2,46 Mb - GuÃaSalud
2,46 Mb - GuÃaSalud
2,46 Mb - GuÃaSalud
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1+ There are no significant differences as regards glycemic control assessed by means of<br />
glycosylated haemoglobin between fast-acting insulin analogues and fast-acting human<br />
insulin. There are no differences in the frequency of hypoglycaemias (149; 150).<br />
Recommendations<br />
A<br />
<br />
A<br />
D CPG<br />
When treatment with insulin is started, it is recommendable to keep up the therapy with<br />
metformin and/or sulfonylureas.<br />
The need to continue with sulfonylureas or to reduce their dosage due to the risk of hypoglycaemias<br />
is to be reviewed.<br />
In DM 2 patients who require insulinization, the general use of insulin analogues is recommended.<br />
The use of slow-acting insulin analogues in patients with increased risk of night<br />
hypoglycaemias is recommended. DM 2 patients who require intensive insulinization, are<br />
not recommended the use of fast-acting analogues, as they present no advantages.<br />
DCPG When selecting an initial insulin schedule, the patient’s preference, the adverse<br />
effects risks (mainly hypoglycaemia) and the costs are to be taken into consideration.<br />
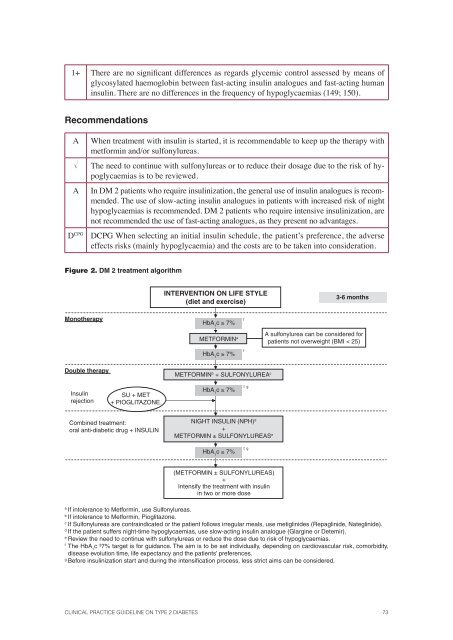
Figure 2. DM 2 treatment algorithm<br />
INTERVENTION ON LIFE STYLE<br />
(diet and exercise)<br />
3-6 months<br />
Monotherapy<br />
HbA 1<br />
c ≥ 7%<br />
f<br />
METFORMIN a<br />
A sulfonylurea can be considered for<br />
patients not overweight (BMI < 25)<br />
HbA 1<br />
c ≥ 7%<br />
f<br />
Double therapy<br />
METFORMIN b + SULFONYLUREA c<br />
Insulin<br />
rejection<br />
SU + MET<br />
+ PIOGLITAZONE.<br />
HbA 1<br />
c ≥ 7%<br />
f, g<br />
Combined treatment:<br />
oral anti-diabetic drug + INSULIN<br />
NIGHT INSULIN (NPH) d<br />
+<br />
METFORMIN ± SULFONYLUREAS e<br />
HbA 1<br />
c ≥ 7%<br />
f, g<br />
(METFORMIN ± SULFONYLUREAS)<br />
+<br />
Intensify the treatment with insulin<br />
in two or more dose<br />
a<br />
If intolerance to Metformin, use Sulfonylureas.<br />
b<br />
If intolerance to Metformin, Pioglitazone.<br />
c<br />
If Sulfonylureas are contraindicated or the patient follows irregular meals, use metiglinides (Repaglinide, Nateglinide).<br />
d<br />
If the patient suffers night-time hypoglycaemias, use slow-acting insulin analogue (Glargine or Detemir).<br />
e<br />
Review the need to continue with sulfonylureas or reduce the dose due to risk of hypoglycaemias.<br />
f<br />
The HbA 1<br />
c ³7% target is for guidance. The aim is to be set individually, depending on cardiovascular risk, comorbidity,<br />
disease evolution time, life expectancy and the patients’ preferences.<br />
g<br />
Before insulinization start and during the intensifi cation process, less strict aims can be considered.<br />
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE ON TYPE 2 DIABETES 73