Neurological Examination, clinical cases and neuropsychological ...
Neurological Examination, clinical cases and neuropsychological ...
Neurological Examination, clinical cases and neuropsychological ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
23/07/54<br />
Brain mechanisms<br />
for olfaction<br />
(Smell), the nose<br />
brain or<br />
“Rhinencephalon”<br />
<strong>and</strong> associated<br />
limbic structures<br />
7/23/2011 NEUROPSYCHIATRY 248<br />
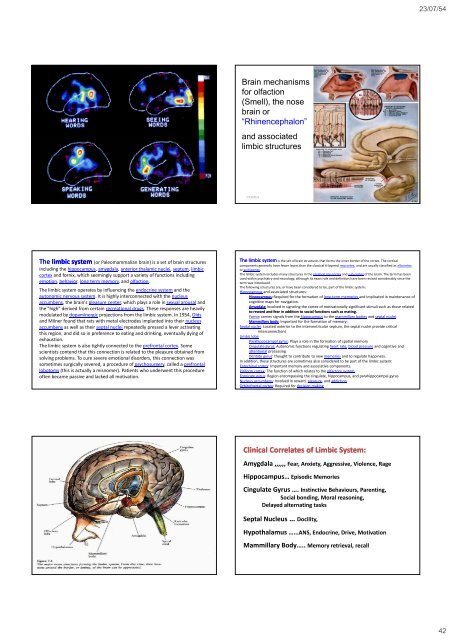
The limbic system (or Paleomammalian brain) is a set of brain structures<br />
including the hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, septum, limbic<br />
cortex <strong>and</strong> fornix, which seemingly support a variety of functions including<br />
emotion, behavior, long term memory, <strong>and</strong> olfaction.<br />
The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system <strong>and</strong> the<br />
autonomic nervous system. It is highly interconnected with the nucleus<br />
accumbens, the brain's pleasure center, which plays a role in sexual arousal <strong>and</strong><br />
the "high" derived from certain recreational drugs. These responses are heavily<br />
modulated by dopaminergic projections from the limbic system. In 1954, Olds<br />
<strong>and</strong> Milner found dthat t rats with metal tlelectrodes implanted dinto their nucleus<br />
accumbens as well as their septal nuclei repeatedly pressed a lever activating<br />
this region, <strong>and</strong> did so in preference to eating <strong>and</strong> drinking, eventually dying of<br />
exhaustion.<br />
The limbic system is also tightly connected to the prefrontal cortex. Some<br />
scientists contend that this connection is related to the pleasure obtained from<br />
solving problems. To cure severe emotional disorders, this connection was<br />
sometimes surgically severed, a procedure of psychosurgery, called a prefrontal<br />
lobotomy (this is actually a misnomer). Patients who underwent this procedure<br />
often became passive <strong>and</strong> lacked all motivation.<br />
The limbic system is the set of brain structures that forms the inner border of the cortex. The cortical<br />
components generally have fewer layers than the classical 6‐layered neocortex, <strong>and</strong> are usually classified as allocortex<br />
or archicortex.<br />
The limbic system includes many structures in the cerebral pre‐cortex <strong>and</strong> sub‐cortex of the brain. The term has been<br />
used within psychiatry <strong>and</strong> neurology, although its exact role <strong>and</strong> definition have been revised considerably since the<br />
term was introduced.<br />
The following structures are, or have been considered to be, part of the limbic system:<br />
Hippocampus <strong>and</strong> associated structures:<br />
Hippocampus: Required for the formation of long‐term memories <strong>and</strong> implicated in maintenance of<br />
cognitive maps for navigation.<br />
Amygdala:Involved in signaling the cortex of motivationally significant stimuli such as those related<br />
to reward <strong>and</strong> fear in addition to social functions such as mating.<br />
Fornix: carries signals from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies <strong>and</strong> septal nuclei.<br />
Mammillary body:Important for the formation of memory;<br />
Septal nuclei: Located anterior to the interventricular septum, the septal nuclei provide critical<br />
interconnections<br />
Limbic lobe<br />
Parahippocampal gyrus: Plays a role in the formation of spatial memory<br />
Cingulate gyrus: Autonomic functions regulating heart rate, blood pressure <strong>and</strong> cognitive <strong>and</strong><br />
attentional processing<br />
Dentate gyrus: thought to contribute to new memories <strong>and</strong> to regulate happiness.<br />
In addition, these structures are sometimes also considered to be part of the limbic system:<br />
Entorhinal cortex: Important memory <strong>and</strong> associative components.<br />
Piriform cortex: The function of which relates to the olfactory system.<br />
Fornicate gyrus: Region encompassing the cingulate, hippocampus, <strong>and</strong> parahippocampal gyrus<br />
Nucleus accumbens: Involved in reward, pleasure, <strong>and</strong> addiction<br />
Orbitofrontal cortex: Required for decision making.<br />
Clinical Correlates of Limbic System:<br />
Amygdala ,,,,,, Fear, Anxiety, Aggressive, Violence, Rage<br />
Hippocampus… Episodic Memories<br />
Cingulate Gyrus …. Instinctive Behaviours, Parenting,<br />
Social bonding, Moral reasoning,<br />
Delayed alternating tasks<br />
Septal Nucleus … Docility,<br />
Hypothalamus ……ANS, Endocrine, Drive, Motivation<br />
Mammillary Body….. Memory retrieval, recall<br />
7/23/2011 NEUROPSYCHIATRY 251<br />
42