1. Basic Concepts in Reliability Design - nl3prc
1. Basic Concepts in Reliability Design - nl3prc
1. Basic Concepts in Reliability Design - nl3prc
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
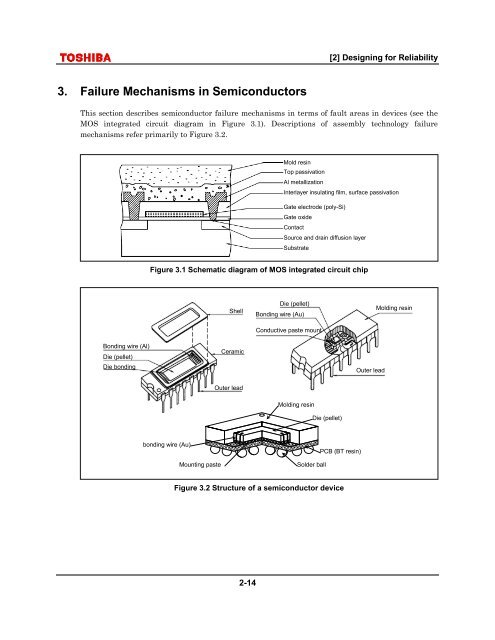
[2] <strong>Design</strong><strong>in</strong>g for <strong>Reliability</strong>3. Failure Mechanisms <strong>in</strong> SemiconductorsThis section describes semiconductor failure mechanisms <strong>in</strong> terms of fault areas <strong>in</strong> devices (see theMOS <strong>in</strong>tegrated circuit diagram <strong>in</strong> Figure 3.1). Descriptions of assembly technology failuremechanisms refer primarily to Figure 3.2.Mold res<strong>in</strong>Top passivationAl metallizationInterlayer <strong>in</strong>sulat<strong>in</strong>g film, surface passivationGate electrode (poly-Si)Gate oxideContactSource and dra<strong>in</strong> diffusion layerSubstrateFigure 3.1 Schematic diagram of MOS <strong>in</strong>tegrated circuit chipShellDie (pellet)Bond<strong>in</strong>g wire (Au)Conductive paste mountMold<strong>in</strong>g res<strong>in</strong>Bond<strong>in</strong>g wire (Al)Die (pellet)Die bond<strong>in</strong>gCeramicOuter leadOuter leadMold<strong>in</strong>g res<strong>in</strong>Die (pellet)bond<strong>in</strong>g wire (Au)Mount<strong>in</strong>g pasteSolder ballPCB (BT res<strong>in</strong>)Figure 3.2 Structure of a semiconductor device2-14