMENT OF AN INFANT W
- Page 34 and 35:
CHAPTER 2 ASSESSMENT OF AN INFANT W
- Page 36 and 37:
CHAPTER 2 ASSESSMENT OF AN INFANT W
- Page 38 and 39:
Chapter 3 Genetic Counseling: Princ
- Page 40 and 41:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 42 and 43:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 44 and 45:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 46 and 47:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 48 and 49:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 50 and 51:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 52 and 53:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 54 and 55:
CHAPTER 3 GENETIC COUNSELING: PRINC
- Page 56 and 57:
Part II Central Nervous System Malf
- Page 58 and 59:
Chapter 4 Spina Bifida BARBARA K. B
- Page 60 and 61:
CHAPTER 4 SPINA BIFIDA 43 (Fig. 4-1
- Page 62 and 63:
CHAPTER 4 SPINA BIFIDA 45 TABLE 4-
- Page 64 and 65:
CHAPTER 4 SPINA BIFIDA 47 function,
- Page 66 and 67:
CHAPTER 4 SPINA BIFIDA 49 of the pr
- Page 68 and 69:
Chapter 5 Anencephaly BARBARA K. BU
- Page 70 and 71:
Chapter 6 Encephalocele BARBARA K.
- Page 72 and 73:
CHAPTER 6 ENCEPHALOCELE 55 TABLE 6
- Page 74 and 75:
Chapter 7 Holoprosencephaly BARBARA
- Page 76 and 77:
CHAPTER 7 HOLOPROSENCEPHALY 59 EVA
- Page 78 and 79:
Chapter 8 Hydrocephalus BARBARA K.
- Page 80 and 81:
CHAPTER 8 HYDROCEPHALUS 63 TABLE 8
- Page 82 and 83:
CHAPTER 8 HYDROCEPHALUS 65 TABLE 8
- Page 84 and 85:
Chapter 9 Dandy-Walker Malformation
- Page 86 and 87:
CHAPTER 9 DANDY-WALKER MALFORMATION
- Page 88 and 89:
Chapter 10 Chiari Malformations BAR
- Page 90 and 91:
CHAPTER 10 CHIARI MALFORMATIONS 73
- Page 92 and 93:
CHAPTER 10 CHIARI MALFORMATIONS 75
- Page 94 and 95:
Chapter 11 Agenesis of the Corpus C
- Page 96 and 97:
CHAPTER 11 AGENESIS OF THE CORPUS C
- Page 98 and 99:
CHAPTER 11 AGENESIS OF THE CORPUS C
- Page 100 and 101:
Chapter 12 Craniosynostosis BARBARA
- Page 102 and 103:
CHAPTER 12 CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS 85 As a
- Page 104 and 105:
CHAPTER 12 CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS 87 cran
- Page 106 and 107:
CHAPTER 12 CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS 89 REFE
- Page 108 and 109:
Part III Craniofacial Malformations
- Page 110 and 111:
Chapter 13 Cleft Lip and Palate BRA
- Page 112 and 113:
CHAPTER 13 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 95
- Page 114 and 115:
CHAPTER 13 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 97
- Page 116 and 117:
CHAPTER 13 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 99
- Page 118 and 119:
Chapter 14 Micrognathia BRAD ANGLE
- Page 120 and 121:
CHAPTER 14 MICROGNATHIA 103 Microgn
- Page 122 and 123:
Chapter 15 Congenital Anomalies Ass
- Page 124 and 125:
CHAPTER 15 CONGENITAL ANOMALIES ASS
- Page 126 and 127:
CHAPTER 15 CONGENITAL ANOMALIES ASS
- Page 128 and 129:
Chapter 16 Ear Anomalies BRAD ANGLE
