Vol 44 # 4 December 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 44 # 4 December 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 44 # 4 December 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>December</strong> <strong>2012</strong><br />
KUWAIT MEDICAL JOURNAL 288<br />
College and associated Lok Nayak Hospital, New<br />
Delhi from <strong>December</strong> 2006 and <strong>December</strong> 2008.<br />
The study included patients selected according to<br />
the criteria given below. Fifty patients were included<br />
in the study.<br />
Inclusion criteria<br />
Pregnancy more than or equal to 20 weeks of<br />
gestation, having severe hypertension i.e., systolic<br />
blood pressure (SBP) of at least 160 mmHg and / or<br />
diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of at least 110 mmHg<br />
with or without proteinuria were included.<br />
Exclusion criteria<br />
Patients with cardiac failure, history of bronchial<br />
asthma, bradycardia (pulse rate < 60 beats per minute),<br />
allergic diathesis and eclampsia were excluded.<br />
After taking history, doing a complete examination<br />
and taking informed consent, either intravenous<br />
labetalol or oral nifedipine were given to the patients<br />
consecutively. Patients were divided into two groups<br />
(i.e., group A - labetalol and group B - nifedipine).<br />
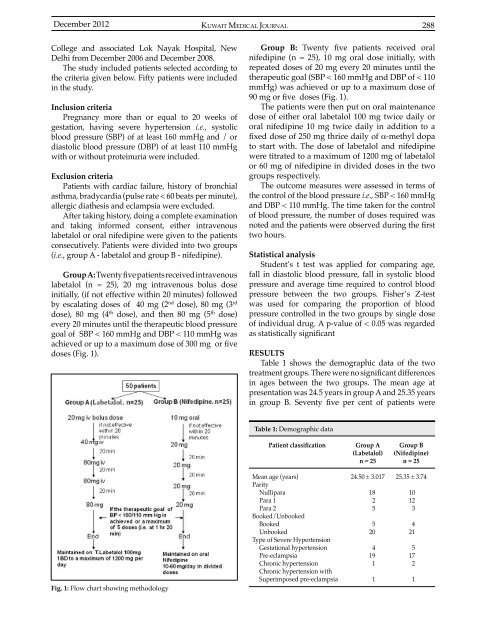
Group A: Twenty fivepatientsreceivedintravenous<br />
labetalol (n = 25), 20 mg intravenous bolus dose<br />
initially, (if not effective within 20 minutes) followed<br />
by escalating doses of 40 mg (2 nd dose), 80 mg (3 rd<br />
dose), 80 mg (4 th dose), and then 80 mg (5 th dose)<br />
every 20 minutes until the therapeutic blood pressure<br />
goal of SBP < 160 mmHg and DBP < 110 mmHg was<br />
achieved or up to a maximum dose of 300 mg or five<br />
doses (Fig. 1).<br />
Group B: Twenty five patients received oral<br />
nifedipine (n = 25), 10 mg oral dose initially, with<br />
repeated doses of 20 mg every 20 minutes until the<br />
therapeutic goal (SBP < 160 mmHg and DBP of < 110<br />
mmHg) was achieved or up to a maximum dose of<br />
90 mg or five doses (Fig. 1).<br />
The patients were then put on oral maintenance<br />
dose of either oral labetalol 100 mg twice daily or<br />
oral nifedipine 10 mg twice daily in addition to a<br />
fixed dose of 250 mg thrice daily of α-methyl dopa<br />
to start with. The dose of labetalol and nifedipine<br />
were titrated to a maximum of 1200 mg of labetalol<br />
or 60 mg of nifedipine in divided doses in the two<br />
groups respectively.<br />
The outcome measures were assessed in terms of<br />
the control of the blood pressure i.e., SBP < 160 mmHg<br />
and DBP < 110 mmHg. The time taken for the control<br />
of blood pressure, the number of doses required was<br />
noted and the patients were observed during the first<br />
two hours.<br />
Statistical analysis<br />
Student’s t test was applied for comparing age,<br />
fall in diastolic blood pressure, fall in systolic blood<br />
pressure and average time required to control blood<br />
pressure between the two groups. Fisher’s Z-test<br />
was used for comparing the proportion of blood<br />
pressure controlled in the two groups by single dose<br />
of individual drug. A p-value of < 0.05 was regarded<br />
as statistically significant<br />
RESULTS<br />
Table 1 shows the demographic data of the two<br />
treatment groups. There were no significant differences<br />
in ages between the two groups. The mean age at<br />
presentation was 24.5 years in group A and 25.35 years<br />
in group B. Seventy five per cent of patients were<br />
Table 1: Demographic data<br />
Patient classification<br />
Group A<br />
(Labetalol)<br />
n = 25<br />
Group B<br />
(Nifedipine)<br />
n = 25<br />
Fig. 1: Flow chart showing methodology<br />
Mean age (years)<br />
Parity<br />
Nullipara<br />
Para 1<br />
Para 2<br />
Booked/Unbooked<br />
Booked<br />
Unbooked<br />
Type of Severe Hypertension<br />
Gestational hypertension<br />
Pre-eclampsia<br />
Chronic hypertension<br />
Chronic hypertension with<br />
Superimposed pre-eclampsia<br />
24.50 ± 3.017<br />
18<br />
2<br />
5<br />
5<br />
20<br />
4<br />
19<br />
1<br />
1<br />
25.35 ± 3.74<br />
10<br />
12<br />
3<br />
4<br />
21<br />
5<br />
17<br />
2<br />
1