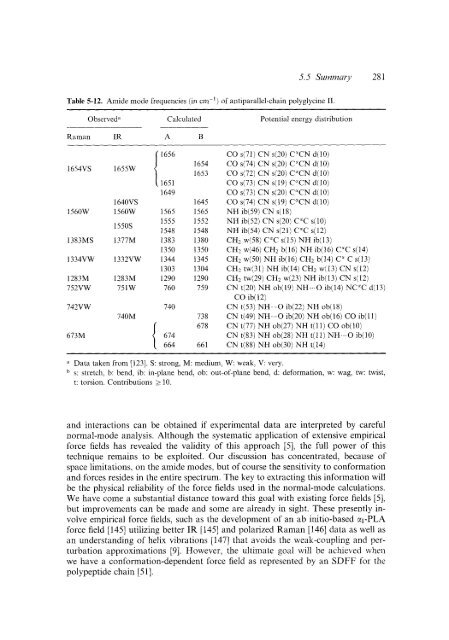
Table 5-12. Aniide mode frequencies (in cm-' ) of antiparallel-chain polyglycine 11. Observed' Calculated Potential energy distribution Rainan IR A B (1656 CO s(71) CN ~(20) C"CN d(l0) 1654 CO s(74) CN s(20) C"CN d( 10) 1654VS 1655W 1653 CO s(72) CN ~(20) CTN dil0) ( 1651 CO s(73) CN ~(19) C"CN d(10) 1649 CO 473) CN s(20) CTN d(10) 1640VS 1645 CO 474) CN s(19) CTN d(l0j 1560W 156OW 1565 1565 NH ib(59) CN s(18) 1550s 1555 1552 NH ib(52) CN s(20) C"C s(10) 1548 1548 NH ib(54) CN s(21) '2°C s(12) 1383MS 1377M 1353 1380 CH? ~(58) C"C ~(15) NH ib(13) 1350 1350 CH2 w(46) CH2 b(16) NH ib(16) C"C s(14) 1334VW 1332VW 1344 1345 CH2 w(50) NH ib(16) CH2 b(14) C" C ~(13) 1303 1304 CH1 tw(31) NH ib(14) CH2 w(13) CN s(12) 1283M 1283M 1290 1290 CH? tw(29) CH2 w(23) NH ib(13) CN s(12) 752VW 751W 760 759 CN t(20) NH ob(19) NH-.O ib(14) NC"C d(13) CO ib( 12) 742VW 740 CN t(53) NH.-.O ib(22) NH ob(l8) 673M 740M 738 678 661 CN t(49) NH...O ib(20) NH ob( 16) CO ib( 11) CN t(77) NH ob(27j NH t(l1) CO ob( 10) CN t(83) NH ob(28) NH t( 11) NH.-O ib( 10) CN t(88) NH ob(30) NH t(14) { a Data taken from [123]. S: strong, M: medium, W: weak, V: very. b s: stretch, b: bend, ib: in-plane bend, ob: out-of-plane bend, d: deformation, w: wag, tw: twist, t: torsion. Contributions 2 10. and interactions can be obtained if experimental data are interpreted by careful normal-mode analysis. Although the systematic application of extensive empirical force fields has revealed the validity of this approach [5], the full power of this technique remains to be exploited. Our discussion has concentrated, because of space limitations, on the amide modes, but of course the sensitivity to conformation and forces resides in the entire spectrum. The key to extracting this information will be the physical reliability of the force fields used in the normal-mode calculations. We have come a substantial distance toward this goal with existing force fields [5], but improvements can be made and some are already in sight. These presently involve empirical force fields, such as the development of an ab initio-based MI-PLA force field [145] utilizing better IR [145] and polarized Raman [146] data as well as an understanding of helix vibrations [ 1471 that avoids the weak-coupling and perturbation approximations 191. However, the ultimate goal will be achieved when we have a conformation-dependent force field as represented by an SDFF for the. polypeptide chain [51].
