Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Topic</strong> 1 - <strong>Matter</strong> . <strong>and</strong> <strong>Energy</strong><br />
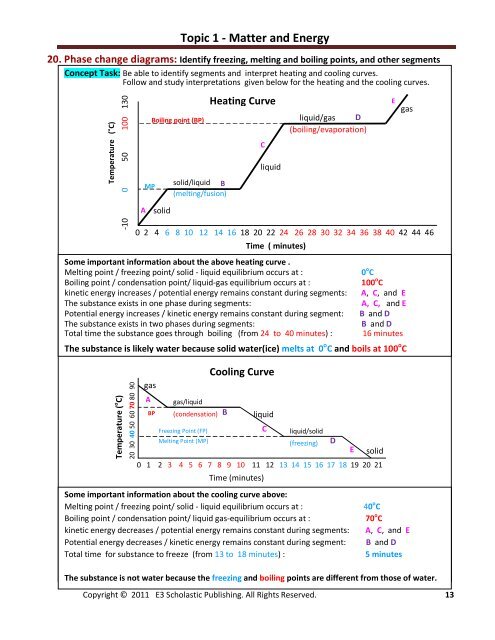
20. Phase change diagrams: Identify freezing, melting <strong>and</strong> boiling points, <strong>and</strong> other segments<br />
Concept Task: Be able to identify segments <strong>and</strong> interpret heating <strong>and</strong> cooling curves.<br />
Follow <strong>and</strong> study interpretations given below for the heating <strong>and</strong> the cooling curves.<br />
Temperature ( o C)<br />
-10 0 50 100 130<br />
A<br />
solid<br />
solid/liquid B<br />
(melting/fusion)<br />
liquid<br />
liquid/gas D<br />
(boiling/evaporation)<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46<br />
Time ( minutes)<br />
Some important information about the above heating curve .<br />
Melting point / freezing point/ solid - liquid equilibrium occurs at :<br />
Boiling point / condensation point/ liquid-gas equilibrium occurs at :<br />
kinetic energy increases / potential energy remains constant during segments:<br />
The substance exists in one phase during segments:<br />
Potential energy increases / kinetic energy remains constant during segment:<br />
The substance exists in two phases during segments:<br />
Total time the substance goes through boiling (from 24 to 40 minutes) :<br />
Copyright © 2011 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. 13<br />
gas<br />
0 o C<br />
100 o C<br />
A, C, <strong>and</strong> E<br />
A, C, <strong>and</strong> E<br />
B <strong>and</strong> D<br />
B <strong>and</strong> D<br />
16 minutes<br />
The substance is likely water because solid water(ice) melts at 0 o C <strong>and</strong> boils at 100 o C<br />
Temperature ( o C)<br />
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90<br />
MP<br />
gas<br />
A<br />
Boiling point (BP)<br />
BP<br />
gas/liquid<br />
(condensation)<br />
Freezing Point (FP)<br />
Melting Point (MP)<br />
Heating Curve<br />
C<br />
Cooling Curve<br />
liquid<br />
liquid/solid<br />
(freezing)<br />
solid<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21<br />
Time (minutes)<br />
Some important information about the cooling curve above:<br />
Melting point / freezing point/ solid - liquid equilibrium occurs at :<br />
Boiling point / condensation point/ liquid gas-equilibrium occurs at :<br />
kinetic energy decreases / potential energy remains constant during segments:<br />
Potential energy decreases / kinetic energy remains constant during segment:<br />
Total time for substance to freeze (from 13 to 18 minutes) :<br />
B<br />
E<br />
40 o C<br />
70 o C<br />
A, C, <strong>and</strong> E<br />
B <strong>and</strong> D<br />
5 minutes<br />
The substance is not water because the freezing <strong>and</strong> boiling points are different from those of water.<br />
C<br />
D<br />
E