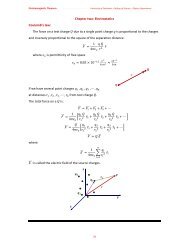
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
Chapter One: Vector Analysis The use of vectors and vector analysis ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Electromagnetic <strong>The</strong>orem<br />
(Dr. Omed Ghareb Abdullah) University <strong>of</strong> Sulaimani –College <strong>of</strong> Science – Physics Department<br />
So the total flux is:<br />
∙ 8 162448<br />
<strong>The</strong> Fundamental <strong>The</strong>orem for Curls:<br />
<strong>The</strong> fundamental theorem <strong>of</strong> Curls, which goes by the special name <strong>of</strong> Stokes’ theorem state<br />
that:<br />
<br />
<br />
∙ V<br />
As always, the integral <strong>of</strong> a derivative (here, the curl) over a region (here, a patch <strong>of</strong> surface)<br />
is equal to value <strong>of</strong> the function at the boundary (here, the perimeter <strong>of</strong> the patch).<br />
∙ <br />
If your finger point in<br />
the direction <strong>of</strong> the line integral, then your thumb fixed the direction<br />
<strong>of</strong> .<br />
Corollary(1):<br />
<br />
∙ depends only on the boundary line, not on the particular surface<br />
<strong>use</strong>d.<br />
Corollary(2):<br />
∮ <br />
∙ 0 for any closed surface.<br />
Example:<br />
Suppose<br />
2 3 4 <br />
Check Stokes’ theorem for the square surface in Fig.