282 5 Vibrational <strong>Spect</strong>roscopy of Polypt>ptiu'c..c Acknowledgments The author's contributions to the development of this field have been supported by the National Science Foundation through grants from its Biophysics and <strong>Polymer</strong>s Programs. Helpful discussions with Noemi G. Mirkin and Kim Palmo are gratefdly acknowledged. 5.6 References Stryer, L., Biocheniistry. Fourth Edition. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co., 1995. Richardson, J., Ad[). Protein Cliem. 1981, 34, 167-339. Surewicz, W. K., Mantsch, H. H.. Bioihini. Biopliys. Acto 1988, 9-72, 115-130. Surewicz, W. K., Mantsch, H. H., Chapman, D., Biochemistry 1993, 32, 389-394. Krinim, S. and Bandekar, J., Ado. Protein Clieni. 1986, 38, 181-364. Herzberg, G., Molecular <strong>Spect</strong>ra and Struelure. I1 Injkved cind Rninan <strong>Spect</strong>in oj'Pulyatornic Molectiles. New Jersey: Van Nostrand-Reinhold, 1945. Wilson, E. B., Decius, J. C., Cross, P. C., Molecular. Vibrations. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1955. Califano, S., Vibrational States. New York: Wiley, 1976. Higgs, P. W., Proc. Roy. Soc. London Ser. A 1953,220, 472-485. Shimanouchi, T., in: Physical Chemistry: An Aducmceti Treatise: Eyring, H., Henderson, D., Jast, W. (Eds.). New York: Academic Press, 1970; Vol. 4, pp. 233-306. Person, W., Zerbi, G., Eds., Vibrationcil Intensities in IrIfitiretl aIid Rtirnnn Siiectroscopy. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1982. Qian, W., Krimni, S., J. Plzys. Chem 1993, 97, 11578-1 1579. Cheam, T. C., Krinim, S., J. Mol. Struct. 1986, 146, 175-189. Tasumi, M., Krimm, S., J. Chem. Plzys. 1967, 46, 755-766. Krimm, S., Abe, Y., Proc. Natl. Act7d. Sci. U.S.A. 1972, 69, 2788-2792. Moore. W. H., Krimm, S., Proc. Nrrtl. Acntl. Sci. U.S.A. 197.5, 7-7, 4933-4935. Cheam, T. C.! Krimm, S.. Chem. Plijx Lett. 1984, 107, 613-616. Abe, Y., Krimm, S., Biopo/ytners 1972, 11, 1817-1839. Moore, W. H., Krimm, S., Biopolymers 1976, 15, 2439-2464. Cheam, T. C., Krimm, S., J. Cliern. Phys. 198.5, S2, 1631-1641. Schachtschneider, J. H., Snyder, R. G., <strong>Spect</strong>rochiin. Actu 1963, 19, 117-168. Dwivedi, A. M., Krimm, S., J. Phy.~. Clzein. 1984, 88, 620-627. Hehre, W. J., Radoni, L., v. R. Schleyer, P., Pople, J. A,, Ab Iizitio Moleciilrir Orbited Theory. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1986. Fogarasi, G., Pulay, P., in Vibrational Siiectm mid Structure: Durig, J. R. (Ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1985; Vol. 14, pp. 125-219. Mirkin, N. G., Krimm, S., J. Mol. Strtrct. (Theockern) 1995, 334, 1-6. Mirkin, N. G., Krimm, S., J. Phys. Cheni. 1993, 97, 13887-13895. Qian, W., Krinim, S., J. Phj>s. Chem. 1994, 98, 9992-10000. Qian, W., Krimm, S., Biopolyiiievs 1994, 34, 1377-1394. Zhao, W., Bandekar, J., Krimm, S., J. Mol. Struct. 1990, 238, 43-54. Qian, W., Zhao, W., Krimm, S., J. Mol. Struct. 1991, 250, 89-102. Qian, W., Krirnm, S., Bio&niers 1992, 32, 1025-1033. Qian, W., Krimm, S., Biopolyniers 1992, 317, 1503-1518. Cheam, T. C., Krimm, S.. J. Mol. Struct. ( Theoclzeni) 1990.206, 173-203. Cheam. T. C., Kriinm, S., J. Md Struct. (Tlzeoclieni) 1989, IS8, 15-43.
