Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Fundamentals</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Circuits</strong> I: <strong>Current</strong> <strong>Models</strong>, <strong>Batteries</strong> & <strong>Bulbs</strong> v 0.1<br />
+<br />
+<br />
VP1<br />
−<br />
−<br />
VP2<br />
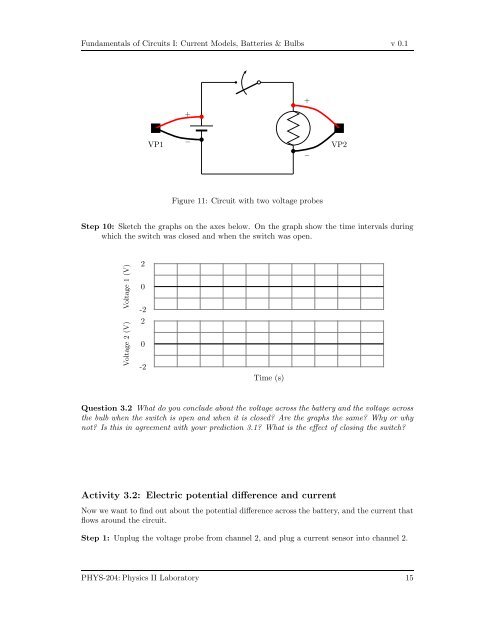
Figure 11: Circuit with two voltage probes<br />
Step 10: Sketch the graphs on the axes below. On the graph show the time intervals during<br />
which the switch was closed and when the switch was open.<br />
Voltage 1 (V)<br />
Voltage 2 (V)<br />
2<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
Time (s)<br />
Question 3.2 What do you conclude about the voltage across the battery and the voltage across<br />
the bulb when the switch is open and when it is closed Are the graphs the same Why or why<br />
not Is this in agreement with your prediction 3.1 What is the effect <strong>of</strong> closing the switch<br />
Activity 3.2: Electric potential difference and current<br />
Now we want to find out about the potential difference across the battery, and the current that<br />
flows around the circuit.<br />
Step 1: Unplug the voltage probe from channel 2, and plug a current sensor into channel 2.<br />
PHYS-204: Physics II Laboratory 15