symbolic dynamic models for highly varying power system loads
symbolic dynamic models for highly varying power system loads
symbolic dynamic models for highly varying power system loads
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
96<br />
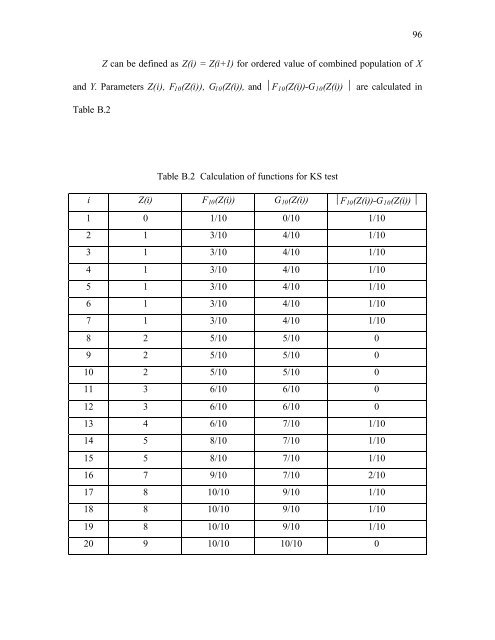
Z can be defined as Z(i) = Z(i+1) <strong>for</strong> ordered value of combined population of X<br />
and Y. Parameters Z(i), F 10 (Z(i)), G 10 (Z(i)), and ⏐F 10 (Z(i))-G 10 (Z(i)) ⏐ are calculated in<br />
Table B.2<br />
Table B.2 Calculation of functions <strong>for</strong> KS test<br />
i Z(i) F 10 (Z(i)) G 10 (Z(i)) ⏐F 10 (Z(i))-G 10 (Z(i)) ⏐<br />
1 0 1/10 0/10 1/10<br />
2 1 3/10 4/10 1/10<br />
3 1 3/10 4/10 1/10<br />
4 1 3/10 4/10 1/10<br />
5 1 3/10 4/10 1/10<br />
6 1 3/10 4/10 1/10<br />
7 1 3/10 4/10 1/10<br />
8 2 5/10 5/10 0<br />
9 2 5/10 5/10 0<br />
10 2 5/10 5/10 0<br />
11 3 6/10 6/10 0<br />
12 3 6/10 6/10 0<br />
13 4 6/10 7/10 1/10<br />
14 5 8/10 7/10 1/10<br />
15 5 8/10 7/10 1/10<br />
16 7 9/10 7/10 2/10<br />
17 8 10/10 9/10 1/10<br />
18 8 10/10 9/10 1/10<br />
19 8 10/10 9/10 1/10<br />
20 9 10/10 10/10 0