- Page 2 and 3:
Modern Polymer Spectroscopy Edited
- Page 4 and 5:
Modern Polymer Spectroscopy Edited
- Page 6 and 7:
Preface For unfortunate reasons the
- Page 8 and 9:
However, theory and calculations yi
- Page 10 and 11:
Contents 1 Two-Dimensional Infrared
- Page 12 and 13:
Con ten t~ xi Index 5.2 Force Field
- Page 14 and 15:
Contributors M. Del Zoppo Dipartime
- Page 16 and 17:
1 Two-Dimensional Infrared (2D IR)
- Page 18 and 19:
1.2 Brick~qrorrnrl 3 . Figure 1-3.
- Page 20 and 21:
1.0 , Figure 1-6. The in-phtrse and
- Page 22 and 23:
1.2 Bcrckgroinizd 7 where AA (i~) i
- Page 24 and 25:
1.2 Background 9 1.2.5 Two-Dimensio
- Page 26 and 27:
1.3 Bnsic Properties of 20 IR Corre
- Page 28 and 29:
2D IR spectrometer coupled with a d
- Page 30 and 31:
1.5 Applirtrtions 15 Unlike a dispe
- Page 32 and 33:
\ '\ Melliyleiie 1'7- -3000 Posiliv
- Page 34 and 35:
11 Amorphous Crystalline ,...." I F
- Page 36 and 37:
1.5 Applications 21 / I 1430 Figure
- Page 38 and 39:
1.5 Appliccitioiis 23 Methylene Fig
- Page 40 and 41:
1.5 Ajqdicrrtions 25 3024 Figure 1-
- Page 42 and 43:
1.5 Applicutions 27 Furthermore. th
- Page 44 and 45:
1.7 Coizclirsions 29 derived in a s
- Page 46 and 47:
1.9 References 31 [9] Colthup, N. B
- Page 48 and 49:
2 Segmental Mobility of Liquid Crys
- Page 50 and 51:
SRMPLE/DETECTOR e3 ‘retardation
- Page 52 and 53:
2.4 Srvuc me-Dependenr Alignment 37
- Page 54 and 55:
2.5 Electric Field-Innductid Orirnt
- Page 56 and 57:
2.5 Electric Field-nclticetl Orient
- Page 58 and 59:
a -@ COWER SRHPLE ._ 2.5 Elec tric
- Page 60 and 61:
2.5 Electric Field-Itzduced Orienta
- Page 62 and 63:
2.5 Electric Field-IwrElrced Orient
- Page 64 and 65:
2.5 Electric Field-Im/irced Orientu
- Page 66 and 67:
2.5 Electric Field-Induced Orientli
- Page 68 and 69:
2.5 Electric Field-Induced Orientat
- Page 70 and 71:
2.5 Electric Field-Induced Orienfat
- Page 72 and 73:
2.5 Elrc tric Field-Iiidircwl Orim
- Page 74 and 75:
2500 2008 I s00 WRVtNdMRtR CM-I Fig
- Page 76 and 77:
-3.6 Aligmient OJ' Side- Clinin Liy
- Page 78 and 79:
~ polyester 2.6 Alignnient qf Side-
- Page 80 and 81:
I." 0.9 0.8 Figure 2-34. FTlR 0.7 p
- Page 82 and 83:
induced alignment of the investigat
- Page 84 and 85:
2.7 Orientation oj Liquid Ci:i,stal
- Page 86 and 87:
2.7 Orieritation of Liquid Ciysttrl
- Page 88 and 89:
0 8 18 16 1 a W u z a m a 0 Ln m Q
- Page 90 and 91:
2.7 Orientation oj Liquid Crystals
- Page 92 and 93:
2.7 Orientation of Liquid Crjvtals
- Page 94 and 95:
2.7 Orientatioiz of Liquid Crystals
- Page 96 and 97:
2.8 Conclusions 81 strain. As A0 is
- Page 98 and 99:
3. I0 Refcreiice.r 83 [I 71 Hoffina
- Page 100 and 101:
