EGAS41 - Swansea University
EGAS41 - Swansea University
EGAS41 - Swansea University
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
41 st EGAS CP 90 Gdańsk 2009<br />
Radiative correlated double electron capture (RDEC) in O 8+ +C<br />
collisions at low energy<br />
A. Simon 1,∗ , J.A. Tanis 2 , A. Warczak 1<br />
1 Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian <strong>University</strong>, ul. Reymonta 4, 30-059 Krakow, Poland<br />
2 Physics Department, Western Michigan <strong>University</strong>, 1903 W. Michigan Avenue,<br />
Kalamazoo MI 49008<br />
∗ Corresponding author: simon@uj.edu.pl<br />
Radiative double electron capture (RDEC) is a one-step process where target electrons<br />
are captured into bound states of the projectile, e.g., into an empty K-shell, and the<br />
excess energy is released as a single photon. This process provides insight into several<br />
very challenging problems in atomic physics, such as the electron-electron interaction in<br />
electromagnetic fields or the search for a proper description of a two electron-continuum<br />
wave function.<br />
number of counts<br />
40<br />
35<br />
30<br />
25<br />
REC<br />
8+<br />
O +C<br />
2.375 MeV/u<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
RDEC<br />
0<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7<br />
E [keV]<br />
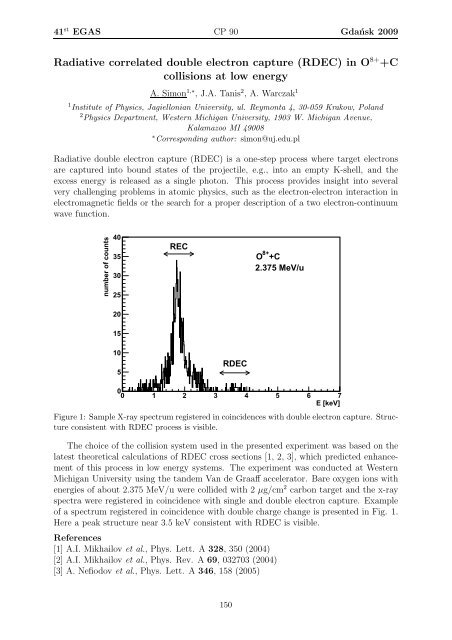
Figure 1: Sample X-ray spectrum registered in coincidences with double electron capture. Structure<br />
consistent with RDEC process is visible.<br />
The choice of the collision system used in the presented experiment was based on the<br />
latest theoretical calculations of RDEC cross sections [1, 2, 3], which predicted enhancement<br />
of this process in low energy systems. The experiment was conducted at Western<br />
Michigan <strong>University</strong> using the tandem Van de Graaff accelerator. Bare oxygen ions with<br />
energies of about 2.375 MeV/u were collided with 2 µg/cm 2 carbon target and the x-ray<br />
spectra were registered in coincidence with single and double electron capture. Example<br />
of a spectrum registered in coincidence with double charge change is presented in Fig. 1.<br />
Here a peak structure near 3.5 keV consistent with RDEC is visible.<br />
References<br />
[1] A.I. Mikhailov et al., Phys. Lett. A 328, 350 (2004)<br />
[2] A.I. Mikhailov et al., Phys. Rev. A 69, 032703 (2004)<br />
[3] A. Nefiodov et al., Phys. Lett. A 346, 158 (2005)<br />
150