GLYCO DOC GEL IMAGING SYSTEM - Bio-Rad
GLYCO DOC GEL IMAGING SYSTEM - Bio-Rad
GLYCO DOC GEL IMAGING SYSTEM - Bio-Rad
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Theory of Operation<br />
3.0 THEORY OF OPERATIONS<br />
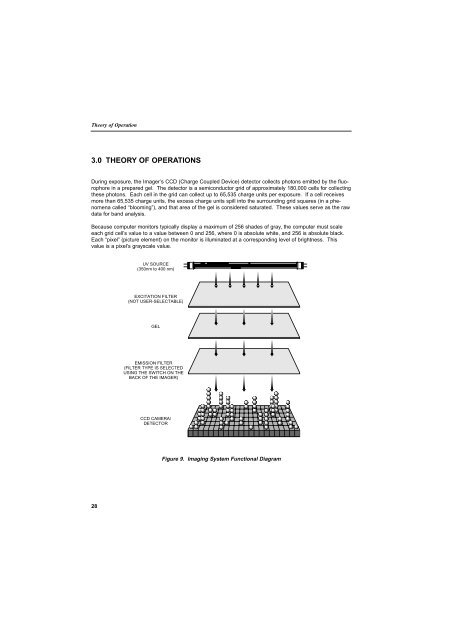
During exposure, the Imager’s CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector collects photons emitted by the fluorophore<br />
in a prepared gel. The detector is a semiconductor grid of approximately 180,000 cells for collecting<br />
these photons. Each cell in the grid can collect up to 65,535 charge units per exposure. If a cell receives<br />
more than 65,535 charge units, the excess charge units spill into the surrounding grid squares (in a phenomena<br />
called “blooming”), and that area of the gel is considered saturated. These values serve as the raw<br />
data for band analysis.<br />
Because computer monitors typically display a maximum of 256 shades of gray, the computer must scale<br />
each grid cell’s value to a value between 0 and 256, where 0 is absolute white, and 256 is absolute black.<br />
Each “pixel” (picture element) on the monitor is illuminated at a corresponding level of brightness. This<br />
value is a pixel’s grayscale value.<br />
UV SOURCE<br />
(350nm to 400 nm)<br />
EXCITATION FILTER<br />
(NOT USER-SELECTABLE)<br />
<strong>GEL</strong><br />
EMISSION FILTER<br />
(FILTER TYPE IS SELECTED<br />
USING THE SWITCH ON THE<br />
BACK OF THE IMAGER)<br />
CCD CAMERA/<br />
DETECTOR<br />
Figure 9. Imaging System Functional Diagram<br />
28