geothermal resource potential of the safford-san simon basin, arizona
geothermal resource potential of the safford-san simon basin, arizona
geothermal resource potential of the safford-san simon basin, arizona
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
flow.<br />
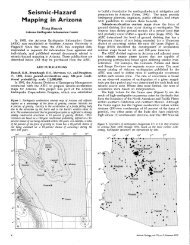
A fault zone(s) is inferred to provide <strong>the</strong> vertical conduit for <strong>the</strong>rmal<br />
water flow at Indian Hot Springs.<br />
Projection <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> NNW-striking Pleistocene zone <strong>of</strong> faults in <strong>the</strong> Cactus<br />
Flat-Artesia area across <strong>the</strong> Indian Hot Springs location is possible.<br />
The<br />
springs are on strike with <strong>the</strong> Cactus Flat fault zone; and <strong>the</strong> Gila River<br />
changes course to conform with <strong>the</strong> inferred trace <strong>of</strong> this fault zone (Figure<br />
~. In addition, Muller (1973) shows degradation <strong>of</strong> chemical quality in<br />
shallow wells «6Sm) which are downstream from <strong>the</strong> inferred trace <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Cactus<br />
Flat zone.<br />
Sodium chloride water may leak upward along <strong>the</strong> fault and<br />
flow into shallow floodplain aquifers.<br />
Ano<strong>the</strong>r fault, crossing <strong>the</strong> Indian Hot Springs area, is inferred from<br />
gravity data and from geologic investigations at Big Springs.<br />
Big Springs, east <strong>of</strong> Indian Hot Springs in D-6-2S-S, is centered on a<br />
WNW alignment <strong>of</strong> springs. Deformation <strong>of</strong> <strong>basin</strong>-fill sediments is observed<br />
in arroyo walls just below Big Springs.<br />
Laminated clay deposits (green clay<br />
facies) are tilted and faulted.<br />
Mud intrusions along shears and faults suggest<br />
liquification during deformation.<br />
This deformation is pre-ancestral Gila<br />
River gravels, which are in angular unconformable contact with underlying<br />
deformed <strong>basin</strong>-fill sediment.<br />
Faults are oriented N2S o W and show downward<br />
displacement to <strong>the</strong> north.<br />
This exposure is interpreted by <strong>the</strong> writer as<br />
anti<strong>the</strong>tic deformation on <strong>the</strong> hanging wall <strong>of</strong> a large unexposed normal fault<br />
which may control spring alignment.<br />
The spring alignment at Big Springs can<br />
be projected northwest through Eden Spring and across Indian Hot Springs.<br />
Apparently, Indian Hot Springs are controlled by a fault(s) which allows<br />
vertical flow out <strong>of</strong> deep «1 km) artesian aquifers.<br />
At least two deep wells in <strong>the</strong> area, <strong>the</strong> Mary Mack well and <strong>the</strong> Mount<br />
31