manual of methods for determining micronutrients in fortified foods
manual of methods for determining micronutrients in fortified foods
manual of methods for determining micronutrients in fortified foods
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
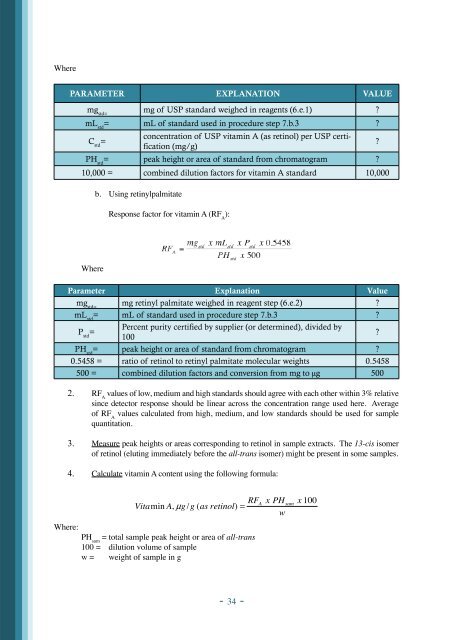
Where<br />
PARAMETER EXPLANATION VALUE<br />
mg std=<br />
mg <strong>of</strong> USP standard weighed <strong>in</strong> reagents (6.e.1) ?<br />
mL std<br />
= mL <strong>of</strong> standard used <strong>in</strong> procedure step 7.b.3 ?<br />
C std<br />
=<br />
concentration <strong>of</strong> USP vitam<strong>in</strong> A (as ret<strong>in</strong>ol) per USP certification<br />
(mg/g)<br />
PH std<br />
= peak height or area <strong>of</strong> standard from chromatogram ?<br />
10,000 = comb<strong>in</strong>ed dilution factors <strong>for</strong> vitam<strong>in</strong> A standard 10,000<br />
b. Us<strong>in</strong>g ret<strong>in</strong>ylpalmitate<br />
Response factor <strong>for</strong> vitam<strong>in</strong> A (RF A<br />
):<br />
?<br />
Where<br />
Parameter Explanation Value<br />
mg std=<br />
mg ret<strong>in</strong>yl palmitate weighed <strong>in</strong> reagent step (6.e.2) ?<br />
mL std<br />
= mL <strong>of</strong> standard used <strong>in</strong> procedure step 7.b.3 ?<br />
P std<br />
=<br />
Percent purity certified by supplier (or determ<strong>in</strong>ed), divided by<br />
100<br />
?<br />
PH std<br />
= peak height or area <strong>of</strong> standard from chromatogram ?<br />
0.5458 = ratio <strong>of</strong> ret<strong>in</strong>ol to ret<strong>in</strong>yl palmitate molecular weights 0.5458<br />
500 = comb<strong>in</strong>ed dilution factors and conversion from mg to µg 500<br />
2. RF A<br />
values <strong>of</strong> low, medium and high standards should agree with each other with<strong>in</strong> 3% relative<br />
s<strong>in</strong>ce detector response should be l<strong>in</strong>ear across the concentration range used here. Average<br />
<strong>of</strong> RF A<br />
values calculated from high, medium, and low standards should be used <strong>for</strong> sample<br />
quantitation.<br />
3. Measure peak heights or areas correspond<strong>in</strong>g to ret<strong>in</strong>ol <strong>in</strong> sample extracts. The 13-cis isomer<br />
<strong>of</strong> ret<strong>in</strong>ol (elut<strong>in</strong>g immediately be<strong>for</strong>e the all-trans isomer) might be present <strong>in</strong> some samples.<br />
4. Calculate vitam<strong>in</strong> A content us<strong>in</strong>g the follow<strong>in</strong>g <strong>for</strong>mula:<br />
Vitam<strong>in</strong> A, µg/g (as ret<strong>in</strong>ol) = RF A<br />
x PH sam<br />
x 100<br />
w<br />
Where:<br />
PH sam<br />
= total sample peak height or area <strong>of</strong> all-trans<br />
100 = € dilution volume <strong>of</strong> sample<br />
w = weight <strong>of</strong> sample <strong>in</strong> g<br />
- 34 -