EGAS41 - Swansea University
EGAS41 - Swansea University
EGAS41 - Swansea University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
41 st EGAS CP 156 Gdańsk 2009<br />
Electron-impact double and triple ionization of tungsten atoms<br />
and ions at low ionization stages<br />
V. Jonauskas, S. Kučas, R. Karazija ∗<br />
Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy of Vilnius <strong>University</strong>,<br />
A. Goštauto 12, Vilnius LT-01108, Lithuania<br />
∗ Corresponding author: karazija@itpa.lt<br />
Due to a very low sputtering rate of tungsten it is used as the first wall material in large<br />
tokamaks, such as ASDEX Upgrade, and is planned to use in ITER. However, some its<br />
ions migrate to the central region of discharge and may be the reason of large radiation<br />
losses. Thus it is up-and-coming to investigate the role of the Auger decay of the states<br />
with a vacancy and the direct multiple ionization in the production of tungsten ions during<br />
their interactions with electrons.<br />
The double and triple ionization of tungsten ions by electron impact at low ionization<br />
stages was measured and described by semiempirical formula [1], but no ab initio<br />
calculations were made. In this work the calculations of cross sections of these processes<br />
are performed taking into account the Auger decay of states with the vacancy in 4d, 4f,<br />
5s, 5p and 5d shells as well as the direct double ionization considered using sudden perturbation<br />
model. The direct single ionization cross section is obtained in the relativistic<br />
distorted wave or binary-encounter-dipole approximations; the contribution from the indirect<br />
ionization by excitation-autoionization process is included too. The calculations<br />
are performed using Flexible Atomic Code [2]. It is shown that both processes − Auger<br />
decay and direct double ionization play an important role in the double ionization process.<br />
The calculated cross sections are compared with experimental data.<br />
The contributions from the Auger transitions and from the sudden perturbation to the<br />
double ionization cross section are obtained of the same order, though the latter process<br />
plays a smaller role, especially for the higher ions. Most of the Auger transitions end in<br />
the configurations of the next ionization stage, thus the triple ionization cross section is<br />
more determined by the direct ionization.<br />
4<br />
W 2+ W 4+<br />
cross section, 10 -17 cm 2<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
30 100 1000<br />
energy, eV<br />
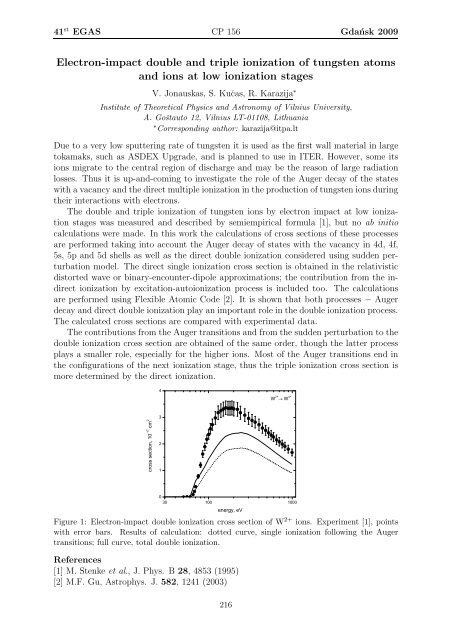
Figure 1: Electron-impact double ionization cross section of W 2+ ions. Experiment [1], points<br />
with error bars. Results of calculation: dotted curve, single ionization following the Auger<br />
transitions; full curve, total double ionization.<br />
References<br />
[1] M. Stenke et al., J. Phys. B 28, 4853 (1995)<br />
[2] M.F. Gu, Astrophys. J. 582, 1241 (2003)<br />
216