Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Topic</strong> 1 - <strong>Matter</strong> . <strong>and</strong> <strong>Energy</strong><br />
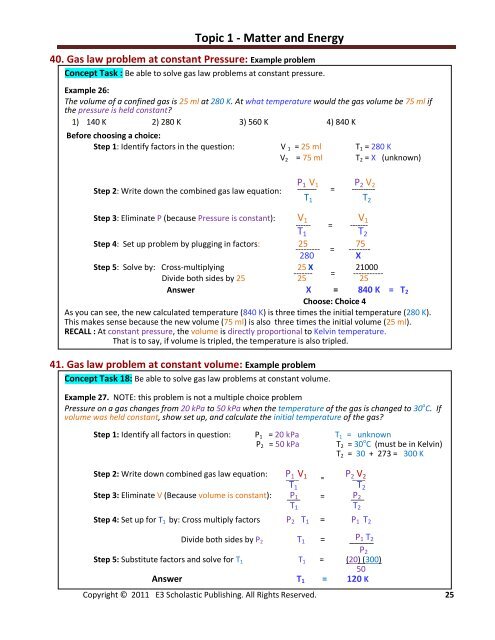
40. Gas law problem at constant Pressure: Example problem<br />
Concept Task : Be able to solve gas law problems at constant pressure.<br />
Example 26:<br />
The volume of a confined gas is 25 ml at 280 K. At what temperature would the gas volume be 75 ml if<br />
the pressure is held constant?<br />
1) 140 K 2) 280 K 3) 560 K 4) 840 K<br />
Before choosing a choice:<br />
Step 1: Identify factors in the question: V 1 = 25 ml T 1 = 280 K<br />
V 2 = 75 ml T 2 = X (unknown)<br />
Step 2: Write down the combined gas law equation:<br />
P 1 V 1 P 2 V 2<br />
--------- = ----------<br />
T 1 T 2<br />
Step 3: Eliminate P (because Pressure is constant): V 1 V 1<br />
------ = -------<br />
T 1 T 2<br />
Step 4: Set up problem by plugging in factors: 25 75<br />
280 X<br />
Step 5: Solve by: Cross-multiplying 25 X 21000<br />
------- = -----------<br />
Divide both sides by 25 25 25<br />
Answer X = 840 K = T 2<br />
Choose: Choice 4<br />
As you can see, the new calculated temperature (840 K) is three times the initial temperature (280 K).<br />
This makes sense because the new volume (75 ml) is also three times the initial volume (25 ml).<br />
RECALL : At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to Kelvin temperature.<br />
That is to say, if volume is tripled, the temperature is also tripled.<br />
41. Gas law problem at constant volume: Example problem<br />
Concept Task 18: Be able to solve gas law problems at constant volume.<br />
--------- = --------<br />
Example 27. NOTE: this problem is not a multiple choice problem<br />
Pressure on a gas changes from 20 kPa to 50 kPa when the temperature of the gas is changed to 30 o C. If<br />
volume was held constant, show set up, <strong>and</strong> calculate the initial temperature of the gas?<br />
Step 1: Identify all factors in question: P 1 = 20 kPa T 1 = unknown<br />
P 2 = 50 kPa T 2 = 30 o C (must be in Kelvin)<br />
T 2 = 30 + 273 = 300 K<br />
Step 2: Write down combined gas law equation: P____ 1 V 1 =<br />
P 2 ____<br />
V 2<br />
T 1 T 2<br />
Step 3: Eliminate V (Because volume is constant): ___ P 1 = ___ P 2<br />
T 1 T 2<br />
Step 4: Set up for T 1 by: Cross multiply factors P 2 T 1 = P 1 T 2<br />
Divide both sides by P 2 T 1 = _____ P 1 T 2<br />
Step 5: Substitute factors <strong>and</strong> solve for T 1 T 1 = (20) (300)<br />
50<br />
Answer T 1 = 120 K<br />
Copyright © 2011 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. 25<br />
P 2