Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Topic</strong> 3 – The Atomic .<br />
structure<br />
<strong>Topic</strong> outline<br />
In this topic, you will learn about:<br />
.The historical development of the modern atom<br />
. Electrons shells <strong>and</strong> electron arrangement<br />
. The subatomic particles; protons, electrons, neutrons . Ground <strong>and</strong> excited state of atom<br />
. Atomic number, mass number <strong>and</strong> atomic mass . Bright-line spectra<br />
. Isotopes <strong>and</strong> isotopes symbols . Valance electrons, neutral atoms <strong>and</strong> ions<br />
Introduction:<br />
Lesson 1 - The historical development of the modern atom<br />
The atom is the most basic unit of matter. Since atoms are very small <strong>and</strong> cannot be seen with the most<br />
sophisticated equipment, several scientists, for thous<strong>and</strong>s of years have proposed different models of<br />
atoms to help explain the nature <strong>and</strong> behavior of matter.<br />
In this lesson, you will learn about these historical scientists, their experiments <strong>and</strong> their proposed<br />
models of atom.<br />
1. Historical development of atom: Definitions <strong>and</strong> facts<br />
Concept Facts: Study to remember the following about the development of the modern atom.<br />
. Many scientists over many years have contributed to the development of the modern atomic model.<br />
. The wave mechanical-model is the current <strong>and</strong> the most widely accepted model of the atom.<br />
The wave-mechanical model of an atom is summarized below.<br />
. Each atom has small dense positive nucleus<br />
. Electrons are found outside the nucleus in a region called an orbital.<br />
. An Orbital is the most probable location of finding an electron with certain energy in an atom.<br />
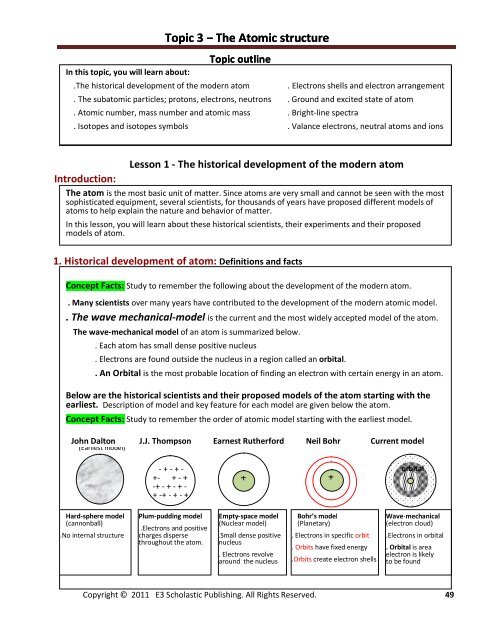
Below are the historical scientists <strong>and</strong> their proposed models of the atom starting with the<br />
earliest. Description of model <strong>and</strong> key feature for each model are given below the atom.<br />
Concept Facts: Study to remember the order of atomic model starting with the earliest model.<br />
John Dalton J.J. Thompson Earnest Rutherford Neil Bohr Current model<br />
(Earliest model)<br />
- + - + -<br />
+- + - +<br />
-+ - + - + -<br />
+ -+ - + - +<br />
+ - + - + -+<br />
+ +<br />
orbital<br />
Hard-sphere model<br />
(cannonball)<br />
.No internal structure<br />
Plum-pudding model<br />
.Electrons <strong>and</strong> positive<br />
charges disperse<br />
throughout the atom.<br />
Empty-space model<br />
(Nuclear model)<br />
.Small dense positive<br />
nucleus<br />
. Electrons revolve<br />
around the nucleus<br />
Bohr’s model<br />
(Planetary)<br />
. Electrons in specific orbit<br />
. Orbits have fixed energy<br />
.Orbits create electron shells<br />
Wave-mechanical<br />
(electron cloud)<br />
.Electrons in orbital<br />
. Orbital is area<br />
electron is likely<br />
to be found<br />
Copyright © 2011 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. 49