Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
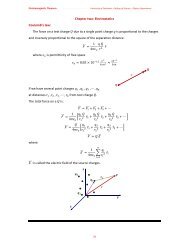
Electromagnetic <strong>The</strong>orem<br />
(Dr. Omed Ghareb Abdullah) University <strong>of</strong> Sulaimani –College <strong>of</strong> Science – Physics Department<br />
1 1 1 <br />
1 1 1 <br />
∙ 1111<br />
|| √3 ; || √3<br />
∙ ⟹ ∙<br />
<br />
1 3<br />
⟹ 70.5288 °<br />
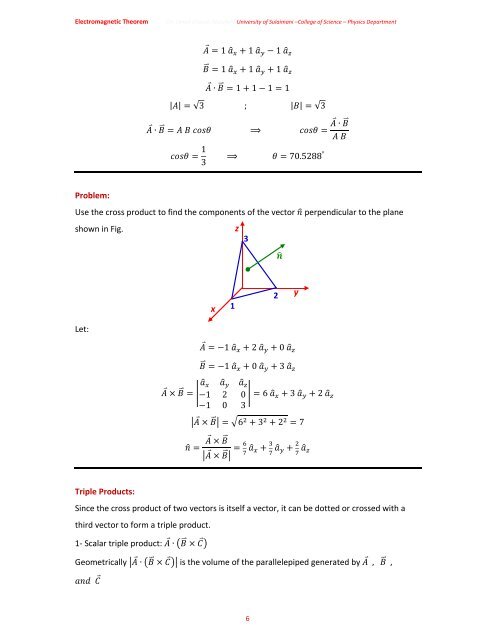
Problem:<br />
Use the cross product to find the components <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vector</strong> perpendicular to the plane<br />
shown in Fig.<br />
z<br />
3<br />
<br />
x<br />
1<br />
2<br />
y<br />
Let:<br />
1 2 0 <br />
1 0 3 <br />
<br />
1 2 0 6 3 2 <br />
1 0 3<br />
6 3 2 7<br />
<br />
<br />
Triple Products:<br />
Since the cross product <strong>of</strong> two <strong><strong>vector</strong>s</strong> is itself a <strong>vector</strong>, it can be dotted or crossed with a<br />
third <strong>vector</strong> to form a triple product.<br />
1‐ Scalar triple product: ∙ <br />
Geometrically ∙ is the volume <strong>of</strong> the parallelepiped generated by , ,<br />
<br />
6