STUDY SUMMARY - IPMU
STUDY SUMMARY - IPMU
STUDY SUMMARY - IPMU
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>SUMMARY</strong> REPORT<br />
WIDE FIELD FIBER-FED OPTICAL<br />
MULTI-OBJECT SPECTROMETER (WFMOS)<br />
ing TMT on the design and development of the Alignment and Phasing system, telescope system<br />
engineering, the Planet Formation Instrument feasibility study, and the telescope optics.<br />
WFMOS aligns with JPL’s Astronomy and Physics Directorate (APD) strategic plan for increased<br />
development of ground and space-based optical instruments and JPL is committed to its<br />
success. Ground instruments allow the development of complex systems with technologies that<br />
can also be applied to space-flight instruments. JPL is a large, diverse organization accustomed<br />
to handling complex, multi-disciplinary challenges and can provide critical resources in various<br />
forms to support WFMOS. The support from the APD has been evident through the study phase<br />
through communication on the study progress and in the coordination and support in the proposal<br />
review and preparation process. In addition to management support, the JPL infrastructure provides<br />
mechanisms and resources for cost and schedule management, document organization and<br />
storage, and configuration control. This project has the advantage of selecting the desired tools<br />
and functions without having to meet the more stringent practices of a flight project.<br />
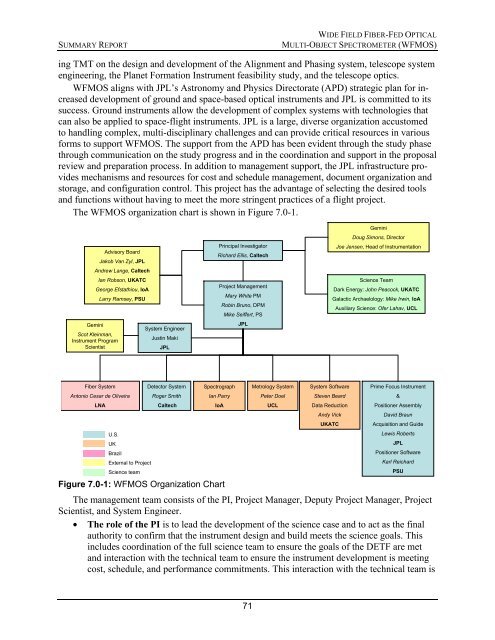
The WFMOS organization chart is shown in Figure 7.0-1.<br />
Advisory Board<br />
Jakob Van Zyl, JPL<br />
Andrew Lange, Caltech<br />
Ian Robson, UKATC<br />
George Efstathiou, IoA<br />
Larry Ramsey, PSU<br />
Gemini<br />
Scot Kleinman,<br />
Instrument Program<br />
Scientist<br />
System Engineer<br />
Justin Maki<br />
JPL<br />
Principal Investigator<br />
Richard Ellis, Caltech<br />
Project Management<br />
Mary White PM<br />
Robin Bruno, DPM<br />
Mike Seiffert, PS<br />
JPL<br />
Gemini<br />
Doug Simons, Director<br />
Joe Jensen, Head of Instrumentation<br />
Science Team<br />
Dark Energy: John Peacock, UKATC<br />
Galactic Archaelology: Mike Irwin, IoA<br />
Auxiliary Science: Ofer Lahav, UCL<br />
Fiber System<br />
Antonio Cesar de Oliveira<br />
LNA<br />
U.S.<br />
UK<br />
Brazil<br />
External to Project<br />
Science team<br />
Detector System<br />
Roger Smith<br />
Caltech<br />
Spectrograph<br />
Ian Parry<br />
IoA<br />
Metrology System<br />
Peter Doel<br />
UCL<br />
System Software<br />
Steven Beard<br />
Data Reduction<br />
Andy Vick<br />
UKATC<br />
Prime Focus Instrument<br />
&<br />
Positioner Assembly<br />
David Braun<br />
Acquisition and Guide<br />
Lewis Roberts<br />
JPL<br />
Positioner Software<br />
Karl Reichard<br />
PSU<br />
Figure 7.0-1: WFMOS Organization Chart<br />
The management team consists of the PI, Project Manager, Deputy Project Manager, Project<br />
Scientist, and System Engineer.<br />
• The role of the PI is to lead the development of the science case and to act as the final<br />
authority to confirm that the instrument design and build meets the science goals. This<br />
includes coordination of the full science team to ensure the goals of the DETF are met<br />
and interaction with the technical team to ensure the instrument development is meeting<br />
cost, schedule, and performance commitments. This interaction with the technical team is<br />
71