Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Electromagnetic <strong>The</strong>orem<br />
(Dr. Omed Ghareb Abdullah) University <strong>of</strong> Sulaimani –College <strong>of</strong> Science – Physics Department<br />
Integral Calculus:<br />
1‐ Line integrals (Path):<br />
A line integral is an expression <strong>of</strong><br />
the form,<br />
∙ <br />
where is a <strong>vector</strong> function, <br />
is the infinitesimal displacement <strong>vector</strong>.<br />
And the integral is to<br />
be carried out along a prescribed path from point to point .<br />
<br />
<br />
If the path in question forms a closed loop (that is if ), I shall put a circle on the integral<br />
sign:<br />
∙ <br />
Example <strong>of</strong> line integrals is the work done by<br />
a force :<br />
∙ <br />
Ordinarily, the value <strong>of</strong> a line integral depends critically on the particular path taken from <br />
to .<br />
But if the<br />
line integral is independent <strong>of</strong> the path; a force<br />
that has this property is called<br />
Conservative.<br />
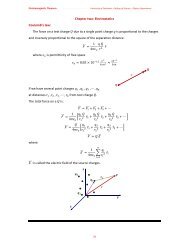
Example:<br />
Calculate<br />
the line integral <strong>of</strong> the function 2 1 from the point<br />
1 ,1<br />
, 0 to the point 2 , 2 , 0 along the paths 1 & 2 in Fig. What is<br />
∮ ∙ <br />
for the loop<br />
that goes from to along 1 <strong>and</strong> returns to along 2?