- Page 130 and 131:
CHAPTER 16 EAR ANOMALIES 113 Figure
- Page 132 and 133:
CHAPTER 16 EAR ANOMALIES 115 Figure
- Page 134 and 135:
Chapter 17 Choanal Atresia BRAD ANG
- Page 136 and 137:
CHAPTER 17 CHOANAL ATRESIA 119 been
- Page 138 and 139:
Chapter 18 Coloboma BRAD ANGLE INT
- Page 140 and 141:
CHAPTER 18 COLOBOMA 123 typically a
- Page 142 and 143:
Chapter 19 Cataract BRAD ANGLE INT
- Page 144 and 145:
CHAPTER 19 CATARACT 127 Isolated Ca
- Page 146 and 147:
CHAPTER 19 CATARACT 129 associated
- Page 148 and 149:
CHAPTER 19 CATARACT 131 2. Zetterst
- Page 150 and 151:
Part IV Respiratory Malformations C
- Page 152 and 153:
Chapter 20 Congenital High Airway O
- Page 154 and 155:
CHAPTER 20 CONGENITAL HIGH AIRWAY O
- Page 156 and 157:
Chapter 21 Pulmonary Agenesis SANDR
- Page 158 and 159:
CHAPTER 21 PULMONARY AGENESIS 141 k
- Page 160 and 161:
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Hypoplasia SAN
- Page 162 and 163:
CHAPTER 22 PULMONARY HYPOPLASIA 145
- Page 164 and 165:
Chapter 23 Congenital Cystic Adenom
- Page 166 and 167:
CHAPTER 23 CONGENITAL CYSTIC ADENOM
- Page 168 and 169:
Chapter 24 Congenital Diaphragmatic
- Page 170 and 171:
CHAPTER 24 CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC
- Page 172 and 173:
CHAPTER 24 CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC
- Page 174 and 175:
CHAPTER 24 CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC
- Page 176 and 177:
Chapter 25 Congenital Hydrothorax S
- Page 178 and 179:
CHAPTER 25 CONGENITAL HYDROTHORAX 1
- Page 180 and 181:
CHAPTER 25 CONGENITAL HYDROTHORAX 1
- Page 182 and 183:
Chapter 26 Congenital Pulmonary Lym
- Page 184 and 185:
CHAPTER 26 CONGENITAL PULMONARY LYM
- Page 186 and 187:
CHAPTER 26 CONGENITAL PULMONARY LYM
- Page 188 and 189:
Part V Cardiac Malformations Copyri
- Page 190 and 191:
Chapter 27 Septal Defects BARBARA K
- Page 192 and 193:
CHAPTER 27 SEPTAL DEFECTS 175 TABL
- Page 194 and 195:
CHAPTER 27 SEPTAL DEFECTS 177 TABL
- Page 196 and 197:
CHAPTER 27 SEPTAL DEFECTS 179 to ri
- Page 198 and 199:
CHAPTER 27 SEPTAL DEFECTS 181 of th
- Page 200 and 201:
Chapter 28 Conotruncal Heart Defect
- Page 202 and 203:
CHAPTER 28 CONOTRUNCAL HEART DEFECT
- Page 204 and 205:
CHAPTER 28 CONOTRUNCAL HEART DEFECT
- Page 206 and 207:
CHAPTER 28 CONOTRUNCAL HEART DEFECT
- Page 208 and 209:
CHAPTER 28 CONOTRUNCAL HEART DEFECT
- Page 210 and 211:
Chapter 29 Right Ventricular Outflo
- Page 212 and 213:
CHAPTER 29 RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLO
- Page 214 and 215:
CHAPTER 29 RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLO
- Page 216 and 217:
Chapter 30 Left Ventricular Outflow
- Page 218 and 219:
CHAPTER 30 LEFT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW
- Page 220 and 221:
CHAPTER 30 LEFT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW
- Page 222 and 223:
Chapter 31 Dextrocardia BARBARA K.
