PHYS07200604007 Manas Kumar Dala - Homi Bhabha National ...
PHYS07200604007 Manas Kumar Dala - Homi Bhabha National ...
PHYS07200604007 Manas Kumar Dala - Homi Bhabha National ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Electronic Structure of Pr 1−x Ca x MnO 3 86<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
Intensity (arb. units)<br />
x=1<br />
x=0.4<br />
1 - 0.2<br />
0.4 - 0.2<br />
x=0.33<br />
x=0.2<br />
0.33 - 0.2<br />
-1 0 1 2 3 4<br />
0 1 2 3 4<br />
Energy Relative to Fermi Energy (eV)<br />
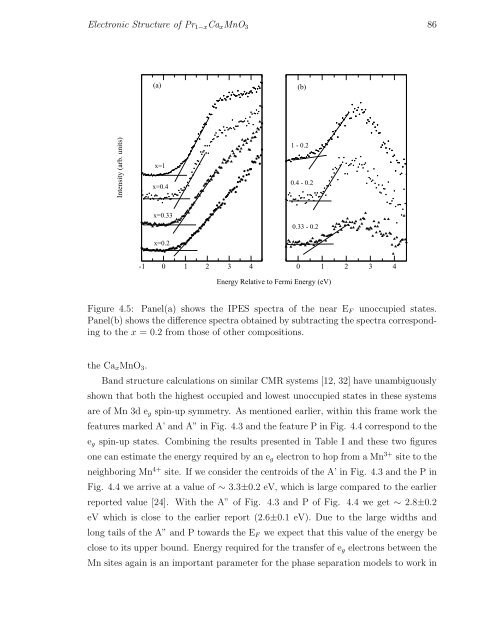
Figure 4.5: Panel(a) shows the IPES spectra of the near E F unoccupied states.<br />
Panel(b) shows the difference spectra obtained by subtracting the spectra corresponding<br />
to the x = 0.2 from those of other compositions.<br />
the Ca x MnO 3 .<br />
Band structure calculations on similar CMR systems [12, 32] have unambiguously<br />
shown that both the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied states in these systems<br />
are of Mn 3d e g spin-up symmetry. As mentioned earlier, within this frame work the<br />
features marked A’ and A” in Fig. 4.3 and the feature P in Fig. 4.4 correspond to the<br />
e g spin-up states. Combining the results presented in Table I and these two figures<br />
one can estimate the energy required by an e g electron to hop from a Mn 3+ site to the<br />
neighboring Mn 4+ site. If we consider the centroids of the A’ in Fig. 4.3 and the P in<br />
Fig. 4.4 we arrive at a value of ∼ 3.3±0.2 eV, which is large compared to the earlier<br />
reported value [24]. With the A” of Fig. 4.3 and P of Fig. 4.4 we get ∼ 2.8±0.2<br />
eV which is close to the earlier report (2.6±0.1 eV). Due to the large widths and<br />
long tails of the A” and P towards the E F we expect that this value of the energy be<br />
close to its upper bound. Energy required for the transfer of e g electrons between the<br />
Mn sites again is an important parameter for the phase separation models to work in