Neurological Examination, clinical cases and neuropsychological ...
Neurological Examination, clinical cases and neuropsychological ...
Neurological Examination, clinical cases and neuropsychological ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
23/07/54<br />
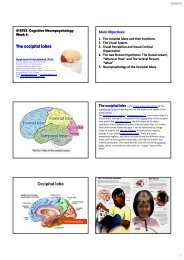
Cerebellum<br />
Vestibular<br />
<strong>and</strong><br />
Cerebellum<br />
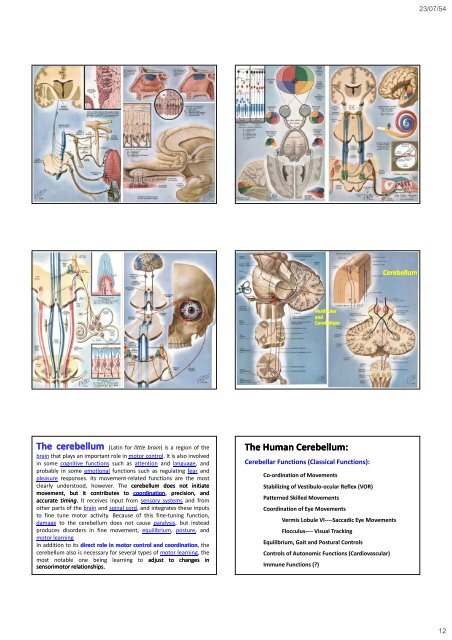
The cerebellum (Latin for little brain) isaregionofthe<br />
brain that plays an important role in motor control.Itisalsoinvolved<br />
in some cognitive functions such as attention <strong>and</strong> language, <strong>and</strong><br />
probably in some emotional functions such as regulating fear <strong>and</strong><br />
pleasure responses. Its movement‐related functions are the most<br />
clearly understood, however. The cerebellum does not initiate<br />
movement, but it contributes to coordination, precision, <strong>and</strong><br />
accurate timing. It receives input from sensory systems <strong>and</strong> from<br />
other parts of the brain <strong>and</strong> spinal cord, <strong>and</strong> integrates these inputs<br />
to fine tune motor activity. Because of this fine‐tuning function,<br />
damage to the cerebellum does not cause paralysis, but instead<br />
produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, <strong>and</strong><br />
motor learning<br />
In addition to its direct role in motor control <strong>and</strong> coordination, the<br />
cerebellum also is necessary for several types of motor learning, the<br />
most notable one being learning to adjust<br />
to changes<br />
in<br />
sensorimotor relationships.<br />
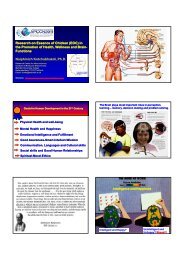
The Human Cerebellum:<br />
Cerebellar Functions (Classical Functions):<br />
Co‐ordination of Movements<br />
Stabilizing of Vestibulo‐ocular Reflex (VOR)<br />
Patterned Skilled Movements<br />
Coordination of Eye Movements<br />
Vermis Lobule VI‐‐‐‐Saccadic Eye Movements<br />
Flocculus‐‐‐‐ Visual Tracking<br />
Equilibrium, Gait <strong>and</strong> Postural Controls<br />
Controls of Autonomic Functions (Cardiovascular)<br />
Immune Functions (?)<br />
12