- Page 224 and 225:
CHAPTER 31 DEXTROCARDIA 207 with fu
- Page 226 and 227:
Chapter 32 Cardiomyopathy BARBARA K
- Page 228 and 229:
CHAPTER 32 CARDIOMYOPATHY 211 TABL
- Page 230 and 231:
CHAPTER 32 CARDIOMYOPATHY 213 of di
- Page 232 and 233:
Part 6 Gastrointestinal Malformatio
- Page 234 and 235:
Chapter 33 Esophageal Atresia and T
- Page 236 and 237: CHAPTER 33 ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA AND T
- Page 238 and 239: CHAPTER 33 ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA AND T
- Page 240 and 241: Chapter 34 Duodenal Atresia PRAVEEN
- Page 242 and 243: CHAPTER 34 DUODENAL ATRESIA 225 TA
- Page 244 and 245: Chapter 35 Anorectal Malformations
- Page 246 and 247: CHAPTER 35 ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
- Page 248 and 249: CHAPTER 35 ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
- Page 250 and 251: Chapter 36 Hirschsprung Disease PRA
- Page 252 and 253: CHAPTER 36 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE 235
- Page 254 and 255: CHAPTER 36 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE 237
- Page 256 and 257: CHAPTER 36 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE 239
- Page 258 and 259: Chapter 37 Omphalocele PRAVEEN KUMA
- Page 260 and 261: CHAPTER 37 OMPHALOCELE 243 TABLE 3
- Page 262 and 263: CHAPTER 37 OMPHALOCELE 245 status,
- Page 264 and 265: Chapter 38 Gastroschisis PRAVEEN KU
- Page 266 and 267: CHAPTER 38 GASTROSCHISIS 249 TABLE
- Page 268 and 269: Part VII Renal Malformations Copyri
- Page 270 and 271: Chapter 39 Renal Agenesis PRAVEEN K
- Page 272 and 273: CHAPTER 39 RENAL AGENESIS 255 propo
- Page 274 and 275: CHAPTER 39 RENAL AGENESIS 257 TABL
- Page 276 and 277: CHAPTER 39 RENAL AGENESIS 259 varia
- Page 278 and 279: Chapter 40 Horseshoe Kidney PRAVEEN
- Page 280 and 281: CHAPTER 40 HORSESHOE KIDNEY 263 TA
- Page 282 and 283: Chapter 41 Renal Cystic Diseases PR
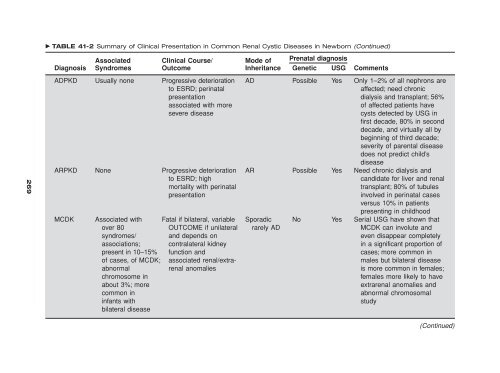
- Page 284 and 285: TABLE 41-2 Summary of Clinical Pres
- Page 288 and 289: CHAPTER 41 RENAL CYSTIC DISEASES 27
- Page 290 and 291: CHAPTER 41 RENAL CYSTIC DISEASES 27
- Page 292 and 293: CHAPTER 41 RENAL CYSTIC DISEASES 27
- Page 294 and 295: Chapter 42 Posterior Urethral Valve
- Page 296 and 297: CHAPTER 42 POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVE
- Page 298 and 299: CHAPTER 42 POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVE
- Page 300 and 301: Part VIII Skeletal Malformations Co
- Page 302 and 303: Chapter 43 Polydactyly PRAVEEN KUMA
- Page 304 and 305: CHAPTER 43 POLYDACTYLY 287 Temtamy
- Page 306 and 307: CHAPTER 43 POLYDACTYLY 289 TABLE 4
- Page 308 and 309: CHAPTER 43 POLYDACTYLY 291 5. Holme
