symbolic dynamic models for highly varying power system loads
symbolic dynamic models for highly varying power system loads
symbolic dynamic models for highly varying power system loads
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
25<br />
3.4 Analysis tools<br />
To analyze the results of the tests, some parameters have been taken into<br />
consideration. Especially while <strong>for</strong>ecasting a signal, it is difficult to comment on the<br />
goodness of the model unless some characteristics of the expected signal and predicted<br />
signal are compared. Two important parameters to be compared in this regard are RMS<br />
and average.<br />
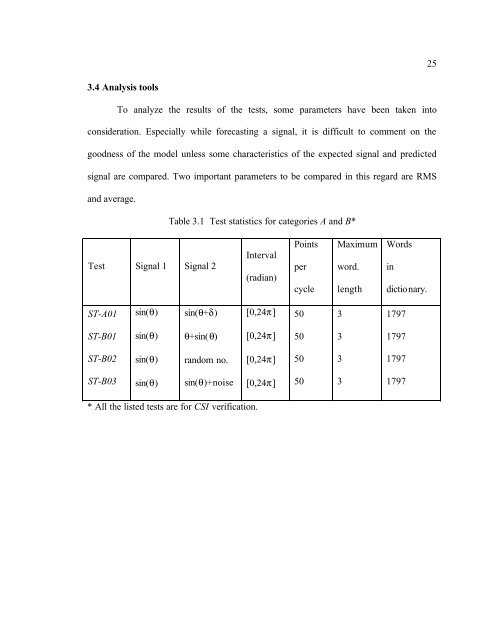
Table 3.1 Test statistics <strong>for</strong> categories A and B*<br />
Test Signal 1 Signal 2<br />
Interval<br />
(radian)<br />
Points<br />
per<br />
cycle<br />
Maximum<br />
word.<br />
length<br />
Words<br />
in<br />
dictionary.<br />
ST-A01<br />
sin(θ)<br />
sin(θ+δ)<br />
[0,24π]<br />
50<br />
3<br />
1797<br />
ST-B01<br />
sin(θ)<br />
θ+sin(θ)<br />
[0,24π]<br />
50<br />
3<br />
1797<br />
ST-B02<br />
sin(θ)<br />
random no.<br />
[0,24π]<br />
50<br />
3<br />
1797<br />
ST-B03<br />
sin(θ)<br />
sin(θ)+noise<br />
[0,24π]<br />
50<br />
3<br />
1797<br />
* All the listed tests are <strong>for</strong> CSI verification.