INCLUSIVE BUSINESS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
DeLab<br />
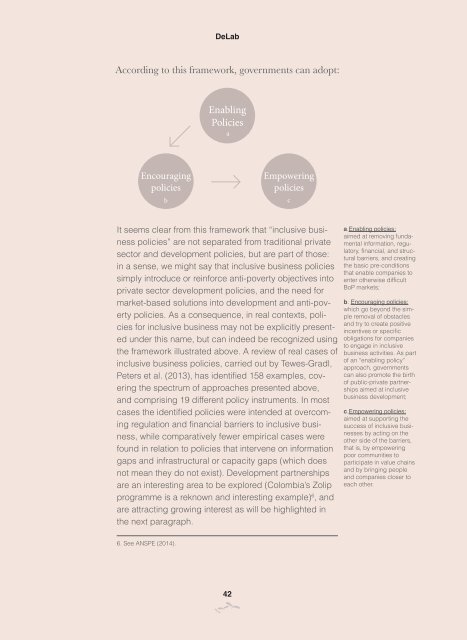
According to this framework, governments can adopt:<br />
It seems clear from this framework that “inclusive business<br />
policies” are not separated from traditional private<br />
sector and development policies, but are part of those:<br />
in a sense, we might say that inclusive business policies<br />
simply introduce or reinforce anti-poverty objectives into<br />
private sector development policies, and the need for<br />
market-based solutions into development and anti-poverty<br />
policies. As a consequence, in real contexts, policies<br />
for inclusive business may not be explicitly presented<br />
under this name, but can indeed be recognized using<br />
the framework illustrated above. A review of real cases of<br />
inclusive business policies, carried out by Tewes-Gradl,<br />
Peters et al. (2013), has identified 158 examples, covering<br />
the spectrum of approaches presented above,<br />
and comprising 19 different policy instruments. In most<br />
cases the identified policies were intended at overcoming<br />
regulation and financial barriers to inclusive business,<br />
while comparatively fewer empirical cases were<br />
found in relation to policies that intervene on information<br />
gaps and infrastructural or capacity gaps (which does<br />
not mean they do not exist). Development partnerships<br />
are an interesting area to be explored (Colombia’s Zolip<br />
programme is a reknown and interesting example) 6 , and<br />
are attracting growing interest as will be highlighted in<br />
the next paragraph.<br />
a.Enabling policies:<br />
aimed at removing fundamental<br />
information, regulatory,<br />
financial, and structural<br />
barriers, and creating<br />
the basic pre-conditions<br />
that enable companies to<br />
enter otherwise difficult<br />
BoP markets;<br />
b. Encouraging policies:<br />
which go beyond the simple<br />
removal of obstacles<br />
and try to create positive<br />
incentives or specific<br />
obligations for companies<br />
to engage in inclusive<br />
business activities. As part<br />
of an “enabling policy”<br />
approach, governments<br />
can also promote the birth<br />
of public-private partnerships<br />
aimed at inclusive<br />
business development;<br />
c.Empowering policies:<br />
aimed at supporting the<br />
success of inclusive businesses<br />
by acting on the<br />
other side of the barriers,<br />
that is, by empowering<br />
poor communities to<br />
participate in value chains<br />
and by bringing people<br />
and companies closer to<br />
each other.<br />
6. See ANSPE (2014).<br />
42