2.10 References 85 [92] Wiesner, U.
- Page 102 and 103:
t Order/Disorder in Chain Molecules
- Page 104 and 105:
onds which hold atoms together thro
- Page 106 and 107:
3.2 The Dyriamical Case qf Simll ar
- Page 108 and 109:
3.2 The Dyrinniical Case of Sinnll
- Page 110 and 111:
3.4 S11or.f- and Loizg-Rcrizye Vibr
- Page 112 and 113:
3.4 Slzort- and Loiig-Range Vibrati
- Page 114 and 115:
eyularity), e.g., 2. During the pol
- Page 116 and 117:
3.5 Towards Lnrger Molecules: From
- Page 118 and 119:
3.5 TOIIYW~ Laiyer Molertiles: Fvoi
- Page 120 and 121:
3.5 Towmu" Larger Molecules: F~om O
- Page 122 and 123:
1700 - CIO --- ca c 22 _- c 12 l l
- Page 124 and 125:
3.6 From Dynamics to Vibrational Sp
- Page 126 and 127:
3.6 Froin Dynaiiiics to T’ihratio
- Page 128 and 129:
3.7 The Case of Isotactic Polypropy
- Page 130 and 131:
3.7 The Cuse of Isotactic Polypvop.
- Page 132 and 133:
3.8 Density of Vibrational States a
- Page 134 and 135:
3.8 Dtvz.sit,v of L’ihrntioizal S
- Page 136 and 137:
3.8 Driisity of Vibratioiid StLitrs
- Page 138 and 139:
3 9 Mouiiiq ToIvmds Rerrlitv: From
- Page 140 and 141:
3.9 Moving Towards Reality: From Or
- Page 142 and 143:
3.9 Moving Towards Reality: Froin O
- Page 144 and 145:
3.10 Wlmt Do We Learn from Cnlcailc
- Page 146 and 147:
+ 3.11 A Very Siriiple Ccrse: Latti
- Page 148 and 149:
3 I1 A Yey) Siiiiple Case: LLittice
- Page 150 and 151:
3.11 A Vq> Siiiiplc Crrw: Luttice D
- Page 152 and 153:
Figure 3-22. Sample eigenvectors in
- Page 154 and 155:
3.12 CIS-trans Opening @the Double
- Page 156 and 157:
3.13 Defect Modes cis Structtrr.al
- Page 158 and 159:
3.13 Defect Mo&s cis Structurcil Pr
- Page 160 and 161:
0 3.14 Case Studies N 0 d - Y N o m
- Page 162 and 163:
3.14 Case Studies 147 OC 60 58 57.
- Page 164 and 165:
3.14 Case Studies 149 GI A V E N U
- Page 166 and 167:
3.14 Case Studies 15 1 correspond t
- Page 168 and 169:
3.14 Case Studies 153 (I10 + 200) +
- Page 170 and 171:
3.14 Case Studies 155 1500 1480 146
- Page 172 and 173:
3.14 Case Studies 157 the molecular
- Page 174 and 175:
17E (ir 1, R): (iii) z = 4, t = 1,
- Page 176 and 177:
3.16 Stnictural Znlioi~zogeneity an
- Page 178 and 179:
3.1 7 Fermi Resonancrs 163 stants.
