HERBICIDES in Asian rice - IRRI books - International Rice ...
HERBICIDES in Asian rice - IRRI books - International Rice ...
HERBICIDES in Asian rice - IRRI books - International Rice ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
as more lucrative, full-time job opportunities become available <strong>in</strong> nonagricultural activities,<br />
<strong>Asian</strong> farmers are f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g it <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>gly difficult to hire seasonal workers for<br />
transplant<strong>in</strong>g and hand weed<strong>in</strong>g <strong>rice</strong>. The current movement of labor from agricultural<br />
to nonagricultural sectors <strong>in</strong> the less developed countries of Asia is characteristic<br />
of a more general process of structural transformation that occurs at vary<strong>in</strong>g rates and<br />
degrees <strong>in</strong> all develop<strong>in</strong>g economies. The process is def<strong>in</strong>ed broadly by a dim<strong>in</strong>ish<strong>in</strong>g<br />
role of agriculture <strong>in</strong> national <strong>in</strong>come and aggregate employment as an economy grows.<br />
A relative decl<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> the agricultural labor force occurs <strong>in</strong> the early to middle stages of<br />
structural transformation; <strong>in</strong> later stages, the absolute number of workers <strong>in</strong> agriculture<br />
also falls (Timmer 1988). The process of structural transformation is already well<br />
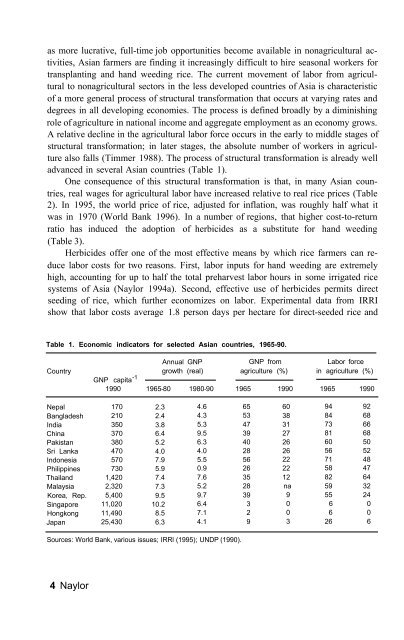
advanced <strong>in</strong> several <strong>Asian</strong> countries (Table 1).<br />
One consequence of this structural transformation is that, <strong>in</strong> many <strong>Asian</strong> countries,<br />
real wages for agricultural labor have <strong>in</strong>creased relative to real <strong>rice</strong> p<strong>rice</strong>s (Table<br />
2). In 1995, the world p<strong>rice</strong> of <strong>rice</strong>, adjusted for <strong>in</strong>flation, was roughly half what it<br />
was <strong>in</strong> 1970 (World Bank 1996). In a number of regions, that higher cost-to-return<br />
ratio has <strong>in</strong>duced the adoption of herbicides as a substitute for hand weed<strong>in</strong>g<br />
(Table 3).<br />
Herbicides offer one of the most effective means by which <strong>rice</strong> farmers can reduce<br />
labor costs for two reasons. First, labor <strong>in</strong>puts for hand weed<strong>in</strong>g are extremely<br />
high, account<strong>in</strong>g for up to half the total preharvest labor hours <strong>in</strong> some irrigated <strong>rice</strong><br />
systems of Asia (Naylor 1994a). Second, effective use of herbicides permits direct<br />
seed<strong>in</strong>g of <strong>rice</strong>, which further economizes on labor. Experimental data from <strong>IRRI</strong><br />
show that labor costs average 1.8 person days per hectare for direct-seeded <strong>rice</strong> and<br />
Table 1. Economic <strong>in</strong>dicators for selected <strong>Asian</strong> countries, 1965-90.<br />
Country<br />
Annual GNP<br />
GNP from<br />
Labor force<br />
growth (real) agriculture (%) <strong>in</strong> agriculture (%)<br />
GNP capita -1<br />
1990 1965-80 1980-90 1965 1990 1965 1990<br />
Nepal<br />
Bangladesh<br />
India<br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>a<br />
Pakistan<br />
Sri Lanka<br />
Indonesia<br />
Philipp<strong>in</strong>es<br />
Thailand<br />
Malaysia<br />
Korea, Rep.<br />
S<strong>in</strong>gapore<br />
Hongkong<br />
Japan<br />
170<br />
210<br />
350<br />
370<br />
380<br />
470<br />
570<br />
730<br />
1,420<br />
2,320<br />
5,400<br />
11,020<br />
11,490<br />
25,430<br />
2.3<br />
2.4<br />
3.8<br />
6.4<br />
5.2<br />
4.0<br />
7.9<br />
5.9<br />
7.4<br />
7.3<br />
9.5<br />
10.2<br />
8.5<br />
6.3<br />
4.6<br />
4.3<br />
5.3<br />
9.5<br />
6.3<br />
4.0<br />
5.5<br />
0.9<br />
7.6<br />
5.2<br />
9.7<br />
6.4<br />
7.1<br />
4.1<br />
65<br />
53<br />
47<br />
39<br />
40<br />
28<br />
56<br />
26<br />
35<br />
28<br />
39<br />
3<br />
2<br />
9<br />
60<br />
38<br />
31<br />
27<br />
26<br />
26<br />
22<br />
22<br />
12<br />
na<br />
9<br />
0<br />
0<br />
3<br />
94<br />
84<br />
73<br />
81<br />
60<br />
56<br />
71<br />
58<br />
82<br />
59<br />
55<br />
6<br />
6<br />
26<br />
92<br />
68<br />
66<br />
68<br />
50<br />
52<br />
48<br />
47<br />
64<br />
32<br />
24<br />
0<br />
0<br />
6<br />
Sources: World Bank, various issues; IRRl (1995); UNDP (1990).<br />
4 Naylor