Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
Topic 1 - Matter and Energy - Revsworld
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Topic</strong> 1 -<strong>Matter</strong> . <strong>and</strong> <strong>Energy</strong><br />
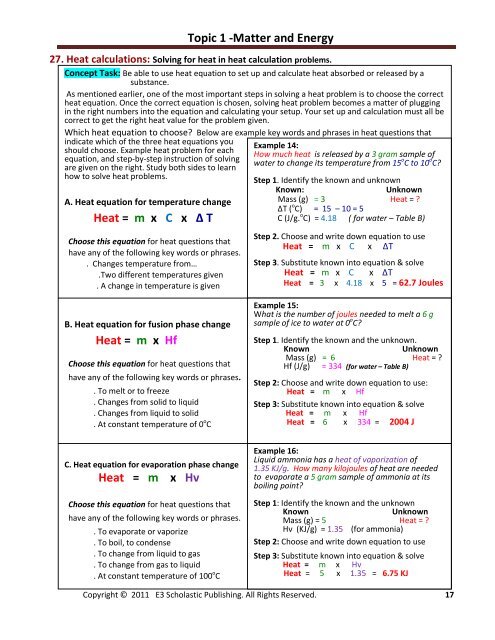
27. Heat calculations: Solving for heat in heat calculation problems.<br />
Concept Task: Be able to use heat equation to set up <strong>and</strong> calculate heat absorbed or released by a<br />
substance.<br />
As mentioned earlier, one of the most important steps in solving a heat problem is to choose the correct<br />
heat equation. Once the correct equation is chosen, solving heat problem becomes a matter of plugging<br />
in the right numbers into the equation <strong>and</strong> calculating your setup. Your set up <strong>and</strong> calculation must all be<br />
correct to get the right heat value for the problem given.<br />
Which heat equation to choose? Below are example key words <strong>and</strong> phrases in heat questions that<br />
indicate which of the three heat equations you<br />
Example 14:<br />
should choose. Example heat problem for each<br />
How much heat is released by a 3 gram sample of<br />
equation, <strong>and</strong> step-by-step instruction of solving<br />
water to change its temperature from 15<br />
are given on the right. Study both sides to learn<br />
o C to 10 o C?<br />
how to solve heat problems.<br />
Step 1. Identify the known <strong>and</strong> unknown<br />
A. Heat equation for temperature change<br />
Heat = m x C x ∆ T<br />
Choose this equation for heat questions that<br />
have any of the following key words or phrases.<br />
. Changes temperature from…<br />
.Two different temperatures given<br />
. A change in temperature is given<br />
Known:<br />
Unknown<br />
Mass (g) = 3 Heat = ?<br />
∆T ( o C) = 15 – 10 = 5<br />
C (J/g. o C) = 4.18 ( for water – Table B)<br />
Step 2. Choose <strong>and</strong> write down equation to use<br />
Heat = m x C x ∆T<br />
Step 3. Substitute known into equation & solve<br />
Heat = m x C x ∆T<br />
Heat = 3 x 4.18 x 5 = 62.7 Joules<br />
B. Heat equation for fusion phase change<br />
Heat = m x Hf<br />
Choose this equation for heat questions that<br />
have any of the following key words or phrases.<br />
. To melt or to freeze<br />
. Changes from solid to liquid<br />
. Changes from liquid to solid<br />
. At constant temperature of 0 o C<br />
C. Heat equation for evaporation phase change<br />
Heat = m x Hv<br />
Choose this equation for heat questions that<br />
have any of the following key words or phrases.<br />
. To evaporate or vaporize<br />
. To boil, to condense<br />
. To change from liquid to gas<br />
. To change from gas to liquid<br />
. At constant temperature of 100 o C<br />
Example 15:<br />
What is the number of joules needed to melt a 6 g<br />
sample of ice to water at 0 o C?<br />
Step 1. Identify the known <strong>and</strong> the unknown.<br />
Known<br />
Unknown<br />
Mass (g) = 6 Heat = ?<br />
Hf (J/g) = 334 (for water – Table B)<br />
Step 2: Choose <strong>and</strong> write down equation to use:<br />
Heat = m x Hf<br />
Step 3: Substitute known into equation & solve<br />
Heat = m x Hf<br />
Heat = 6 x 334 = 2004 J<br />
Example 16:<br />
Liquid ammonia has a heat of vaporization of<br />
1.35 KJ/g. How many kilojoules of heat are needed<br />
to evaporate a 5 gram sample of ammonia at its<br />
boiling point?<br />
Step 1: Identify the known <strong>and</strong> the unknown<br />
Known<br />
Unknown<br />
Mass (g) = 5 Heat = ?<br />
Hv (KJ/g) = 1.35 (for ammonia)<br />
Step 2: Choose <strong>and</strong> write down equation to use<br />
Step 3: Substitute known into equation & solve<br />
Heat = m x Hv<br />
Heat = 5 x 1.35 = 6.75 KJ<br />
Copyright © 2011 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. 17