CHAPTER 3 Tumours of the Stomach - Pathology Outlines
CHAPTER 3 Tumours of the Stomach - Pathology Outlines
CHAPTER 3 Tumours of the Stomach - Pathology Outlines
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
A B C<br />
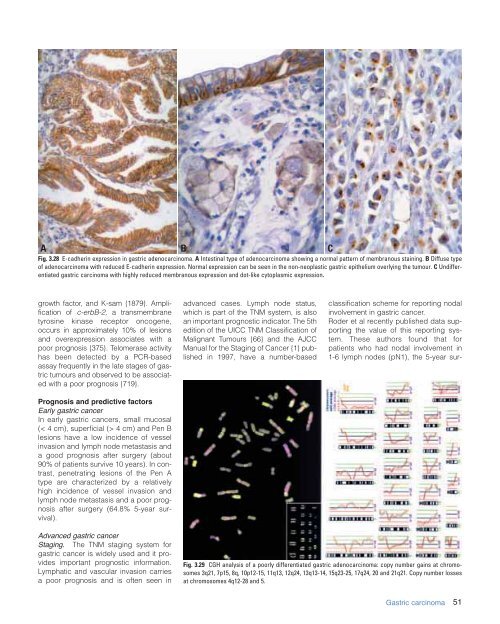
Fig. 3.28 E-cadherin expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. A Intestinal type <strong>of</strong> adenocarcinoma showing a normal pattern <strong>of</strong> membranous staining. B Diffuse type<br />
<strong>of</strong> adenocarcinoma with reduced E-cadherin expression. Normal expression can be seen in <strong>the</strong> non-neoplastic gastric epi<strong>the</strong>lium overlying <strong>the</strong> tumour. C Undifferentiated<br />
gastric carcinoma with highly reduced membranous expression and dot-like cytoplasmic expression.<br />
growth factor, and K-sam {1879}. Amplification<br />
<strong>of</strong> c-erbB-2, a transmembrane<br />
tyrosine kinase receptor oncogene,<br />
occurs in approximately 10% <strong>of</strong> lesions<br />
and overexpression associates with a<br />
poor prognosis {375}. Telomerase activity<br />
has been detected by a PCR-based<br />
assay frequently in <strong>the</strong> late stages <strong>of</strong> gastric<br />
tumours and observed to be associated<br />
with a poor prognosis {719}.<br />
Prognosis and predictive factors<br />
Early gastric cancer<br />
In early gastric cancers, small mucosal<br />
(< 4 cm), superficial (> 4 cm) and Pen B<br />
lesions have a low incidence <strong>of</strong> vessel<br />
invasion and lymph node metastasis and<br />
a good prognosis after surgery (about<br />
90% <strong>of</strong> patients survive 10 years). In contrast,<br />
penetrating lesions <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Pen A<br />
type are characterized by a relatively<br />
high incidence <strong>of</strong> vessel invasion and<br />
lymph node metastasis and a poor prognosis<br />
after surgery (64.8% 5-year survival).<br />
advanced cases. Lymph node status,<br />
which is part <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> TNM system, is also<br />
an important prognostic indicator. The 5th<br />
edition <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> UICC TNM Classification <strong>of</strong><br />
Malignant <strong>Tumours</strong> {66} and <strong>the</strong> AJCC<br />
Manual for <strong>the</strong> Staging <strong>of</strong> Cancer {1} published<br />
in 1997, have a number-based<br />
classification scheme for reporting nodal<br />
involvement in gastric cancer.<br />
Roder et al recently published data supporting<br />
<strong>the</strong> value <strong>of</strong> this reporting system.<br />
These authors found that for<br />
patients who had nodal involvement in<br />
1-6 lymph nodes (pN1), <strong>the</strong> 5-year sur-<br />
Advanced gastric cancer<br />
Staging. The TNM staging system for<br />
gastric cancer is widely used and it provides<br />
important prognostic information.<br />
Lymphatic and vascular invasion carries<br />
a poor prognosis and is <strong>of</strong>ten seen in<br />
Fig. 3.29 CGH analysis <strong>of</strong> a poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma: copy number gains at chromosomes<br />
3q21, 7p15, 8q, 10p12-15, 11q13, 12q24, 13q13-14, 15q23-25, 17q24, 20 and 21q21. Copy number losses<br />
at chromosomes 4q12-28 and 5.<br />
Gastric carcinoma<br />
51