Vol 44 # 4 December 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 44 # 4 December 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 44 # 4 December 2012 - Kma.org.kw
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
313<br />
Synergy between Dendritic Cell-Based Vaccine and Anti-CD137 Monoclonal ...<br />
<strong>December</strong> <strong>2012</strong><br />
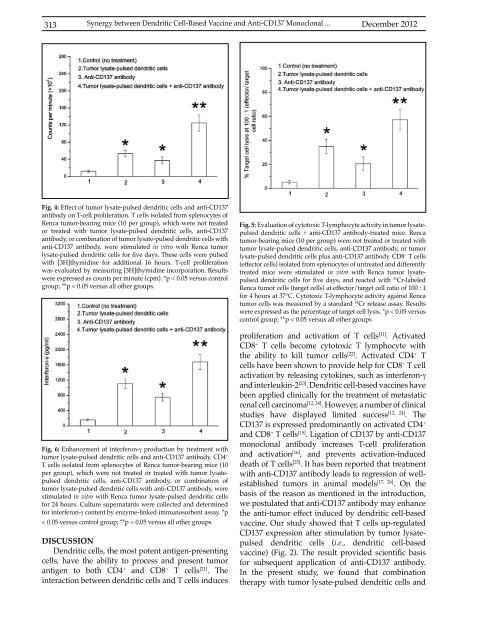
Fig. 4: Effect of tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells and anti-CD137<br />
antibody on T-cell proliferation. T cells isolated from splenocytes of<br />
Renca tumor-bearing mice (10 per group), which were not treated<br />
or treated with tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells, anti-CD137<br />
antibody, or combination of tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells with<br />
anti-CD137 antibody, were stimulated in vitro with Renca tumor<br />
lysate-pulsed dendritic cells for five days. These cells were pulsed<br />
with [3H]thymidine for additional 16 hours. T-cell proliferation<br />
was evaluated by measuring [3H]thymidine incorporation. Results<br />
were expressed as counts per minute (cpm). *p < 0.05 versus control<br />
group; **p < 0.05 versus all other groups.<br />
Fig. 6: Enhancement of interferon-γ production by treatment with<br />
tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells and anti-CD137 antibody. CD4 +<br />
T cells isolated from splenocytes of Renca tumor-bearing mice (10<br />
per group), which were not treated or treated with tumor lysatepulsed<br />
dendritic cells, anti-CD137 antibody, or combination of<br />
tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells with anti-CD137 antibody, were<br />
stimulated in vitro with Renca tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells<br />
for 24 hours. Culture supernatants were collected and determined<br />
for interferon-γ content by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. *p<br />
< 0.05 versus control group; **p < 0.05 versus all other groups<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
Dendritic cells, the most potent antigen-presenting<br />
cells, have the ability to process and present tumor<br />
antigen to both CD4 + and CD8 + T cells [21] . The<br />
interaction between dendritic cells and T cells induces<br />
Fig. 5: Evaluation of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity in tumor lysatepulsed<br />
dendritic cells + anti-CD137 antibody-treated mice. Renca<br />
tumor-bearing mice (10 per group) were not treated or treated with<br />
tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells, anti-CD137 antibody, or tumor<br />
lysate-pulsed dendritic cells plus anti-CD137 antibody. CD8 + T cells<br />
(effector cells) isolated from splenocytes of untreated and differently<br />
treated mice were stimulated in vitro with Renca tumor lysatepulsed<br />
dendritic cells for five days, and reacted with 51 Cr-labeled<br />
Renca tumor cells (target cells) at effector/target cell ratio of 100 : 1<br />
for 4 hours at 37°C. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity against Renca<br />
tumor cells was measured by a standard 51 Cr release assay. Results<br />
were expressed as the percentage of target cell lysis. *p < 0.05 versus<br />
control group; **p < 0.05 versus all other groups<br />
proliferation and activation of T cells [11] . Activated<br />
CD8 + T cells become cytotoxic T lymphocyte with<br />
the ability to kill tumor cells [22] . Activated CD4 + T<br />
cells have been shown to provide help for CD8 + T cell<br />
activation by releasing cytokines, such as interferon-γ<br />
and interleukin-2 [23] . Dendritic cell-based vaccines have<br />
been applied clinically for the treatment of metastatic<br />
renal cell carcinoma [12, 24] . However, a number of clinical<br />
studies have displayed limited success [12, 24] . The<br />
CD137 is expressed predominantly on activated CD4 +<br />
and CD8 + T cells [15] . Ligation of CD137 by anti-CD137<br />
monoclonal antibody increases T-cell proliferation<br />
and activation [16] , and prevents activation-induced<br />
death of T cells [25] . It has been reported that treatment<br />
with anti-CD137 antibody leads to regression of wellestablished<br />
tumors in animal models [17, 26] . On the<br />
basis of the reason as mentioned in the introduction,<br />
we postulated that anti-CD137 antibody may enhance<br />
the anti-tumor effect induced by dendritic cell-based<br />
vaccine. Our study showed that T cells up-regulated<br />
CD137 expression after stimulation by tumor lysatepulsed<br />
dendritic cells (i.e., dendritic cell-based<br />
vaccine) (Fig. 2). The result provided scientific basis<br />
for subsequent application of anti-CD137 antibody.<br />
In the present study, we found that combination<br />
therapy with tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells and