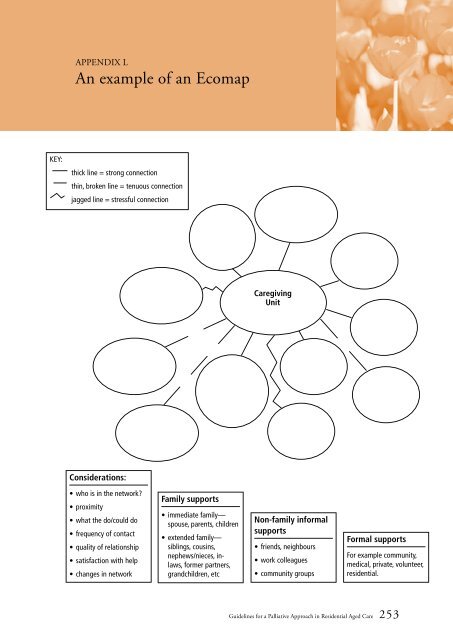
- Page 1 and 2:
Guidelines for a Palliative Approac
- Page 3 and 4:
NHMRC APPROVAL These guidelines wer
- Page 5 and 6:
4 ADVANCE CARE PLANNING 55 4.1 Impl
- Page 7 and 8:
16 MANAGEMENT’S ROLE IN IMPLEMENT
- Page 9 and 10:
17 Ann and Mr Wells’ family Helpi
- Page 12:
IMPORTANT NOTICE On 8 December 2005
- Page 15 and 16:
achieved for these guidelines from
- Page 17 and 18:
facets of a palliative approach are
- Page 19 and 20:
Additional levels of evidence The N
- Page 21 and 22:
Guidelines Ref No. Evidence level A
- Page 23 and 24:
Guidelines Ref No. Evidence Cachexi
- Page 25 and 26:
Guidelines Ref No. Evidence Anxiety
- Page 27 and 28:
Guidelines Ref No. Evidence 70. Und
- Page 29 and 30:
1.1.1 Aims The aims of the systemat
- Page 31 and 32:
Table 1: Search terms Terms Aborigi
- Page 33 and 34:
1.1.5 Exclusion Criteria Although t
- Page 35 and 36:
in the methodology that may invalid
- Page 37 and 38:
To ensure the reliability of the re
- Page 39 and 40:
1.2.2 Methodology When the first re
- Page 41 and 42:
1.4.2 Method When feedback was requ
- Page 43 and 44:
Several Working Party members conve
- Page 45 and 46:
or disagreed with each stakeholder
- Page 47 and 48:
All the feedback received was colla
- Page 50 and 51:
CHAPTER 2 A PALLIATIVE APPROACH A s
- Page 52 and 53:
• Profound weakness • Trouble s
- Page 54 and 55:
• Has the resident had a recent d
- Page 56 and 57:
in the RACF rather than transferrin
- Page 58:
palliative care teams is more appro
- Page 61 and 62:
or ageing progression (see Table 4)
- Page 63 and 64:
Table 7: A practical model of socia
- Page 65 and 66:
Vignette 2: Robert’s story Robert
- Page 68 and 69:
CHAPTER 4 ADVANCE CARE PLANNING Car
- Page 70 and 71:
efore discussing the advance care p
- Page 72 and 73:
• A change in their health status
- Page 74 and 75:
CHAPTER 5 ADVANCED DEMENTIA Advance
- Page 76 and 77:
A study was conducted to investigat
- Page 78 and 79:
5.3.2 Acute illness One study found
- Page 80:
Vignette 5: Anna’s story Anna was
- Page 83 and 84:
(see Fainsinger, Miller and Bruera
- Page 85 and 86:
Dame Cicely Saunders first describe
- Page 87 and 88:
Table 8: Common myths about pain ma
- Page 89 and 90:
6.2.4 Breakthrough pain The term
- Page 91 and 92:
Pain can lead to behavioural change
- Page 93 and 94:
Vignette 7: Mrs Harris’ story Mrs
- Page 95 and 96:
examined the addition of paracetamo
- Page 97 and 98:
provision and storage of drugs, whe
- Page 99 and 100:
successfully tested predominantly w
- Page 101 and 102:
The reasons for malnutrition in old
- Page 103 and 104:
The diets of residents should also
- Page 105 and 106:
To assist in such a discussion, a d
- Page 107 and 108:
appear until dehydration is far adv
- Page 109 and 110:
Guideline: Hydration 24. Recommenda
- Page 111 and 112:
6.7 NAUSEA AND VOMITING Nausea is t
- Page 113 and 114:
• Do you have any problem control
- Page 115 and 116:
6.9.1 Assessment A thorough oral as
- Page 117 and 118:
6.10 SKIN INTEGRITY The major skin
- Page 119 and 120:
Wounds can occur in residents for a
- Page 121 and 122:
Brocklehurst and colleagues (1999)
- Page 123 and 124:
medication treatment along with non
- Page 125 and 126:
• CAM therapies may be culturally
- Page 127 and 128:
word games, the present day, and fa
- Page 130 and 131:
CHAPTER 7 PSYCHOLOGICAL SUPPORT A r
- Page 132 and 133:
7.1.1 Death statements and depressi
- Page 134 and 135:
