Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Fundamentals</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Circuits</strong> I: <strong>Current</strong> <strong>Models</strong>, <strong>Batteries</strong> & <strong>Bulbs</strong> v 0.1<br />
Investigation 3:<br />
<strong>Current</strong> and Electric Potential Difference<br />
Since a battery is a device that has an electric potential difference across its terminals, it<br />
is capable <strong>of</strong> giving energy to charges, which can then flow as a current through a circuit.<br />
Exploring the relationship between the potential differences in a circuit and the currents that<br />
flow in that circuit is an essential part <strong>of</strong> developing an understanding <strong>of</strong> electrical circuits.<br />
Since potential differences are measured in volts, a potential difference is informally referred<br />
to as a voltage, and usually denoted by the symbol V . Voltage is an informal term for potential<br />
difference. If you want to talk to physicists, you should refer to potential difference. Communicating<br />
with a sales person at the local Radio Shack store or buying batteries at a hardware<br />
store is another story. There you should probably refer to voltage. We will use these two terms<br />
interchangeably.<br />
You will use voltage probes to measure electric potential difference. The voltage probe has<br />
two clips. When the clips at the ends <strong>of</strong> the wires are connected at two points in a circuit the<br />
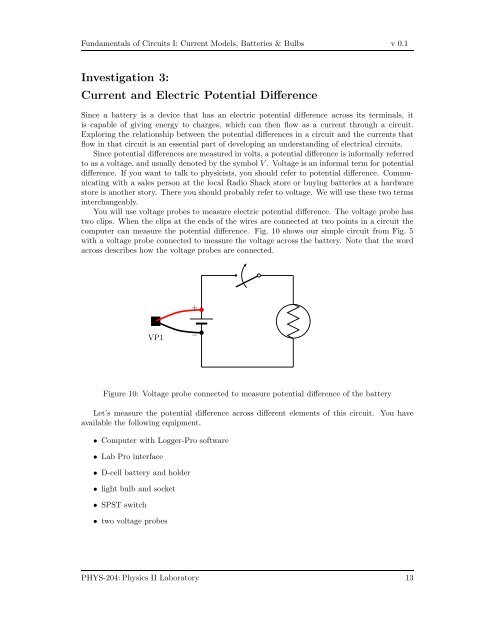
computer can measure the potential difference. Fig. 10 shows our simple circuit from Fig. 5<br />
with a voltage probe connected to measure the voltage across the battery. Note that the word<br />
across describes how the voltage probes are connected.<br />
+<br />
VP1<br />
−<br />
Figure 10: Voltage probe connected to measure potential difference <strong>of</strong> the battery<br />
Let’s measure the potential difference across different elements <strong>of</strong> this circuit. You have<br />
available the following equipment.<br />
• Computer with Logger-Pro s<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
• Lab Pro interface<br />
• D-cell battery and holder<br />
• light bulb and socket<br />
• SPST switch<br />
• two voltage probes<br />
PHYS-204: Physics II Laboratory 13