Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Fundamentals</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Circuits</strong> I: <strong>Current</strong> <strong>Models</strong>, <strong>Batteries</strong> & <strong>Bulbs</strong> v 0.1<br />
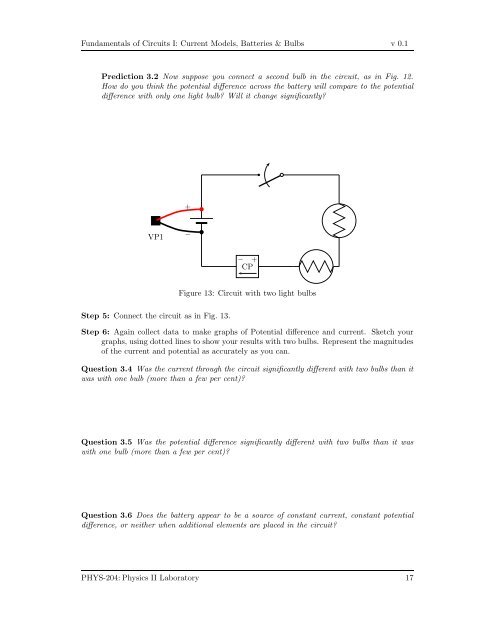
Prediction 3.2 Now suppose you connect a second bulb in the circuit, as in Fig. 12.<br />
How do you think the potential difference across the battery will compare to the potential<br />
difference with only one light bulb Will it change significantly<br />
+<br />
VP1<br />
−<br />
− +<br />
CP<br />
Figure 13: Circuit with two light bulbs<br />
Step 5: Connect the circuit as in Fig. 13.<br />
Step 6: Again collect data to make graphs <strong>of</strong> Potential difference and current. Sketch your<br />
graphs, using dotted lines to show your results with two bulbs. Represent the magnitudes<br />
<strong>of</strong> the current and potential as accurately as you can.<br />
Question 3.4 Was the current through the circuit significantly different with two bulbs than it<br />
was with one bulb (more than a few per cent)<br />
Question 3.5 Was the potential difference significantly different with two bulbs than it was<br />
with one bulb (more than a few per cent)<br />
Question 3.6 Does the battery appear to be a source <strong>of</strong> constant current, constant potential<br />
difference, or neither when additional elements are placed in the circuit<br />
PHYS-204: Physics II Laboratory 17