the factor structure of the CSDD. I
- Page 136 and 137:
7.2.2 Management Non-pharmacologica
- Page 138 and 139:
Table 17: Distinguishing delirium f
- Page 140:
is recognised that in many rural an
- Page 143 and 144:
important [305] (Level QE). Familie
- Page 145 and 146:
8.4 FAMILY INVOLVEMENT The role of
- Page 148 and 149:
CHAPTER 9 SOCIAL SUPPORT, INTIMACY
- Page 150 and 151:
Rather than denying the existence o
- Page 152 and 153:
9.2.2 Management Imaginative progra
- Page 154:
Guideline: Social Support Social Su
- Page 157 and 158:
include lack of information about t
- Page 160 and 161:
CHAPTER 11 CULTURAL ISSUES Australi
- Page 162 and 163:
11.2 Assessment The best approach t
- Page 164 and 165:
CHAPTER 12 SPIRITUAL SUPPORT Dein a
- Page 166 and 167:
Vignette 13: Jack’s story Jack wa
- Page 168:
Guideline: Spiritual Support 68. A
- Page 171 and 172:
interpersonal and leadership skills
- Page 174 and 175:
CHAPTER 14 END-OF-LIFE (TERMINAL) C
- Page 176 and 177:
mood (61%), constipation (59%) and
- Page 178 and 179:
e relevant, and may even worsen sym
- Page 180 and 181:
Treatment involves changes in posit
- Page 182 and 183:
14.5 PREPARING FOR IMMINENT DEATH
- Page 184:
education of the aged care team and
- Page 187 and 188:
Table 21: Grief, loss and bereaveme
- Page 189 and 190:
• excessively avoiding tasks remi
- Page 191 and 192:
Vignette 18: Reflections When provi
- Page 193 and 194:
may have been able to contribute to
- Page 196 and 197:
CHAPTER 16 Management’s role in i
- Page 198 and 199:
REFERENCES 1. World Health Organiza
- Page 200 and 201:
31. Hanson, L. C., Danis, M. & Garr
- Page 202 and 203:
60. World Health Organization Quali
- Page 204 and 205:
89. McCarthy, M., Addington-Hall, J
- Page 206 and 207:
121. Saunders, C. M. (1998). Forewo
- Page 208 and 209:
150. Sindrup, S. H. & Jensen, T. S.
- Page 210 and 211:
177. Berry, E. M. & Marcus, E.-L. (
- Page 212 and 213:
208. Robinson, S. B. & Rosher, R. B
- Page 214 and 215: 237. Brocklehurst, J., Dickinson, E
- Page 216 and 217: 265. Barraclough, J. (1997). ABC of
- Page 218 and 219: 295. Brown, T. M. & Boyle, M. F. (2
- Page 220 and 221: 328. Kristjanson, L. J., Leis, A.,
- Page 222 and 223: 360. McGrath, P., Vun, M. & McLeod,
- Page 224 and 225: 392. Saunders, C. M. & Baines, M. J
- Page 226 and 227: 424. Rawlings, D. & Glynn, T. (2002
- Page 228 and 229: Glossary acetaminophen Acetaminophe
- Page 230 and 231: coordinator of volunteers coping A
- Page 232 and 233: geropsychologist A geropsychologist
- Page 234 and 235: opioids Opioid is a specific term u
- Page 236: specialised palliative team A speci
- Page 239 and 240: Ms Wendy Shiels Dr Jane Sims Dr Chr
- Page 242: APPENDIX B The Australian Governmen
- Page 245 and 246: APRAC GUIDELINES: EVIDENCE EVALUATI
- Page 247 and 248: APRAC GUIDELINES: EVIDENCE EVALUATI
- Page 250 and 251: APPENDIX F: Summary of the frequenc
- Page 252: APPENDIX G: An example of how the g
- Page 256 and 257: APPENDIX I: Resource list PALLIATIV
- Page 258 and 259: Psychological Challenge Depression
- Page 260 and 261: APPENDIX J: Examples of advance dir
- Page 262 and 263: Schedule 1 MEDICAL POWER OF ATTORNE
- Page 264: APPENDIX K An example of a Genogram
- Page 269 and 270: cognitive ability 49 cognitive beha
- Page 271 and 272: Mini Mental State Examination 123,
- Page 274 and 275: Guidelines for a Palliative Approac
- Page 276: For more information about the Nati