Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Topic</strong> 1 - <strong>Matter</strong> . <strong>and</strong> <strong>Energy</strong><br />
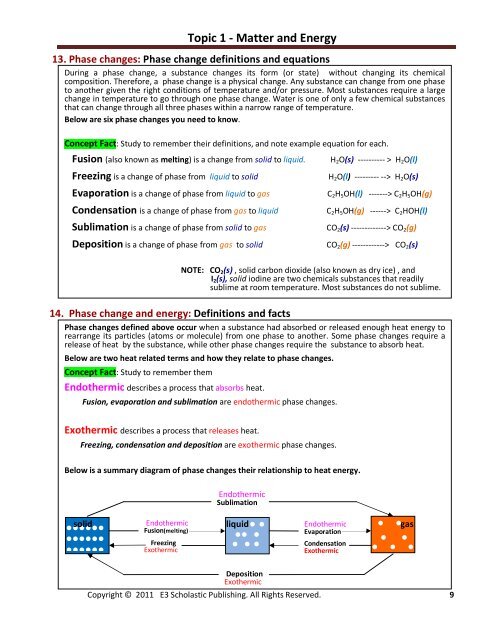
13. Phase changes: Phase change definitions <strong>and</strong> equations<br />
During a phase change, a substance changes its form (or state) without changing its chemical<br />
composition. Therefore, a phase change is a physical change. Any substance can change from one phase<br />
to another given the right conditions of temperature <strong>and</strong>/or pressure. Most substances require a large<br />
change in temperature to go through one phase change. Water is one of only a few chemical substances<br />
that can change through all three phases within a narrow range of temperature.<br />
Below are six phase changes you need to know.<br />
Concept Fact: Study to remember their definitions, <strong>and</strong> note example equation for each.<br />
Fusion (also known as melting) is a change from solid to liquid.<br />
Freezing is a change of phase from liquid to solid<br />
Evaporation is a change of phase from liquid to gas<br />
Condensation is a change of phase from gas to liquid<br />
Sublimation is a change of phase from solid to gas<br />
Deposition is a change of phase from gas to solid<br />
H 2 O(s) ---------- > H 2 O(l)<br />
H 2 O(l) --------- --> H 2 O(s)<br />
C 2 H 5 OH(l) -------> C 2 H 5 OH(g)<br />
C 2 H 5 OH(g) ------> C 2 HOH(l)<br />
CO 2 (s) -------------> CO 2 (g)<br />
CO 2 (g) ------------> CO 2 (s)<br />
NOTE: CO 2 (s) , solid carbon dioxide (also known as dry ice) , <strong>and</strong><br />
I 2 (s), solid iodine are two chemicals substances that readily<br />
sublime at room temperature. Most substances do not sublime.<br />
14. Phase change <strong>and</strong> energy: Definitions <strong>and</strong> facts<br />
Phase changes defined above occur when a substance had absorbed or released enough heat energy to<br />
rearrange its particles (atoms or molecule) from one phase to another. Some phase changes require a<br />
release of heat by the substance, while other phase changes require the substance to absorb heat.<br />
Below are two heat related terms <strong>and</strong> how they relate to phase changes.<br />
Concept Fact: Study to remember them<br />
Endothermic describes a process that absorbs heat.<br />
Fusion, evaporation <strong>and</strong> sublimation are endothermic phase changes.<br />
Exothermic describes a process that releases heat.<br />
Freezing, condensation <strong>and</strong> deposition are exothermic phase changes.<br />
Below is a summary diagram of phase changes their relationship to heat energy.<br />
••••••<br />
••••••<br />
••••••<br />
Endothermic<br />
Sublimation<br />
• •<br />
•• •<br />
• • •<br />
• •<br />
• •<br />
• • •<br />
solid Endothermic liquid Endothermic<br />
gas<br />
Fusion(melting)<br />
Evaporation<br />
Freezing<br />
Exothermic<br />
Deposition<br />
Exothermic<br />
Condensation<br />
Exothermic<br />
Copyright © 2011 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. 9