- Page 180 and 181:
3.1 7 Femi Resorinnces 165 2 L 1 29
- Page 182 and 183:
lowing. The CHl-bending mode 6 [cer
- Page 184 and 185:
3.17 Ferini Re.sonrriire.s 169 a Fi
- Page 186 and 187:
3. I7 Fernii Resoiiances 17 1 terin
- Page 188 and 189:
3.18 Band Broadening and Confonnati
- Page 190 and 191:
3.18 Bmd Brourleiziriy md Cmforrnat
- Page 192 and 193:
3.18 Band Bvoaderiing arid Conjonna
- Page 194 and 195:
3.18 Band Broadening and Confornmti
- Page 196 and 197:
3.19 A Worked E.utinple 181 pre-mel
- Page 198 and 199:
3.19 A Wovh-ecl E.uanzple 183
- Page 200 and 201:
3.19 A Worked Example 185 19 5°C 2
- Page 202 and 203:
3.19 A Workrd Example 187 Figure 3-
- Page 204 and 205:
3.19 A Worked E.rcnniplr 189 LAM I
- Page 206 and 207:
3.19 A Worked E.xuniple 191 Figure
- Page 208 and 209:
3.19 A Worked E.vnn~yle 193 Figure
- Page 210 and 211:
3.19 A Worked E.vnrqde 195 009.1 00
- Page 212 and 213:
3.19 A Worked Example 197 existence
- Page 214 and 215:
3.1 9 A Worked Example 199 The soli
- Page 216 and 217:
3.20 References 201 very important,
- Page 218 and 219:
3.20 References 203 [41] M. Gussoni
- Page 220 and 221:
3.20 Refeeveiicrs 205 [I 171 P. Jon
- Page 222 and 223:
4 Vibrational Spectroscopy of Intac
- Page 224 and 225:
4.3 Georrietvy oj Intuct Po1vniev.r
- Page 226 and 227:
1'45 4.4 Geometric Chunges I?zditce
- Page 228 and 229:
4.4 Geometric Chmges Iiid~lrcecl bj
- Page 230 and 231:
4 5 Mer1iodolog.v of Raiii~11 Studi
- Page 232 and 233:
4.7 Poly(p-pheiq.lene) 217 with an
- Page 234 and 235:
4.7 Pol)~(p-pheiz~~lene) 219 ENERGY
- Page 236 and 237:
is worthwhile pointing out that the
- Page 238 and 239:
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 801 Table 4-3
- Page 240 and 241:
4.7 Poly(y-phenylene) 225 Figure 4-
- Page 242 and 243:
Table 4-4. Observed Raman frequenci
- Page 244 and 245:
4.8 Other Polwieys 229 Table 4-5. T
- Page 246 and 247: under various models. According to
- Page 248 and 249: 4. I0 Mechnriism oj Charge. Transpo
- Page 250 and 251: 4.12 Reftrences 235 [ 131 Kuzmany,
- Page 252 and 253: 4.12 References 237 [98j Matsunuma,
- Page 254 and 255: 5 Vibrational Spectroscopy of Polyp
- Page 256 and 257: 5.2 FOYCC Fields 241 such calculati
- Page 258 and 259: 5.2 Force Fields 243 accounts for o
- Page 260 and 261: 5.2 Force Fields 245 centers of the
- Page 262 and 263: 5.2 Force Fields 247 ture with conf
- Page 264 and 265: 5.3 Amide Modes 249 to the nh initi
- Page 266 and 267: 5.3 Ainide Modes 251 Table 5-1. Ami
- Page 268 and 269: Table 5-2. Some amide modes of four
- Page 270 and 271: 5.3 Amidc Modes 255 Figure 5-1. Opt
- Page 272 and 273: 5.4 Polypeptides 257 nonhydrogen-bo
- Page 274 and 275: 5.4 Polvpeptida 259 Figure 5-2. Ant
- Page 276 and 277: I 5.4 Polypeptides 261 )I .- + $ 80
- Page 278 and 279: 1226M 1222s (1 1165W 1167s (1 1120V
- Page 280 and 281: 135s 9 1 Ms1i 122Wbr 147 NH ob(37)
- Page 282 and 283: 5.4 Polypeptides 267 glycine residu
- Page 284 and 285: 5.4 Polypeptides 269 Raman bands in
- Page 286 and 287: 5.4 Polypeptides 271 Figure 5-7. St
- Page 288 and 289: Frequency (cm-'1 100% b 700 500 300
- Page 290 and 291: 5.4 Polypptidt~s 215 Table 5-9. Obs
- Page 292 and 293: ~~ ~~ ~~~ ~ ~ ~~ 5.4 Polypeptides 2
- Page 294 and 295: 5.4 Poliyeptides 219 Table 5-11. Co
- Page 298 and 299: 1351 Lifson, S., Stern, P. S., J. C
- Page 300 and 301: 5.6 Refeverices 285 [130] Tiffany,
- Page 302 and 303: Index Amide modes 249 Amorphous pol
- Page 304 and 305: Step-scan FTIR spectroscopy 14,34 -