PHYS07200604007 Manas Kumar Dala - Homi Bhabha National ...
PHYS07200604007 Manas Kumar Dala - Homi Bhabha National ...
PHYS07200604007 Manas Kumar Dala - Homi Bhabha National ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Experimental Techniques 35<br />
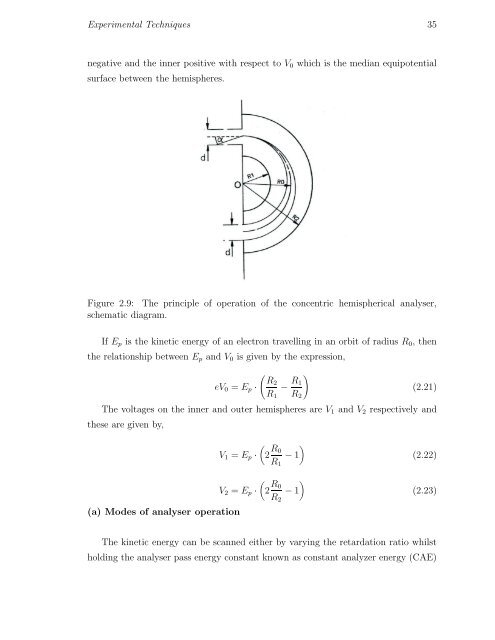
negative and the inner positive with respect to V 0 which is the median equipotential<br />
surface between the hemispheres.<br />
Figure 2.9: The principle of operation of the concentric hemispherical analyser,<br />
schematic diagram.<br />
If E p is the kinetic energy of an electron travelling in an orbit of radius R 0 , then<br />
the relationship between E p and V 0 is given by the expression,<br />
eV 0 = E p ·<br />
(<br />
R2<br />
− R )<br />
1<br />
R 1 R 2<br />
(2.21)<br />
The voltages on the inner and outer hemispheres are V 1 and V 2 respectively and<br />
these are given by,<br />
V 1 = E p ·<br />
V 2 = E p ·<br />
(a) Modes of analyser operation<br />
(<br />
2 R )<br />
0<br />
− 1<br />
R 1<br />
(<br />
2 R )<br />
0<br />
− 1<br />
R 2<br />
(2.22)<br />
(2.23)<br />
The kinetic energy can be scanned either by varying the retardation ratio whilst<br />
holding the analyser pass energy constant known as constant analyzer energy (CAE)