- Page 310 and 311: Chapter 44 Syndactyly PRAVEEN KUMAR
- Page 312 and 313: CHAPTER 44 SYNDACTYLY 295 ASSOCIAT
- Page 314 and 315: CHAPTER 44 SYNDACTYLY 297 REFERENCE
- Page 316 and 317: Chapter 45 Limb Reduction Defects P
- Page 318 and 319: CHAPTER 45 LIMB REDUCTION DEFECTS 3
- Page 320 and 321: TABLE 45-2 Syndromes Associated wit
- Page 322 and 323: CHAPTER 45 LIMB REDUCTION DEFECTS 3
- Page 324 and 325: Chapter 46 Skeletal Dysplasias PRAV
- Page 326 and 327: CHAPTER 46 SKELETAL DYSPLASIAS 309
- Page 328 and 329: 311 Achondrogenesis Autosomal Sever
- Page 330 and 331: 313 Chondrodysplasia X-linked Short
- Page 332 and 333: CHAPTER 46 SKELETAL DYSPLASIAS 315
- Page 334 and 335: CHAPTER 46 SKELETAL DYSPLASIAS 317
- Page 336 and 337:
Pathological Fractures or Abnormal
- Page 338 and 339:
Chapter 47 Arthrogryposis PRAVEEN K
- Page 340 and 341:
CHAPTER 47 ARTHROGRYPOSIS 323 in ot
- Page 342 and 343:
CHAPTER 47 ARTHROGRYPOSIS 325 obscu
- Page 344 and 345:
327 Type 5 Proximal & distal Club f
- Page 346 and 347:
CHAPTER 47 ARTHROGRYPOSIS 329 unkno
- Page 348 and 349:
Part IX Miscellaneous Malformations
- Page 350 and 351:
Chapter 48 Single Umbilical Artery
- Page 352 and 353:
CHAPTER 48 SINGLE UMBILICAL ARTERY
- Page 354 and 355:
CHAPTER 48 SINGLE UMBILICAL ARTERY
- Page 356 and 357:
Chapter 49 Sacral Dimple and Other
- Page 358 and 359:
CHAPTER 49 SACRAL DIMPLE AND OTHER
- Page 360 and 361:
CHAPTER 49 SACRAL DIMPLE AND OTHER
- Page 362 and 363:
CHAPTER 49 SACRAL DIMPLE AND OTHER
- Page 364 and 365:
Chapter 50 Hemihyperplasia and Over
- Page 366 and 367:
CHAPTER 50 HEMIHYPERPLASIA AND OVER
- Page 368 and 369:
CHAPTER 50 HEMIHYPERPLASIA AND OVER
- Page 370 and 371:
CHAPTER 50 HEMIHYPERPLASIA AND OVER
- Page 372 and 373:
Chapter 51 Cystic Hygroma PRAVEEN K
- Page 374 and 375:
CHAPTER 51 CYSTIC HYGROMA 357 in la
- Page 376 and 377:
Trisomy 18 IUGR, low-set malformed
- Page 378 and 379:
CHAPTER 51 CYSTIC HYGROMA 361 and o
- Page 380 and 381:
Glossary of Genetic Terms A Acquire
- Page 382 and 383:
GLOSSARY OF GENETIC TERMS 365 Codon
- Page 384 and 385:
GLOSSARY OF GENETIC TERMS 367 Gene
- Page 386 and 387:
GLOSSARY OF GENETIC TERMS 369 Locus
- Page 388 and 389:
GLOSSARY OF GENETIC TERMS 371 Prena
- Page 390 and 391:
GLOSSARY OF GENETIC TERMS 373 X X c
- Page 392 and 393:
Web Resources General Birth Defect
- Page 394 and 395:
WEB RESOURCES 377 Children’s Brit
- Page 396 and 397:
Index Page numbers followed by f or
- Page 398 and 399:
INDEX 381 polydactyly and, 288t ren
- Page 400 and 401:
INDEX 383 genetic counseling, 225 m
- Page 402 and 403:
INDEX 385 Haddad syndrome, 238t Hai
- Page 404 and 405:
INDEX 387 Neurofibromatosis type I,
- Page 406 and 407:
INDEX 389 clinical presentation, 30